lombok 설치/적용
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.projectlombok/lombok/1.18.38
lombok.jar 다운
C:\busan_d\jars>java -jar lombok-1.18.38.jar
패키지에 build path 설정해주기
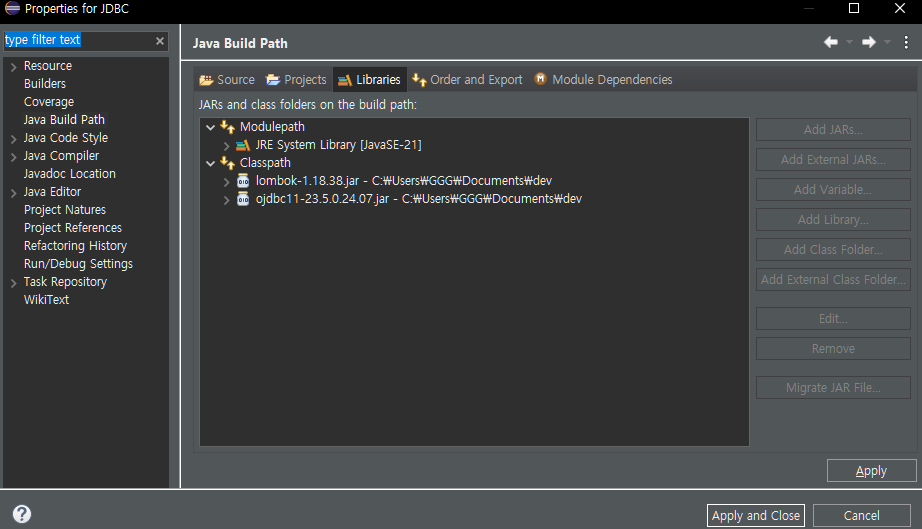
Test하기
이제 Getter, Setter, ToString을 만들 필요가 없다.
Getter, Setter, toString
package ex0414;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
@Setter
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
// @Data
public class A {
private int n;
}
package ex0414;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
A a = new A();
a.setN(10);
System.out.println(a.getN());
A a2 = new A(20);
System.out.println(a2);
}
}
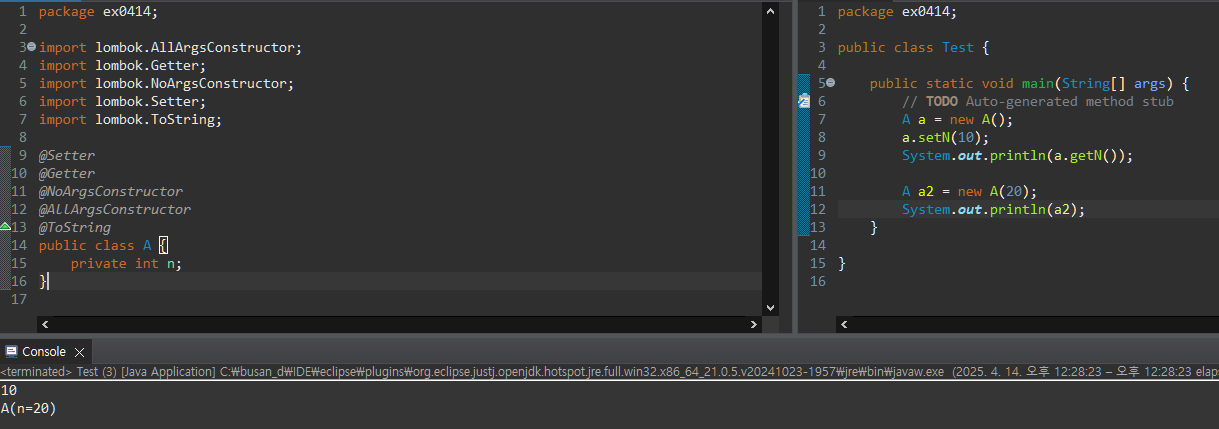
equals
Object에서 정의된 메소드, 두 가지를 비교
ctl 누른 상태에서 equals를 누르면 아래와 같이 나온다.
