💻 구현 기능
- 리액트에서 스프링부트로 프로필 이미지 전달
- 이후 해당 이미지 db에 저장 후, 바로 리액트에서 바로 보여줌
✨ 실시간으로 db와 실제파일이 이미지가 교체되고, 삭제되는 게 목표!
✏️ 기능 설계
- 리액트에서 스프링부트로 이미지를 file - formData로 넘김
- MultipartFile로 파일(이미지)를 받아오고, 서비스로 넘김
- 서비스에서 유저정보 체크 후, 파일핸들러를 이용해 실제파일을 저장
- 이후 저장된 위치 (URL)를 받아와서 db에 해당 경로 저장
- 리액트에서 다시 fetch 실행해서 유저 이미지 스프링부트에서 받아옴
- 받아올 때는 바이너리 데이터로 응답 받아 IMG 출력
📌 구현 과정
1. 리액트에서 데이터 넘기기
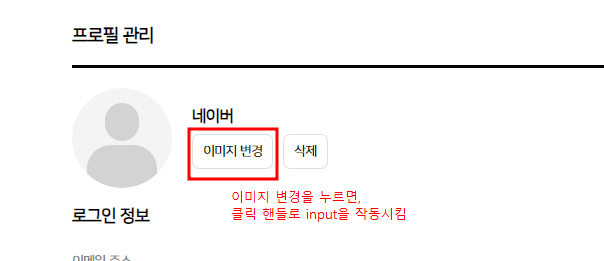

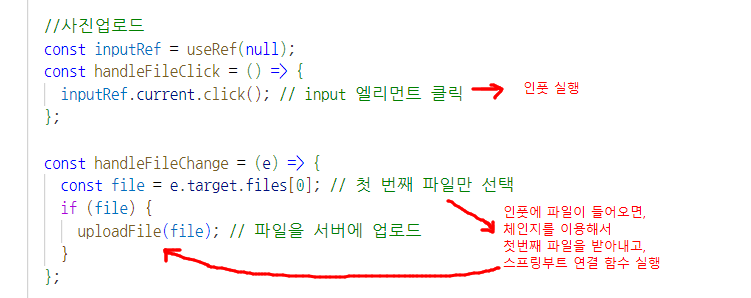
FormData 웹 애플리케이션에서 폼 데이터를 쉽게 생성하고 제어하기 위한 JavaScript의 내장 객체로 주로 HTTP POST 요청을 보낼 때 사용
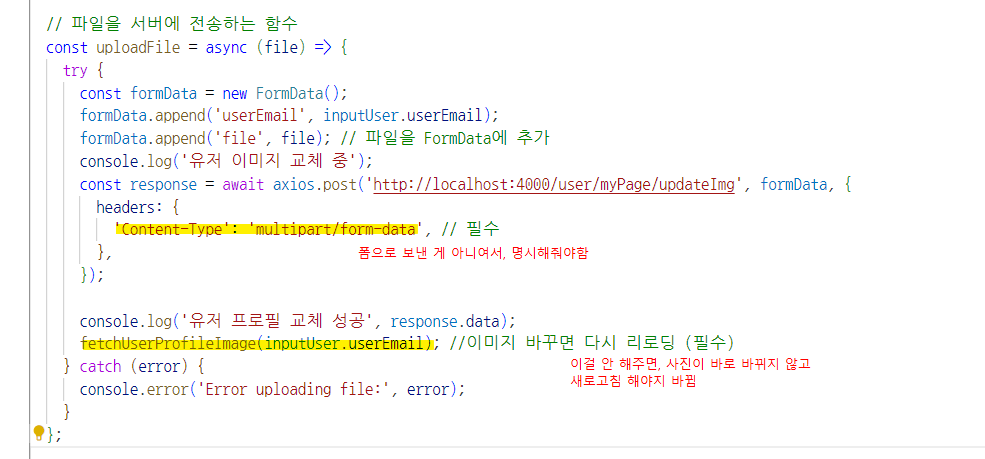
2. 스프링부트에서 데이터 받아서 저장
2-1. 컨트롤러

2-2. updateUserImg

2-3. fileHandler
public UserEntity fileHandler(MultipartFile file, String userEmail) throws Exception {
// 현재 작업경로의 절대경로
// File.separator (/)
String absolutePath = new File("").getAbsolutePath() + File.separator;
// 파일 저장 위치
String path = "src" + File.separator + "main" + File.separator + "resources" + File.separator + "static"
+ File.separator + "images" + File.separator + "userImg";
