18352
- 한노드 -> 다른노드로 가는 최단경로 + 가중치 양수 -> 다익스트라
11404
- 왜 숫자범위 적당히 크게 하면되는거지. 어느정도인지 내가 어떻게 알지?
어느정도까지 크게해야하는지 어떻게알지?
- nm까지 max의 값은 커질 수 있다. 왜냐하면 a->b가 일렬로 나열되어있고, 100개이며 각각의 가중치가 1000000이면 nm만큼의 가중치가 될것이기때문이다.
11403
- 임의의 한 노드 -> 다른 노드에 대한 모든 경로니까 플로이드 워샬적용
13549 숨박꼭질
- 이 노드를 백트래킹으로 풀면 왜안되는건지 모르겠다 stackoverflow가 터지는군
public static int solve(int t, int current){
if(current<0 || current> 100000) return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(current==k){
return t;
}
int a = solve(t+1, current-1);
int b = solve(t-1, current+1);
int c = solve(t, current *2);
return Math.min(Math.min(a,b),c);
}
시도1
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import javax.management.ObjectName;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Main{
static int n;
static int k;
static boolean visited[];
public static class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
int t;
int x;
Node(int t, int x){
this.t=t;
this.x=x;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.t-o.t;
}
}
public static int solve(int s){
PriorityQueue<Node> q = new PriorityQueue<>();
q.add(new Node(0, s));
visited[s]= true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Node node = q.poll();
if(node.x == k) {
return node.t;
}
add(q,node.x*2, node.t);
add(q,node.x+1, node.t+1);
add(q,node.x-1, node.t+1);
}
return -1;
}
public static void add(PriorityQueue<Node> q, int x, int t){
if(x<0 || x>100000||visited[x]) return;
visited[x] = true;
q.add(new Node(t, x));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String input[] = br.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
visited = new boolean[100001];
k = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
bw.write(solve(n)+"\n");
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
}
문제1
- 구현의도는 이랬다. time을 기준으로 우선순위큐를 생성한다
- 그러면 time이 적은것부터 먼저 꺼내게 될것이고, 그러다보면 시간이 가장 적게 든 x의 좌표를 바로 꺼낼 수 있을것이다.
- 하지만 이 풀이법은 문제가 존재한다
- q에 넣는 순간 q는 정렬되기때문에 visited코드를 add할때 넣어주면 안되고 poll할때 넣어주어야한다 < 이 부분이 이해가 안간다. 왜 add할때 넣어주는 점이 문제가 되는것이며, 그 문제를 poll할때 visited를 true로 지정해줌으로써 해결할 수 있는것인가?
- 하지만 visited의 위치를 바꿈으로서 정답이 떴다.
- 내가 add할때 방문처리를 했던이유는 poll할때방문처리를 하게 되면 poll하기전까지는 그 지점을 계속 중복해서 방문하게되기때문이다.
어쨋든 큐에 넣게되는순간이라는 것은 그 좌표까지 왔다는얘기다. 방문처리를 해주는 이유도 계속 그 좌표에 중복방문하는것을 막기위한 것이다. 어차피 그 좌표까지 오면 그 뒤의 일은 똑같다 +1, -1, *2 세가지 경우를 q에 또 삽입할 것이다.
해결
- 5-10-9-18-17 을 생각해보자
반복이 1회 진행될때마가 5,6,7,...visited칸들은 모두 true가 될것이다.
방문처리 된 이후에 더적은 t를 가지는 node가 나타나서 해당 지점을 방문하려고했다
근데 이미 다른 경로에의해(더오래걸리는경로)방문처리가 되었다면?
-> 내가 큐에 넣는다. 그러면 우선순위큐에 의해 정렬이될것이다. 정렬이 되고 나서. 그 순서에 의해서 뽑힌 대로 방문처리를 해주어야지 오래걸리는 경로에 의해 방문처리가 되지않는다
- 큐에넣고 바로 visited를 하라는얘기가 아니다. 큐에 넣고 해당노드가 poll되는 시점이여야한다. 그래야 그 노드가 적절하게 호출되는 시점인거고. 그떄 방문처리를 해주어야한다
- (그 노드는 가장 t가 빠른 노드임 그래서 그 노드를 먼저 방문처리해줘도됨. 왜냐면 우리가 걱정하는것은 다른 더 오래걸리는경로에 의해 노드가 먼저 방문처리되는것을 걱정하는거기때문)
문제2
- visited의 위치를 바꾸고싶지않다면 어떻게 해야할까?
