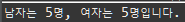
JVM memory manage
- Method area: member mothod와 static 변수들이 저장되는 곳
- Stack area: 변수들이 만들어지는 곳
- Heap area: 인스턴스가 만들어지는 곳
변수
- 인스턴스 변수: 무한정 생성 가능, n은 클래스로부터 만들어진 인스턴스 갯수만큼 생성된다.
참조변수를 통해서 접근한다.
class C{
int n;
}- 클래스 변수: 1개만(클래스 갯수만큼) 존재, static 변수, 인스턴스들이 공유 가능
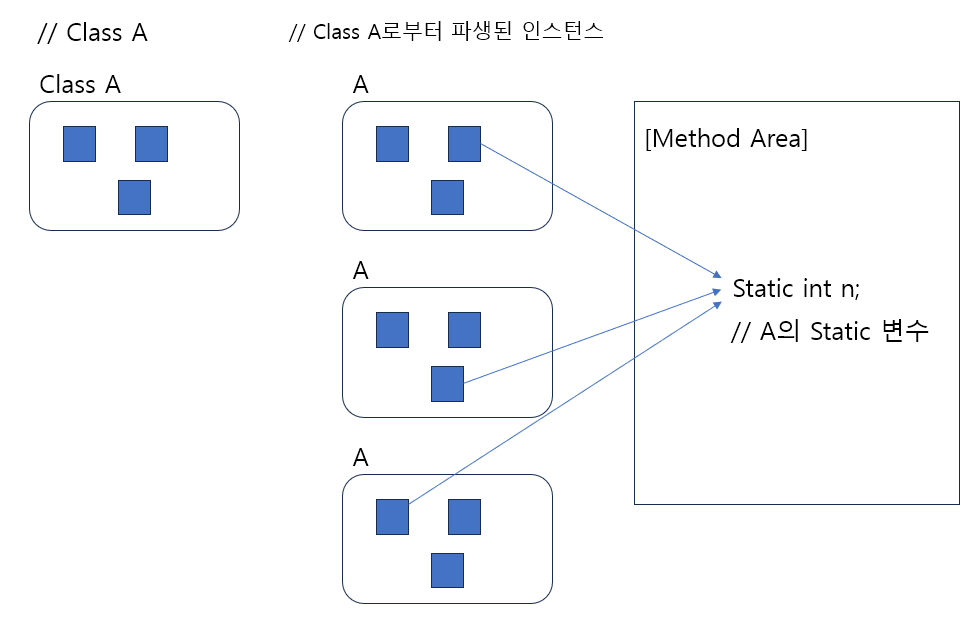
참조변수로부터 인스턴스변수나 static변수의 구별이 어렵다.
클래스명을 참조변수처럼 활용하면 static 변수가 어떤 것인지 알 수 있다.
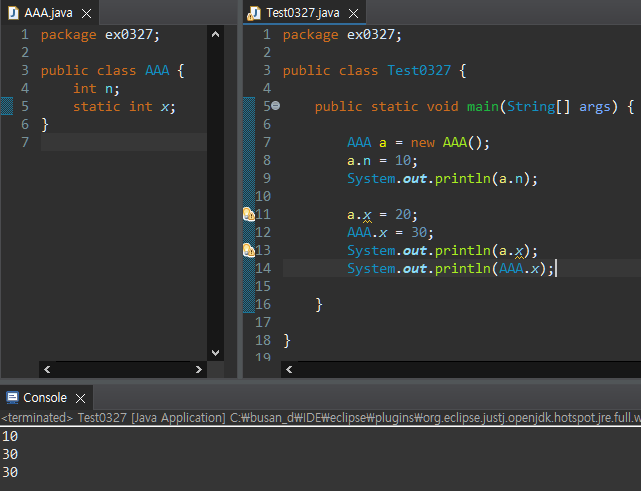
인스턴스가 없더라도 static 변수에 접근할 수 있다.
