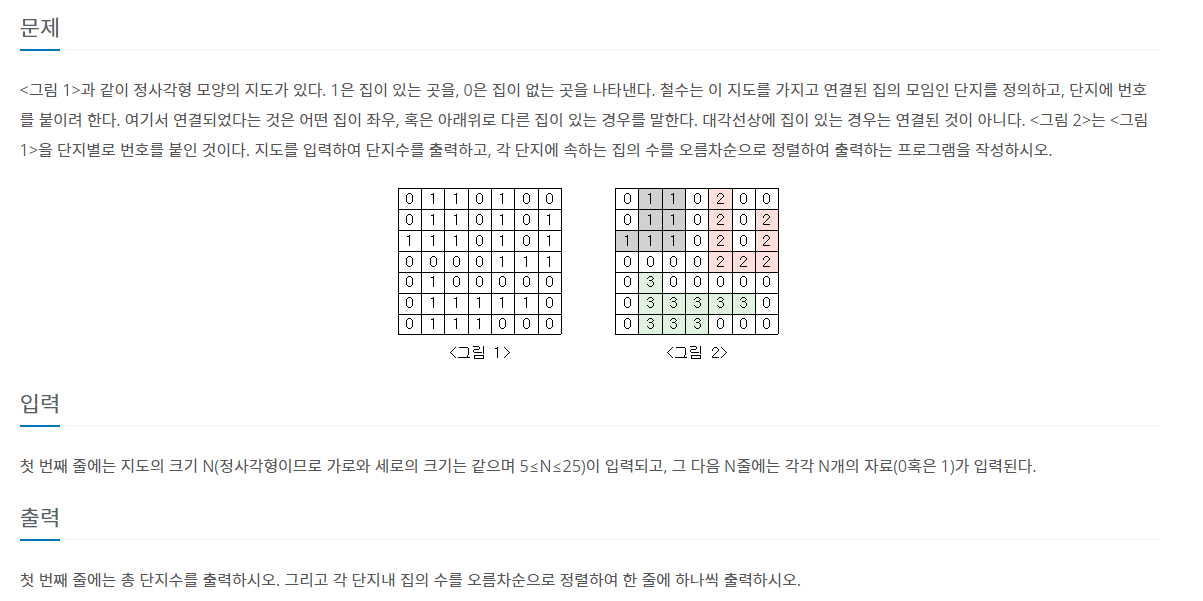
설명
2차원 배열을 쭉 돌면서 아직 방문하지 않은 1을 발견하면 queue에다 넣고 다시 빼서 상하좌우도 똑같이 조건을 만족하면 queue에다 넣고 다시 빼고를 반복해서 queue가 빌 때까지 그짓을 반복한다. queue가 비었다는 것은 연결된 단지가 더 이상 없다는 뜻이므로 house를 1 증가시킨다.
코드
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int map[27][27] = {0};
int visited[25][25] = { 0 };
typedef struct _pos
{
int x, y;
_pos(int _x, int _y) : x(_x), y(_y) {}
}Pos;
int dirX[4] = { -1, 0, 1, 0 };
int dirY[4] = { 0, 1, 0, -1 };
vector<int> result;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin.tie(0);
queue<Pos> q;
string input;
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> input;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (input[j-1] == '1')
map[i][j] = 1;
}
int house = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (map[i][j] == 1 && visited[i-1][j-1] == 0)
{
house++;
int cnt = 1;
visited[i - 1][j - 1] = 1;
q.push(Pos(i, j));
while (!q.empty())
{
Pos p = q.front();
q.pop();
int k = 0;
while (k < 4)
{
int x = p.x + dirX[k];
int y = p.y + dirY[k];
if (map[x][y] == 1 && visited[x - 1][y - 1] == 0)
{
cnt++;
visited[x - 1][y - 1] = 1;
q.push(Pos(x, y));
}
k++;
}
}
result.push_back(cnt);
}
}
}
sort(result.begin(), result.end());
cout << house << '\n';
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++)
cout << result[i] << '\n';
return 0;
}