- 그 경우엔 우선순위 큐말고 그냥 큐를 쓰면된다!
- 그리고 add하는 순서에 신경을쓴다(t가 변하지 않는
x*2부터 add)
x*2부분을 먼저 add한다고 하더라도, 다음 반복때 시간이 더 적게 드는 Node가 Queue의뒤쪽에 배치될것이다. 그러니까 이 풀이법은 min을 찾는다고 바로 return하면 안된다. 큐에 있는 내용을 다 뒤져보고, node.x == k인 node중. 가장 적은 t를 가지는 node를뽑아내는 코드가 필요하다.
public static int solve(int s){
PriorityQueue<Node> q = new PriorityQueue<>();
q.add(new Node(0, s));
visited[s]= true;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Node node = q.poll();
if(node.x == k) {
min = Math.min(min, node.t);
}
add(q,node.x*2, node.t);
add(q,node.x+1, node.t+1);
add(q,node.x-1, node.t+1);
}
return min;
}
public static void add(PriorityQueue<Node> q, int x, int t){
if(x<0 || x>100000||visited[x]) return;
q.add(new Node(t, x));
visited[x] = true;
}
가중치가 존재하는 간선?
결론
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import javax.management.ObjectName;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Main{
static int n;
static int k;
static boolean visited[];
public static class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
int t;
int x;
Node(int t, int x){
this.t=t;
this.x=x;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.t-o.t;
}
}
public static int solve(int s){
PriorityQueue<Node> q = new PriorityQueue<>();
q.add(new Node(0, s));
visited[s]= true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Node node = q.poll();
visited[node.x] = true;
if(node.x == k) {
return node.t;
}
add(q,node.x*2, node.t);
add(q,node.x+1, node.t+1);
add(q,node.x-1, node.t+1);
}
return -1;
}
public static void add(PriorityQueue<Node> q, int x, int t){
if(x<0 || x>100000||visited[x]) return;
q.add(new Node(t, x));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String input[] = br.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
visited = new boolean[100001];
k = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
bw.write(solve(n)+"\n");
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
}
11265
- 모든 노드간의 최단경로를 구함 -> 플로이드 워샬
1753
시도1
public static void solve(){
PriorityQueue<Node> q = new PriorityQueue<>();
q.add(new Node(s, 0));
distance[s] = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Node node = q.poll();
isVisited[node.n] = true;
for (Node neighbor:list[node.n]) {
if(distance[neighbor.n]> distance[node.n] + neighbor.cost && !isVisited[node.n]){
distance[neighbor.n] = Math.min(distance[neighbor.n], distance[node.n] + neighbor.cost);
q.add(new Node(neighbor.n, distance[neighbor.n]));
}
}
}
}
- 방문처리를 poll을 하고 나서 해줘야하는것은 알겠다. (인접노드에 대해서 방문처리를 해버리고, 인접노드를 큐에 추가하는 if문에서 방문된건 건너뛰는 코드를 작성하면 인접노드에 대한 인접노드는 파악할 수 없어지기때문)
- 근데 그럼. 방문된것은 건너뛰는코드를 어디에다 작성해야하나? < 이걸 잘 모르겠음
- 나는 예제를 들어서 생각을 해봤음
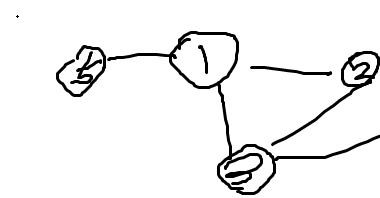
- 일단 1을 방문함. 그럼 큐에 2,3,5가쌓임. 그리고 1을 방문처리함
그리고 235를 큐에 넣음. 그리고 2에 들어감. 2의 인접노드 1 3 4 을 모두 큐에 추가하기전, 방문 했던 1은 제외함 -> 즉, 인접노드를 추가하는 코드에서 방문한노드면 제외시키는 코드를 넣으면되겠다고 생각을하게됨. 근데 그게 오답이 떠서 왜그런가했더니 이웃노드.n이 아니라 node.n을 넣어서그런거였음
!isVisited[node.n] < 이부분
- 근데 그래도 궁금한점이있음. 내가 코드를 짠것은 이해감. 근데

- 이렇게 구현해도 될수있다는게 막 와닿진 않음. 이 처리로 인해서 한번 방문한것은 다시 처리안되겠구나 정도만 알겠음 !