File userImg = new File(path);
if (!userImg.exists()) {
// 폴더없으면 생성
userImg.mkdirs();
}
if (!file.isEmpty()) {
// 파일이 비어있지 않으면
String contentType = file.getContentType();
String originalFileExtension;
// 타입에 따른 확장자 결정
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(contentType)) {
// 타입 없으면 null
return null;
} else {
if (contentType.contains("image/jpeg")) {
originalFileExtension = ".jpg";
} else if (contentType.contains("image/png")) {
originalFileExtension = ".png";
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 파일저장 이름
String originalFileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
// 확장자를 제외한 파일 이름과 확장자 추출
int lastIndex = originalFileName.lastIndexOf('.');
String fileName = originalFileName.substring(0, lastIndex);
String userImgName = fileName + System.nanoTime() + originalFileExtension;
// 파일 저장
userImg = new File(absolutePath + path + File.separator + userImgName);
System.out.println("파일 저장경로:" + absolutePath + path + File.separator + userImgName);
file.transferTo(userImg);
// 새로운 UserEntity 생성 및 파일 경로 전달 (db 저장에 사용)
UserEntity userEntity = new UserEntity();
userEntity.setUserProfile(path + File.separator + userImgName); // 실제 저장된 위치
return userEntity;
}
return null;
}2-4. deleteUserImg
public ResponseEntity<String> deleteUserImg(String userEmail) {
Optional<UserEntity> userOptional = userRepository.findByUserEmail(userEmail);
if (userOptional.isPresent()) {
// 유저 정보가 있으면
UserEntity userEntity = userOptional.get();
try {
File imageFile = new File(userEntity.getUserProfile());
if (imageFile.exists()) {
// 파일이 존재하면 삭제
System.out.println("파일 존재함");
if (imageFile.delete()) { // 파일삭제
// db 삭제
userEntity.setUserProfile(null);
userRepository.save(userEntity);
return ResponseEntity.ok("이미지 삭제 성공");
} else {
// 파일 삭제 실패 시 오류 메시지 반환
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).body("이미지 파일 삭제 실패");
}
} else {
// 파일이 존재하지 않으면
return ResponseEntity.ok("이미지 파일이 이미 존재하지 않습니다.");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 파일 처리 실패 시 에러 메시지 반환