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}→ 주소를 비교하는 것으로 내부 정의, 따라서 두 가지는 같은 의미
m1 == m2
m1.equals(m2)
만약 두 가지의 인스턴스의 값을 비교해야할 때, equals를 재정의 해야한다.
ctl + spacebar 누르면 오버라이드 가능한 항목이 나온다.
Member 클래스에서 Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(this == obj)
return true;
if(obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Member target = (Member) obj;
return mno == target.mno && name.equals(target.name) && phone.equals(target.phone);
}[참고] Member 클래스 내에서 정의
public boolean equals(Member m) {
if(this.getMno() == m.getMno()
&& this.getName() == m.getName()
&& this.getPhone() == m.getPhone())
return true;
else
return false;
}[참고] Main에서 함수로 정의
public static boolean equals(Member m1, Member m2) {
if(m1.getMno() == m2.getMno() &&
m1.getName() == m2.getName() &&
m1.getPhone() == m2.getPhone())
return true;
else
return false;
}HashCode
Member타입을 저장할 HashSet을 만들고 m1, m2를 add
HashSet은 중복된 데이터를 받지 않는다.
HashSet<Member> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(m1);
System.out.println("m1추가: "+set.size());
set.add(m2);
System.out.println("m2추가: "+set.size());
set.add(m3);
System.out.println("m3추가: "+set.size());결과
m1추가: 1
m2추가: 2
m3추가: 2우리는 m1과 m2를 같은 것으로 보고 있는데, set에서는 다른 것으로 보고 추가를 한다.
JAVA> 인스턴스를 비교하려면 equals랑 hash도 같이 오버라이드해야한다.
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(mno, name, phone);
}결과
m1추가: 1
m2추가: 2
m3추가: 1→ @EqualsAndHashCode 추가해주면 됨(lombok)
@Data
EqualsAndHashCode, Getter, Setter, ToString을
Data로 한 번에 import 가능하다.
//import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
//import lombok.Getter;
//import lombok.Setter;
//import lombok.ToString;
import lombok.Data;
//@Getter
//@Setter
//@ToString
//@EqualsAndHashCode
@Data인스턴스 복사(clone)
implements Cloneable을 해주어야 CloneNotSupportedException가 생기지 않는다.
복제 가능한 클래스다라는 의미로 표시
→마커 인터페이스(메서드가 없는 인터페이스)
point.java
package ex0414;
public class Point implements Cloneable{
private int xPos;
private int yPos;
public Point(int xPos, int yPos){
this.xPos = xPos;
this.yPos = yPos;
}
public void showPosition() {
System.out.printf("[%d, %d]", xPos, yPos);
System.out.println();
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//상속관계에서 접속할 수 있게 protected
return super.clone();
}
}
PointTest.java
package ex0414;
public class PointTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point org = new Point(3, 5);
Point cpy;
try {
cpy = (Point) org.clone();
org.showPosition();
cpy.showPosition();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}오버라이드는 접근제한자 범위가 더 넓어질 수 있다.
