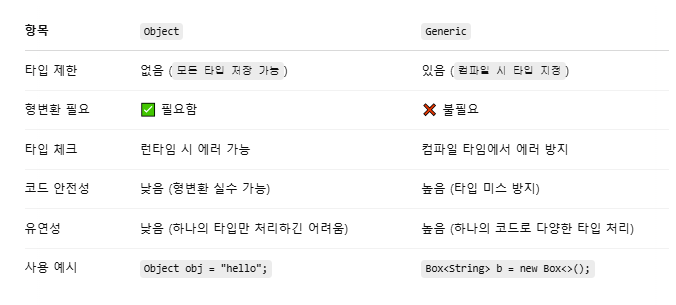
제네릭과 Object의 차이점
ArrayList도 제네릭 클래스
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("apple");
list.add("banana");ArrayList <.E> 내부정의
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable {
HashMap도 제네릭 클래스
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("math", 95);
map.put("science", 88);HashMap<K,V> 내부 정의
public class HashMap<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V> implements Map<K, V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
Key는 중복불가, Value는 중복가능
제네릭은 타입에 제한이 없기 때문에 HashMap<HashMap, Integer> 형태로도 선언이 가능하다.
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> innerMap1 = new HashMap<>();
innerMap1.put("name", "Alice");
HashMap<String, String> innerMap2 = new HashMap<>();
innerMap2.put("name", "Bob");
HashMap<HashMap<String, String>, Integer> outerMap = new HashMap<>();
outerMap.put(innerMap1, 100);
outerMap.put(innerMap2, 200);
for (HashMap<String, String> key : outerMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println("Key: " + key + " | Value: " + outerMap.get(key));
}
}
}하지만 HashMap은 mutable이기 때문에 key로 쓰면 위험하다. 수정이 불가능한 객체를 Key로 사용하는 것이 좋다.

제네릭이 없다면? Object로 하게 될 경우
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); // 타입 명시 X → 모두 Object로 처리
list.add("apple");
list.add(123); // 타입 혼합 가능
String str = (String) list.get(0); // 형변환 필요
Integer n = (Integer) list.get(1); // 잘못 캐스팅하면 런타임 에러 발생Student 클래스를 만든다.
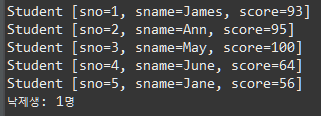
Student 배열을 만들어서 사용하는 방법
Student s1 = new Student("James", 93);
Student s2 = new Student("Ann", 95);
Student s3 = new Student("May", 100);
Student s4 = new Student("June", 64);
Student s5 = new Student("Jane", 56);
Student[] students = new Student[5];
students[0]=s1;
students[1]=s2;
students[2]=s3;
students[3]=s4;
students[4]=s5;
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0; i<students.length; i++) {
if(students[i].getScore()<60)
cnt++;
System.out.println(students[i]);
}
System.out.println("낙제생: "+cnt+"명");ArrayList를 사용하는 방법
Student s1 = new Student("James", 93);
Student s2 = new Student("Ann", 95);
Student s3 = new Student("May", 100);
Student s4 = new Student("June", 64);
Student s5 = new Student("Jane", 56);
ArrayList<Student> sList = new ArrayList<>();
sList.add(s1);
sList.add(s2);
sList.add(s3);
sList.add(s4);
sList.add(s5);
int count=0;
for(int i=0; i<sList.size(); i++) {
if(sList.get(i).getScore()<60)
count++;
System.out.println(sList.get(i));
}
System.out.println("낙제생: "+cnt+"명");같은 결과값을 보여준다.
for문 사용
기본 for문: for(초기값; 범위; 반복){}
향상된 for문: for(배열의 요소 타입변수 선언: 배열){}
int count=0;
for(int i=0; i<sList.size(); i++) {
if(sList.get(i).getScore()<60)
count++;
System.out.println(sList.get(i));
}
System.out.println("낙제생: "+cnt+"명");
int count2=0;
for(Student s: sList) {
if(s.getScore()<60)
count2++;
System.out.println(s);
}예제
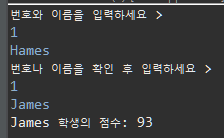
학생의 점수를 알려주는 프로그램
번호와 이름을 입력하세요.