궁금증2
- 왜
distance[neighbor.n]> distance[node.n] + neighbor.cost 이 경우에 대해서만 큐에 이웃을 집어넣는것인지?
- 아래코드에 답을 적어놨다.
해결
public static void solve(){
PriorityQueue<Node> q = new PriorityQueue<>();
q.add(new Node(s, 0));
distance[s] = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Node node = q.poll();
isVisited[node.n] = true;
for (Node neighbor:list[node.n]) {
if(distance[neighbor.n]> distance[node.n] + neighbor.cost && !isVisited[neighbor.n]){
distance[neighbor.n] = Math.min(distance[neighbor.n], distance[node.n] + neighbor.cost);
q.add(new Node(neighbor.n, distance[neighbor.n]));
}
}
}
}
다익스트라구현에 대한 의문
- 시작노드를 큐에 넣는다
- 큐에서 뺀 노드의 인접노드에 대해 조사한다.
그리고 거리를 최소로 갱신한다(자신의 이전 distance값, 시작노드의 distance+시작노드~해당노드의 거리) 둘중에 작은걸로 갱신한다
그리고 만약 갱신이 된다면 큐에 다시 넣는다 <- 왜 갱신이 된애들에대해서만 큐에 넣지? - 위에 적음
14938
- 한노드 - 다른모든노드들에 대한 최단경로를 구하면 될것같다
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int n;
static int w;
static float m;
static int item[];
static final int MAX = 1000000000;
static double arr[][];
static Point plant[];
static double distance[];
static boolean isVisited[];
public static class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
int n;
double distance;
Node(int n, double distance){
this.n=n;
this.distance = distance;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return (int)(this.distance - o.distance);
}
}
public static class Point{
int x;
int y;
Point(int x,int y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}
public static int solve(int s){
PriorityQueue<Node> q = new PriorityQueue<>();
q.add(new Node(s, 0));
distance[s] = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Node node = q.poll();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(arr[i][node.n]!=MAX && distance[i] > distance[node.n]+arr[i][node.n]){
distance[i] = distance[node.n]+arr[i][node.n];
q.add(new Node(i, distance[i]));
}
}
}
return print(distance[n]);
}
public static int print(double a){
return (int)(a*1000);
}
public static double getDistance(int s, int e){
double a = Math.pow(plant[s].x - plant[e].x, 2);
double b = Math.pow(plant[s].y - plant[e].y, 2);
return Math.sqrt(a+b);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String input[] = br.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
w = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
m = Float.parseFloat(br.readLine());
arr = new double[n+1][n+1];
plant = new Point[n+1];
distance = new double[n+1];
isVisited = new boolean[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
String input2[] = br.readLine().split(" ");
int x = Integer.parseInt(input2[0]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(input2[1]);
plant[i] = new Point(x,y);
distance[i] = MAX;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
double temp = getDistance(i, j);
if(temp <m){
arr[j][i]=arr[i][j] = temp;
}
else arr[j][i]=arr[i][j] = MAX;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<w;i++){
String input3[] = br.readLine().split(" ");
int x = Integer.parseInt(input3[0]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(input3[1]);
arr[x][y] = arr[y][x] = 0;
}
bw.write(solve(1)+"");
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
}
2224
시도1
- 일단 map을 사용해보려고했다. 그 이유는 보통은 노드를 번호로 매기고, 번호는 int형으로 표현할 수있어서 인덱스 대신 사용이 가능하다. 근데이건 알파벳이여서 int대신사용하기가 좀 그렇다..