protected → public
@Override
public Point clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//상속관계에서 접속할 수 있게 protected
return (Point)super.clone();
}Getter, Setter 추가 후, org의 값 변경하면 cpy의 값은 변경되지 않는다. 각자 독립적인 것
package ex0414;
public class PointTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point org = new Point(3, 5);
Point cpy;
try {
cpy = (Point) org.clone();
org.showPosition();
cpy.showPosition();
System.out.println("------------");
cpy.setXPos(10);
cpy.setYPos(30);
org.showPosition();
cpy.showPosition();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}결과
[3, 5]
[3, 5]
------------
[3, 5]
[10, 30]
Rectangle.java
package ex0414;
public class Rectangle implements Cloneable{
private Point upperLeft;
private Point lowerRight;
public Rectangle(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
upperLeft = new Point(x1, y1);
lowerRight = new Point(x2, y2);
}
public void changePos(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
upperLeft.changePos(x1, y1);
lowerRight.changePos(x2, y2);
}
public void showPosition() {
System.out.print("좌측 상단: ");
upperLeft.showPosition();
System.out.print("우측 하단: ");
lowerRight.showPosition();
System.out.println();
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.clone();
}
}RectangleTest.java
package ex0414;
public class RectangleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle org = new Rectangle(3,5,7,10);
Rectangle cpy;
try {
cpy = (Rectangle) org.clone();
org.showPosition();
cpy.showPosition();
System.out.println("-------------");
cpy.changePos(1, 1, 9, 9); // cpy가 가리키는 org의 changePos메소드호출
org.showPosition();
cpy.showPosition();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}결과
좌측 상단: [3, 5]
우측 하단: [7, 10]
좌측 상단: [3, 5]
우측 하단: [7, 10]
-------------
좌측 상단: [1, 1]
우측 하단: [9, 9]
좌측 상단: [1, 1]
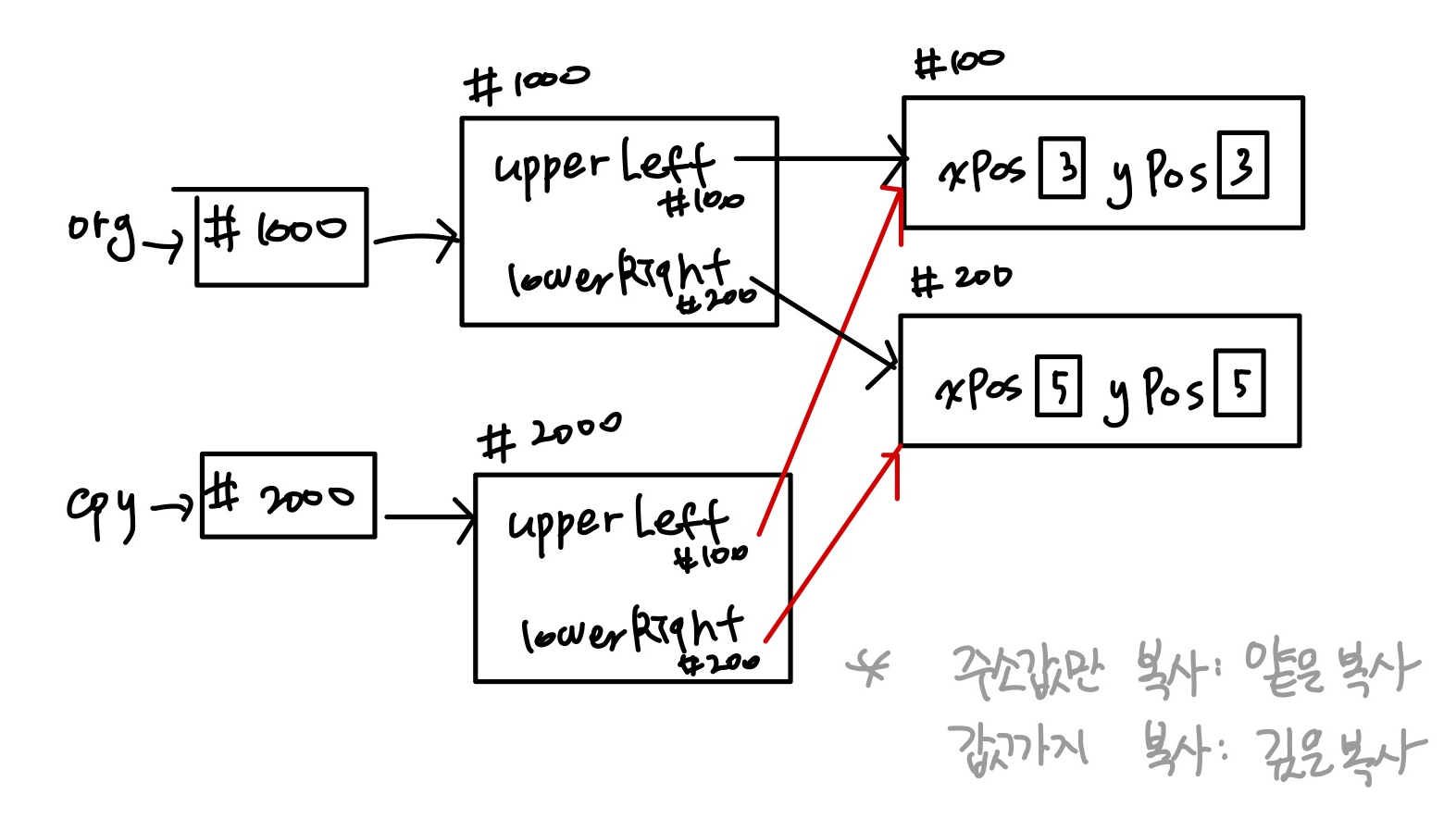
우측 하단: [9, 9]얕은 복사
PointTest와는 달리 cpy.changePos를 하면 cpy와 org의 값이 모두 바뀐다.