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).body("이미지 삭제 오류");
}
} else {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND).body(userEmail + " 해당 이메일을 가진 사용자를 찾을 수 없습니다");
}
}3. 바이너리 데이터 형태 요청
3-1. 리액트
arraybuffer 바이트 단위로 데이터를 다룰 때 사용되는 버퍼로, 이진 데이터를 효율적으로 다룰 수 있도록 해줌 (주로 이미지, 오디오, 비디오 등의 바이너리 데이터를 다룰 때 사용)
Blob Binary Large Object의 약자로, 이진 대형 객체
URL.createObjectURL() 주어진 객체나 데이터를 나타내는 URL을 생성하는 메서드로 이 URL은 브라우저 세션 동안만 유효하며, 해당 객체나 데이터에 대한 임시 URL을 생성
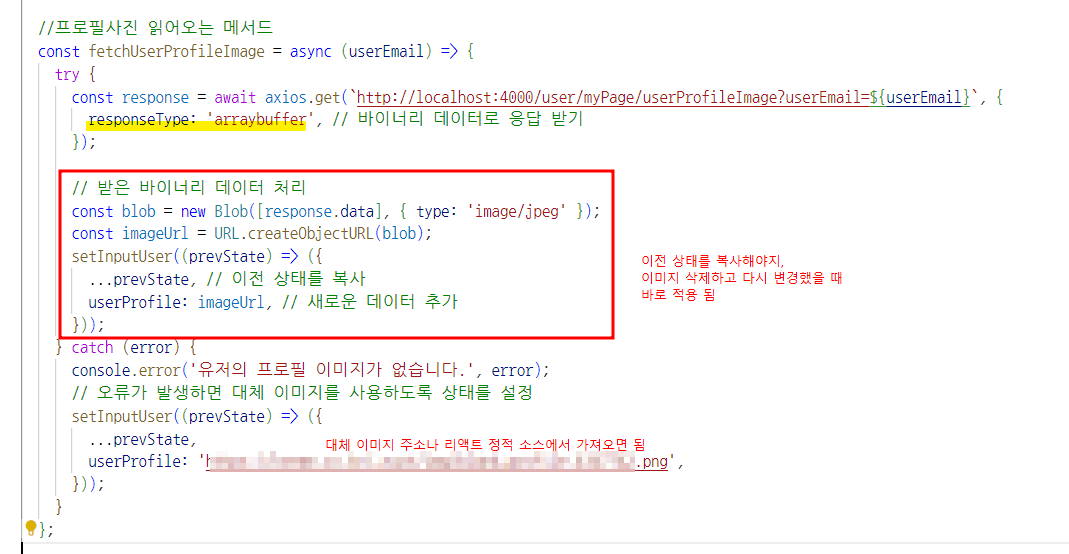
- 프로필 이미지는 useEfect로 페이지 실행시 바로 갖고오게 설정
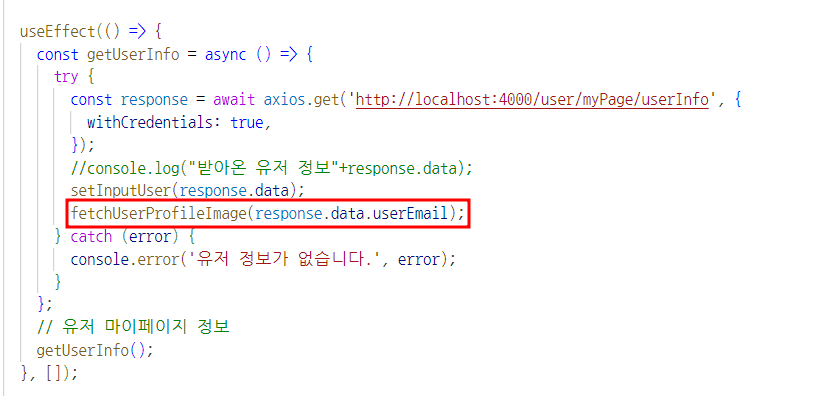
4. 바이너리 데이터 형태 전달
4-1. 컨트롤러
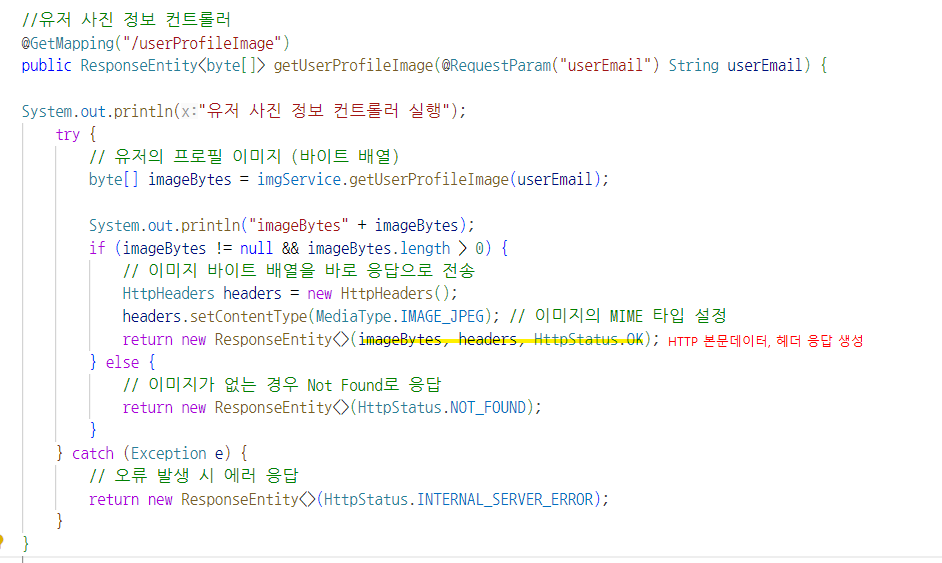
4-2. getUserProfileImage
- 파일의 위치를 읽어와서 해당 파일을 바이트 형식으로 바꿔서 전달
public byte[] getUserProfileImage(String userEmail) throws IOException {
System.out.println("getUserProfileImage 실행");
Optional<UserEntity> userOptional = userRepository.findByUserEmail(userEmail);
if (userOptional.isPresent()) {
UserEntity userEntity = userOptional.get();
String profileImagePath = userEntity.getUserProfile();