해당되는 학생이 있으면 번호나 이름을 확인하세요.
해당되는 학생이 있으면 해당 학생에 대한 점수는 몇 점이에요.
package ex0408;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("James", 93);
Student s2 = new Student("Ann", 95);
Student s3 = new Student("May", 100);
Student s4 = new Student("June", 64);
Student s5 = new Student("Jane", 56);
ArrayList<Student> sList = new ArrayList<>();
sList.add(s1);
sList.add(s2);
sList.add(s3);
sList.add(s4);
sList.add(s5);
checkScore(sList);
}
public static void checkScore(ArrayList<Student> sList) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int idx = 999;
int inputNum;
String inputName;
System.out.println("번호와 이름을 입력하세요 > ");
while(true) {
inputNum = sc.nextInt();
inputName = sc.next();
for(int i=0; i<sList.size(); i++) {
if(sList.get(i).getSno()==inputNum && inputName.equals(sList.get(i).getSname())) {
idx = i;
break;
}
}
if(idx!=999) {
System.out.println(sList.get(idx).getSname()+" 학생의 점수: " +sList.get(idx).getScore());
break;
}
else{
System.out.println("번호나 이름을 확인 후 입력하세요 >");
}
}
}
}
Student.java
package ex0408;
public class Student {
private static int cnt;
private int sno;
private String sname;
private int score;
public Student(String sname, int score){
sno = ++cnt;
this.sname = sname;
this.score = score;
}
public int getSno() {
return sno;
}
public String getSname() {
return sname;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setSno(int sno) {
this.sno = sno;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [sno=" + sno + ", sname=" + sname + ", score=" + score + "]";
}
}
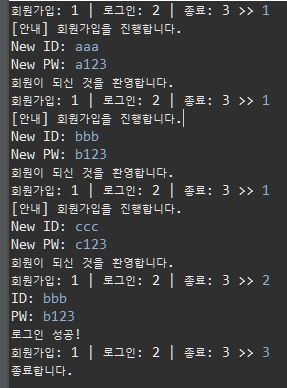
로그인 프로그램
회원가입, 로그인하는 프로그램
LoginTest.java
package ex0408;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LoginTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Login> lList = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("회원가입: 1 | 로그인: 2 | 종료: 3 >> ");
int choice = sc.nextInt();
while(choice!=3) {
if(choice==1) {
join(lList);
}
else if(choice==2){
login(lList);
}
System.out.print("회원가입: 1 | 로그인: 2 | 종료: 3 >> ");
choice = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("종료합니다.");
}
public static void join(ArrayList<Login> lList) {
System.out.println("[안내] 회원가입을 진행합니다.");
Join j = new Join();
j.JoinProcess();
lList.add(new Login(j.getId(),j.getPw()));
System.out.println("회원이 되신 것을 환영합니다.");
}
public static void login(ArrayList<Login> lList) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean flag = true;
String id;
String pw;
while(flag) {
System.out.print("ID: ");
id=sc.next();
System.out.print("PW: ");
pw=sc.next();
flag=LoginChecker.checkLoginInfo(lList, id, pw);
if(flag) {
System.out.println("ID와 PW를 확인하세요.");
}else {
System.out.println("로그인 성공!");
}
}
}
}
Join.java
package ex0408;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Join {
String id;
String pw;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getPw() {
return pw;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setPw(String pw) {
this.pw = pw;
}
public void JoinProcess() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("New ID: ");
id = sc.next();
System.out.print("New PW: ");
pw = sc.next();
}
}
Login.java
package ex0408;
public class Login {
private String id;
private String pw;
public Login(String id, String pw){
this.id=id;
this.pw=pw;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getPw() {
return pw;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setPw(String pw) {
this.pw = pw;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Login [id=" + id + ", pw=" + pw + "]";
}
}
LoginChecker.java
package ex0408;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class LoginChecker {
public static boolean checkLoginInfo(ArrayList<Login> lList, String id, String pw) {
for(Login l : lList) {
if(l.getId().equals(id) && l.getPw().equals(pw)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
결과