Rectangle org이 가진 point upperLeft와 point lowerRight을
Rectangle cpy도 같이 가리키는 얕은 복사를 하기 때문이다.
이런 현상을 예방하기 위해서 아래와 같이 하기 위해 clone() 메서드를 수정해준다.
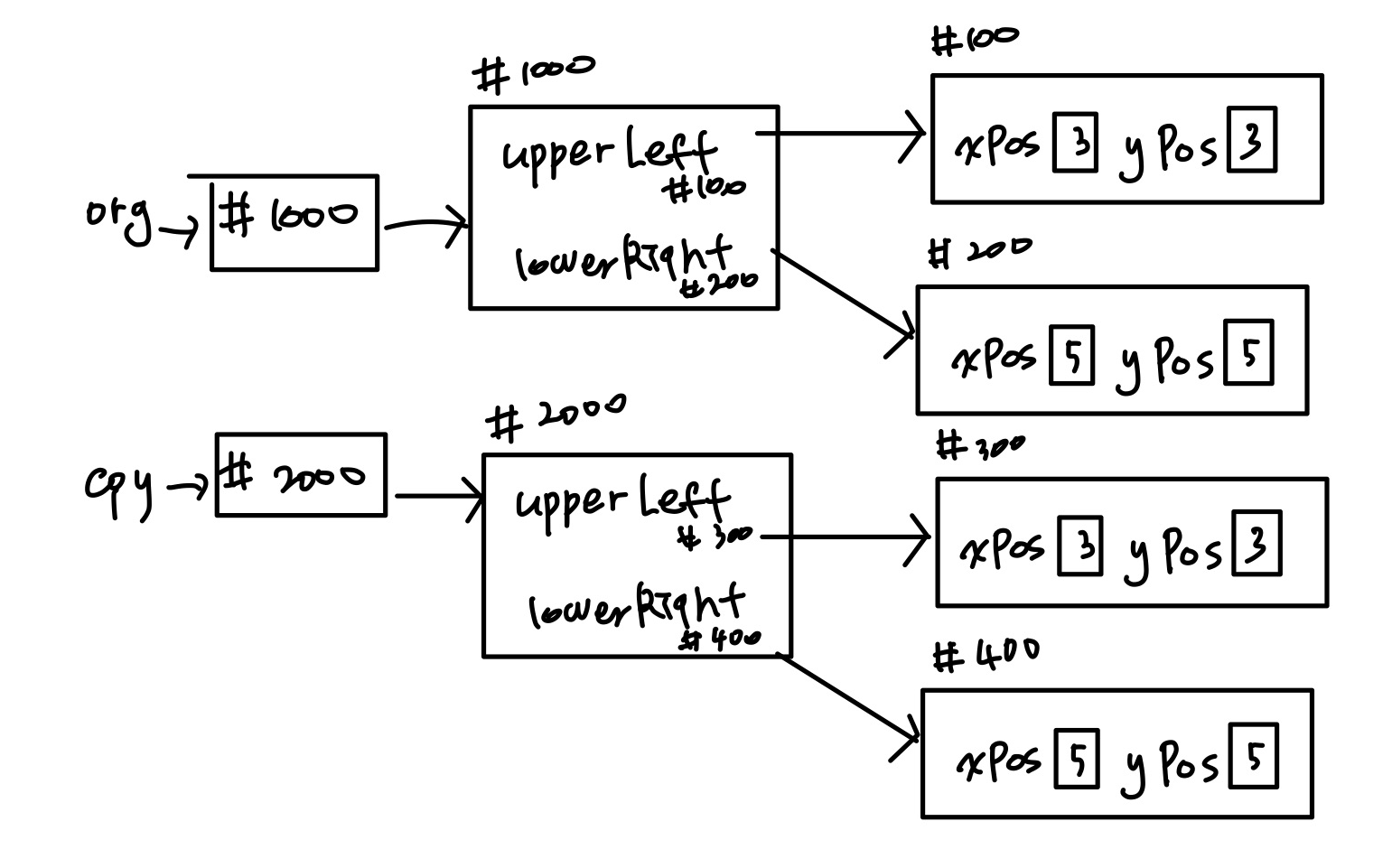
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Rectangle cpy = new Rectangle(upperLeft.getXPos(), upperLeft.getYPos(), lowerRight.getXPos(), lowerRight.getYPos());
return cpy;
}결과
좌측 상단: [3, 5]
우측 하단: [7, 10]
좌측 상단: [3, 5]
우측 하단: [7, 10]
-------------
좌측 상단: [3, 5]
우측 하단: [7, 10]
좌측 상단: [1, 1]
우측 하단: [9, 9]Rectangle을 HashSet에 넣어보기
opg과 cpy를 같은 형태로 만들어주었을 때, HashSet에 넣으면 size가 1이 나와야하는데 size가 2가 나오므로,
결과
좌측 상단: [3, 5]
우측 하단: [7, 10]
좌측 상단: [3, 5]
우측 하단: [7, 10]
HashSet size: 1
HashSet size: 2
Rectangle.java에서 equals()와 hashCode()를 수정해주었다.
RectangleTest.java
package ex0414;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class RectangleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle org = new Rectangle(3,5,7,10);
Rectangle cpy = null;
try {
cpy = (Rectangle) org.clone();
org.showPosition();
cpy.showPosition();
// System.out.println("-------------");
// cpy.changePos(1, 1, 9, 9);
// org.showPosition();
// cpy.showPosition();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
HashSet<Rectangle> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(org);
System.out.println("HashSet size: "+set.size());
set.add(cpy);
System.out.println("HashSet size: "+set.size());
}
}Rectangle.java
package ex0414;
import java.util.Objects;
//import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
