생각
- 변수
- 자료형
- 대입연산자
- 조건분기
- 반복
- 함수
*리터럴: 하나의 실제 값
10이라는 리터럴은 5+5와 같은 수식으로 만들 수 있음
십진수를 입력받으면 이진수로 변환하기
input 값을 2로 나눈 몫과 remain ...
몫을 2로 나눈 나머지 ... x반복
2 | 11
2 | 5 ... 0
2 | 2 ... 1
1 ... 0
좌하단부터 1011 로 출력해주기
사용자의 입력받기(숫자): 범위 지정해주기
값을 저장할 배열 result
배열에 순서대로 저장하는 변수 cnt
입력값 복사 input
2로 나누고 나머지 저장 remain
input을 2로 계속 나눠 나머지를 저장하는 함수 (input>0)
result를 출력 cnt 큰 것부터
package ex01;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test0320 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
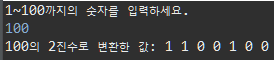
System.out.println("1~100까지의 숫자를 입력하세요.");
int userInput = sc.nextInt();
int[] result = new int[10];
int cnt = 0;
int input = userInput;
int remain=0;
while(input>0) {
remain = input%2;
result[cnt] = remain;
input = input/2;
cnt++;
}
System.out.print(userInput+"을 2진수로 변환한 값: ");
for(int i=cnt-1;i>=0;i--)
System.out.print(result[i]+" ");
}
}
결 과
리 뷰
- String 이나 StringBuffer 등 다른 함수를 사용하지 않고,
- 배열의 크기는 최초에 어떻게 설정?
→ 입력하는 수에 대한 범위 설정? 1~100까지는 7개로 표현 가능 / 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
십진수를 2, 8, 16진수로 바꾸는 함수
- 2진수로 변환한 코드를 함수로 만든다.
- 2진수를 이용해서 8진수와 16진수 함수로 만든다.
- 16진수의 경우 10은 A, 11은 B, ... 15는 F로 출력해주는 것만 추가해준다.
*2진수를 배열 8개까지 허용한다면 256까지 가능하므로 사용자 입력 범위를 수정함.
package ex01;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test0320 {
static int userInput = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("1~255까지의 숫자를 입력하세요.");
userInput = sc.nextInt();
binary(userInput);
oct(userInput);
hex(userInput);
}
static void binary(int x) {
int[] result = new int[8];
int cnt = 0;
int input = x;
int remain=0;
while(input>0) {
remain = input%2;
result[cnt] = remain;
input = input/2;
cnt++;
}
System.out.print(userInput+"을 2진수로 변환한 값: ");
for(int i=cnt-1;i>=0;i--)
System.out.print(result[i]+" ");
System.out.println("");
}
static void oct(int x) {
int[] result = new int[4];
int cnt = 0;
int input = x;
int remain=0;
while(input>0) {
remain = input%8;
result[cnt] = remain;
input = input/8;
cnt++;
}
System.out.print(userInput+"을 8진수로 변환한 값: ");
for(int i=cnt-1;i>=0;i--)
System.out.print(result[i]+" ");
System.out.println("");
}
static void hex(int x) {
int[] result = new int[3];
int cnt = 0;
int input = x;
int remain=0;
while(input>0) {
remain = input%16;
result[cnt] = remain;
input = input/16;
cnt++;
}
System.out.print(userInput+"을 16진수로 변환한 값: ");
for(int i=cnt-1;i>=0;i--)
switch(result[i]) {
case 10: System.out.print("A ");break;
case 11: System.out.print("B ");break;
case 12: System.out.print("C ");break;
case 13: System.out.print("D ");break;
case 14: System.out.print("E ");break;
case 15: System.out.print("F ");break;
default: System.out.print(result[i]+" "); break;
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
이진수를 십진수로 바꾸기
4자리의 이진수 값만 받기
Math.pow를 이용해서 제곱수 구하기
package ex01;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test0320_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("4자리 이진수를 입력");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int userInput=sc.nextInt();
int input=userInput;
int remain=0;
int[] arr = new int[10];
int cnt=0;
int sum=0; // 10진수로 변환했을 때 값
int pow=0; // 10진수로 변환할 때 필요한 제곱수
// Math.pow(5, 2); 5의 제곱
for(int i=1000;i>0;i=i/10) {
remain = input%i;
input = input/i;
arr[cnt++] = input;
input = remain;
}
for(int i=cnt-1; i>=0; i--) {
sum+=arr[i]*Math.pow(2,pow++);
}
System.out.println(userInput+"을 십진수로 변환한 값: "+ sum);
}
}
결 과

5개씩 무한히 크기가 늘어나는 배열 만들기
처음 배열은 5개가 들어가 있는 배열
무한히는 너무 계속 돌아갈테니 사용자에게 몇 번 늘릴 것인지 SC
package ex01;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test0320_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
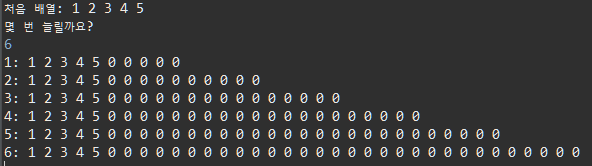
System.out.print("처음 배열: ");
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("몇 번 늘릴까요?");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int input = sc.nextInt();
int cnt = 0;
while(cnt<input) {
int[] copyArr = new int[arr.length+5];
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
copyArr[i]=arr[i];
arr = copyArr;
System.out.print(cnt+1 + ": ");
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
System.out.println("");
cnt++;
}
}
}
사용자가 입력하는 대로 배열이 계속 늘어나게 하기(1개씩)
package ex01;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test0320_4 {
static int[] arr = new int[5];
static int cnt = 0;
static int goStop = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
firstArr5();
addArr();
printResult();
}
static void firstArr5() {
inputNum();
System.out.println("배열이 다 찼습니다.");
}
static void inputNum() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("숫자 5개를 입력하세요 >>");
while(cnt<arr.length) {
int input = sc.nextInt();
arr[cnt++]=input;
}
}
static void addArr() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
if(cnt>=arr.length)
System.out.println("더 입력하시겠습니까?(Y:1, N:0)");
goStop = sc.nextInt();
if(goStop==0) break;
else {
int[] copyArr = new int[arr.length+1];
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
copyArr[i]=arr[i];
arr = copyArr;
System.out.println("추가 숫자 입력 >>");
int input = sc.nextInt();
arr[cnt++]=input;
}
}
}
static void printResult() {
System.out.print("최종 배열 출력:");
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}

사용자가 입력하는 대로 배열이 계속 늘어나게 하기(5개씩)
기능별로 함수로 다시 만들었다.
package ex01;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test0320_4 {
static int[] arr = new int[5];
static int cnt = 0;
static int goStop = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
firstArr5();
addArr();
printResult();
}
static void firstArr5() {
inputNum();
System.out.println("배열이 다 찼습니다.");
}
static void inputNum() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("숫자 5개를 입력하세요 >>");
while(cnt<arr.length) {
int input = sc.nextInt();
arr[cnt++]=input;
}
}
static void addArr() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
if(cnt>=arr.length)
System.out.println("더 입력하시겠습니까? 배열이 5개가 늘어납니다.(Y:1, N:0)");
goStop = sc.nextInt();
if(goStop==0) break;
else {
copyArray();
inputNum();
}
}
}
static void copyArray() {
int[] copyArr = new int[arr.length+5];
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
copyArr[i]=arr[i];
arr = copyArr;
}
static void printResult() {
System.out.print("최종 배열 출력:");
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}