System.out.println("profileImagePath: " + profileImagePath);
// 프로필 이미지 경로가 null이 아니고 빈 문자열이 아닌 경우에만 이미지를 읽어옴
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(profileImagePath)) {
Path imagePath = Paths.get(profileImagePath);
System.out.println("imagePath: " + imagePath);
if (Files.exists(imagePath)) {
// 파일이 존재하는 경우에만 읽어옴
return Files.readAllBytes(imagePath);
} else {
System.out.println("파일이 존재하지 않습니다.");
}
} else {
System.out.println("프로필 이미지 경로가 비어 있습니다.");
}
} else {
System.out.println("해당 유저가 존재하지 않습니다.");
}
// 만약 프로필 이미지를 찾을 수 없는 경우 빈 바이트 배열 반환
return new byte[0];
}5. 결과
이미지 변경, 변경 해도 문제없고 삭제해도 잘 되는 걸 볼 수 있다.
*db와 파일도 실시간으로 잘 지워짐!
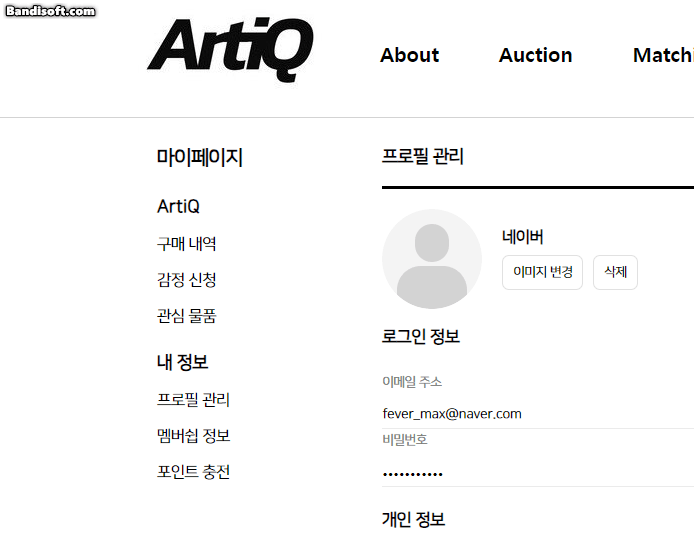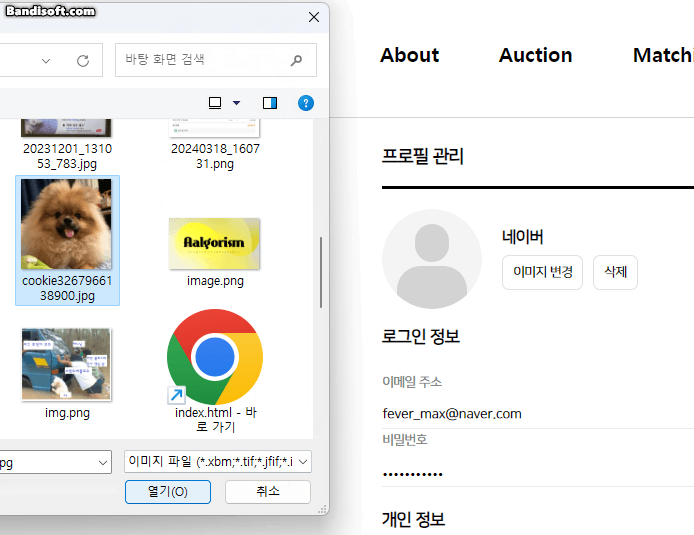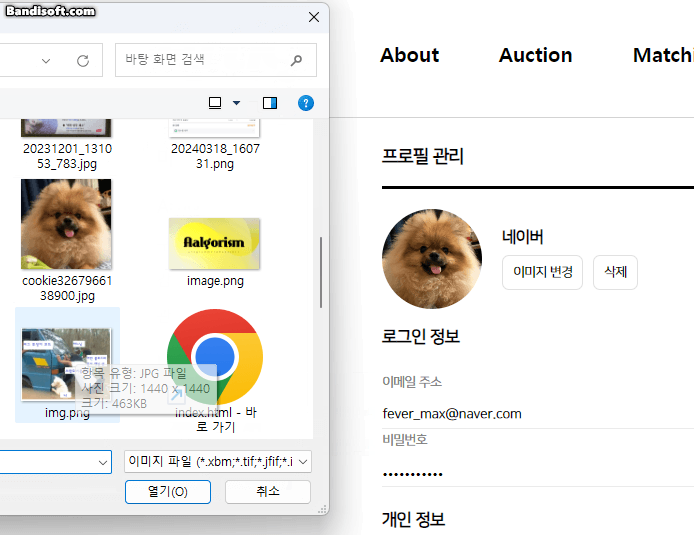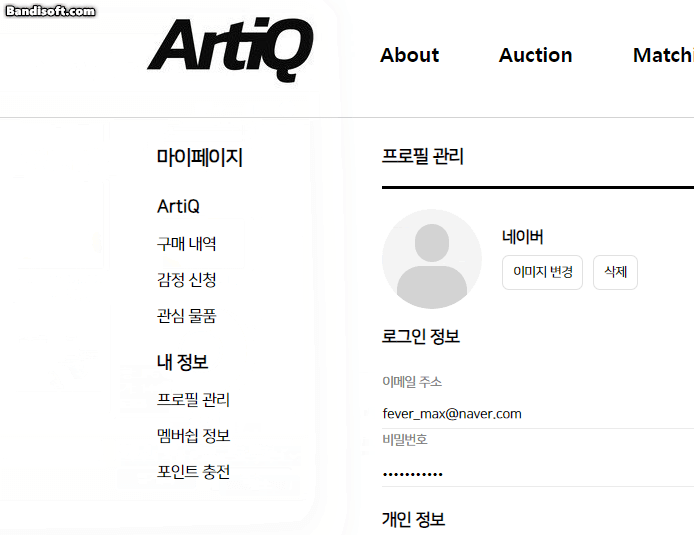
🤔 느낀점
항상 스프링부트에서 이미지만 다뤄봤지 리액트에서 다뤄보긴 처음이라 어려웠다
이곳저곳 찾아보았지만 내가 원하는 실시간 교체 형식은 잘 없어서 이렇게 해보았는데, 이게 올바른 코드인지는 모르겠다.
여전히 프론트에서 백으로 데이터 주고 받기는 어렵고, 생소해서 전달방식에 대한 공부가 더 필요하고 절실히 느꼈다.