//@EqualsAndHashCode
public class Rectangle implements Cloneable{
private Point upperLeft;
private Point lowerRight;
public Rectangle(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
upperLeft = new Point(x1, y1);
lowerRight = new Point(x2, y2);
}
public void changePos(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
upperLeft.changePos(x1, y1);
lowerRight.changePos(x2, y2);
}
public void showPosition() {
System.out.print("좌측 상단: ");
upperLeft.showPosition();
System.out.print("우측 하단: ");
lowerRight.showPosition();
System.out.println();
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Rectangle cpy = new Rectangle(upperLeft.getXPos(), upperLeft.getYPos(), lowerRight.getXPos(), lowerRight.getYPos());
return cpy;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(this == obj)
return true;
if(obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Rectangle target = (Rectangle) obj;
return upperLeft.getXPos() == target.upperLeft.getXPos()
&& upperLeft.getYPos() == target.upperLeft.getYPos()
&& lowerRight.getXPos() == target.lowerRight.getXPos()
&& lowerRight.getYPos() == target.lowerRight.getYPos();
//return super.equals(obj);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(upperLeft.getXPos(), upperLeft.getYPos(), lowerRight.getXPos(), lowerRight.getYPos());
}
}결과
좌측 상단: [3, 5]
우측 하단: [7, 10]
좌측 상단: [3, 5]
우측 하단: [7, 10]
HashSet size: 1
HashSet size: 1
간단하게 @EqualsAndHashCode를 추가했는데 반영이 안된다.
왜냐하면 Rectangle 클래스에만 추가해주었기 때문인데,
Point 자료형 변수를 사용하므로 Point 클래스에도 동일하게 추가해주면 가능하다.