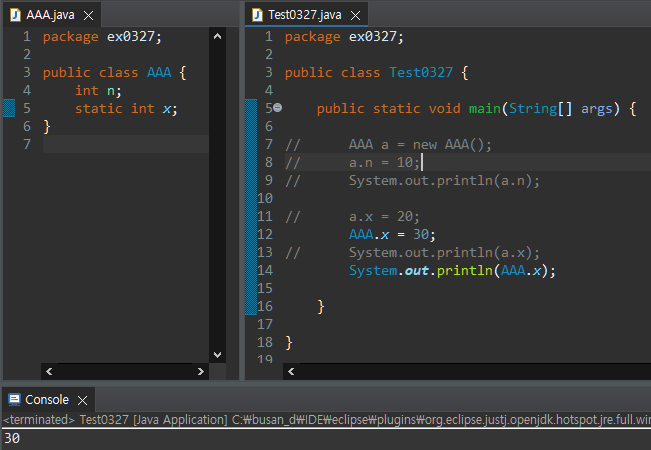
static 변수는 class 변수라고도 부른다.
인스턴스 생성을 하지 않더라도 존재한다.
함수
static method: class method이며 인스턴스없이도 바로 사용할 수 있다.
클래스명.함수명
static 함수에서는 non-static 함수를 호출할 수가 없다.
아마 static 함수는 생성하지 않아도 호출할 수 있지만 non-static 함수가 포함되어 있다면 논리가 맞지 않기 때문인 듯하다.
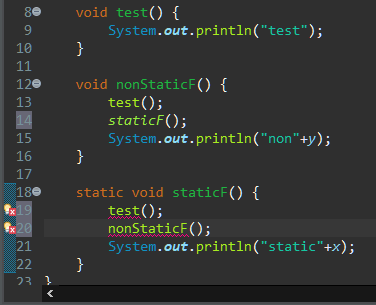
메인함수에도 static이 붙는데 없다면 인스턴스를 생성해서 참조변수를 통해 실행해주어야한다.
static이 있어서 인스턴스와 참조변수 없이 최초 실행이 가능한 것이다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
}[예제]
Person() 클래스 생성
- 인간고유번호(no)는 중복되면 안된다.
- 인간고유번호는 인스턴스를 생성할 때 자동으로 부여한다.
main method
- 만약 i번이 생성되었다면, 인간이 몇 명 만들어졌는지 알려준다.
Person.java
package vo;
public class Person {
static private int cnt=0; // 인간의 수 카운트
private int number; // 인간의 고유번호
private int age;
private String name;
public Person() {
System.out.println("현재까지 생성된 인간은 "+getNumber()+"명 입니다.");
cnt++; // 인간의 고유번호 증가
number=cnt; // 생성된 사람별로 번호 부여
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
public int getNo() {
return cnt;
}
public String toString() {
return "Person] number="+number+", age=" +age+ ", name="+name;
}
}Test0327.java
package ex0327;
import vo.Person;
public class Test0327 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.setAge(10);
p1.setName("AAA");
System.out.println(p1.toString());
Person p2 = new Person();
p2.setAge(15);
p2.setName("BBB");
System.out.println(p2.toString());
Person p3 = new Person();
p3.setAge(17);
p3.setName("CCC");
System.out.println(p3.toString());
System.out.println(p1.toString());
}
}결과
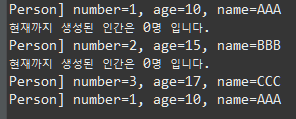
[추가]
성별을 넣는다. 남M 여F
인스턴스는 10개(남4, 여6)
기본생성자는 없다.
배열에 저장하고 남자는 몇 명, 여자는 몇 명인지 출력하자.
Person.java
package vo;
public class Person {
static private int cnt=0; // 인간의 수 카운트
private int id; // 인간의 고유번호
private int age;
private String name;
private char gender;
static private int mCnt;
static private int fCnt;
public Person(char gender) {
// System.out.println("현재까지 생성된 인간은 "+getNumber()+"명 입니다.");
id=++cnt; // 생성된 사람별로 번호 부여
if(gender=='M') mCnt++;
else fCnt++;
this.gender=gender;
}
/*
public Person() {
// System.out.println("현재까지 생성된 인간은 "+getNumber()+"명 입니다.");
id=++cnt; // 생성된 사람별로 번호 부여
}*/
// setter, cnt와 number는 자동생성이므로 setter가 필요 없음
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 트렌스젠더도 있을 수 있으니 setter를 만든다.
public void setGender(char gender) {
if(gender=='M') {
mCnt++;
fCnt--;
}
else{
fCnt++;
mCnt--;
}
this.gender = gender;
}
// getter
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getNumber() {
return id;
}
public int getNo() {
return cnt;
}
public char getGender() {
return gender;
}
public int getMCnt() {
return mCnt;
}
public int getFCnt() {
return fCnt;
}
public String toString() {
return "Person] id="+id+", age=" +age+ ", name="+name+", gender="+gender;
}
}Test0327.java
package ex0327;
import vo.Person;
public class Test0327 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] people = new Person[10];
Person p1 = new Person('M');
people[0] = p1;
Person p2 = new Person('M');
people[1] = p2;
Person p3 = new Person('M');
people[2] = p3;
Person p4 = new Person('M');
people[3] = p4;
Person p5 = new Person('F');
people[4] = p5;
Person p6 = new Person('F');
people[5] = p6;
Person p7 = new Person('F');
people[6] = p7;
Person p8 = new Person('F');
people[7] = p8;
Person p9 = new Person('F');
people[8] = p9;
Person p10 = new Person('F');
people[9] = p10;
// 트렌스젠더인 경우 추가
p10.setGender('M');
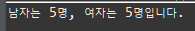
System.out.println("남자는 "+p1.getMCnt()+"명,"+ " 여자는 "+p1.getFCnt()+"명입니다.");
}
}결과
age와 name은 사용하지 않았다.
처음에는 남4, 여6을 만들었고,
여 → 남이 된 경우를 하나 추가해주어 남5, 여5이 나와야한다.
번호가 4번인 사람의 성별을 알아내시오
for(int i=0; i<people.length; i++)
if(people[i].getNumber()==4)
System.out.println("번호가 4번인 사람의 성별: "+people[i].getGender());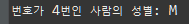
사람 배열을 넣어주면 배열에서 남자, 여자가 몇 명인지 출력해주는 함수
static void howMany(Person[] people) {
System.out.println("남자는 "+people[0].getMCnt()+"명,"+ " 여자는 "+people[0].getFCnt()+"명입니다.");
}근데 Person 클래스에서는 다른 사람의 성별이 몇명인지 static private int mCnt or fCnt가 필요하지 않으므로 삭제하고
Test0327.java에서 별도로 함수로 만들어 카운트해준다.
void howMany(Person[] people) {
int mCnt=0;
int fCnt=0;
for(int i=0; i<people.length; i++) {
if(people[i].getGender()=='M')
mCnt++;
else
fCnt++;
}
System.out.println("남자는 "+mCnt+"명,"
+ " 여자는 "+fCnt+"명입니다.");
}howMany를 static으로 하지 않고 메인에서 호출하면 오류가 난다.
Test0327 t = new Test0327();
t.howMany(people);챗지피티의 도움을 받아, 같은 패키지에 있는 클래스는 static으로 선언하지 않더라도 사용할 수 있다는 걸 확인했다.
그러면 Person 클래스에서 사용할 수 있게 함수를 만들어준다.
public void accHowMany(Person[] people) {
howMany hm = new howMany();
hm.cntPeople(people);
}그럼 다른 패키지에 있는 메인에서도 Person으로 생성한 참조변수를 통해 accHowMany메서드를 사용할 수 있다.
p1.accHowMany(people);