- 일단 이 문제는 정렬이 되어있는상태에서 dfs로 방문할때마다 출력을 해주면될것같다.
시도2
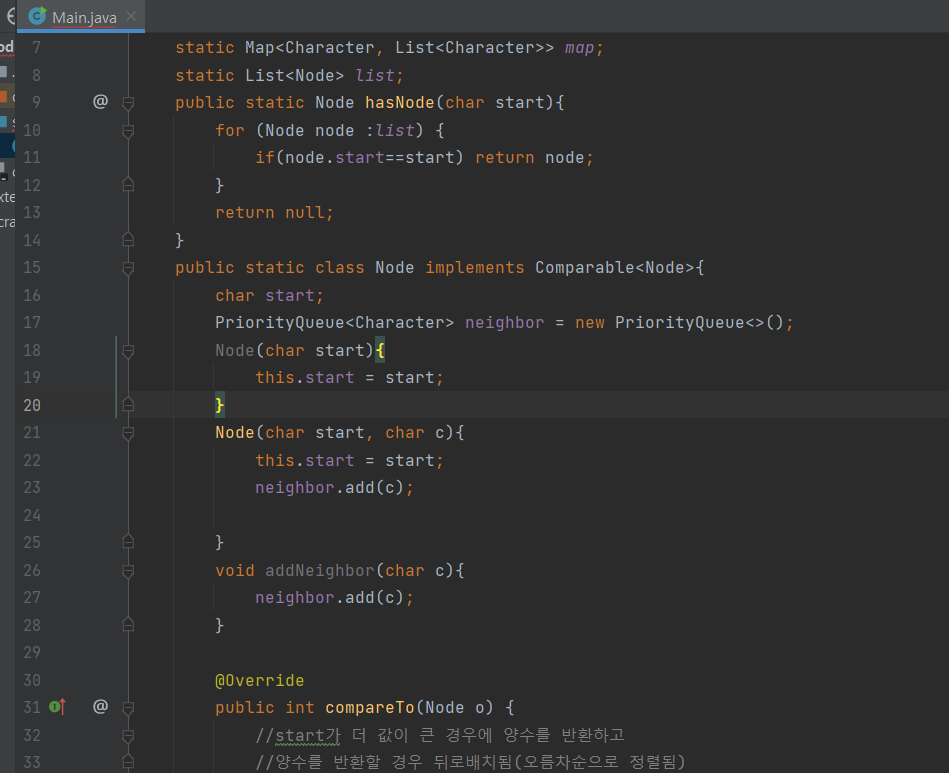
- 명제를 담을 start(명제시작점)라는 변수를 가지는 Node라는 변수를 만들었다
하지만 이렇게하면 인덱스로 노드를 찾는게 너무 어렵다. 인덱스는 start인데말이다
그래서 그냥 조금 큰 배열을 만들고 char->int화해보기로했다
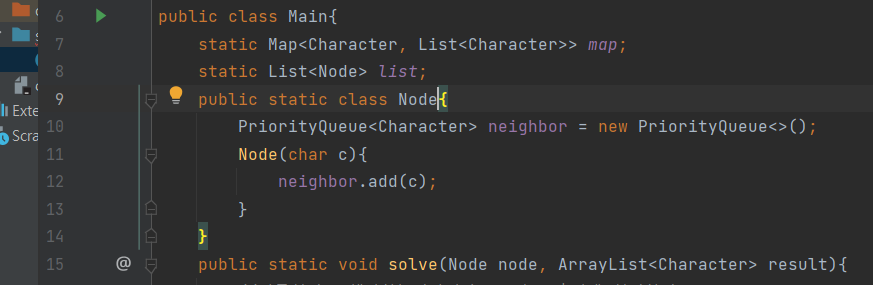
- 그렇게 생각하니 코드가 많이 줄었다. 코드의 복잡성도 줄인것같다.하지만 char을 인덱스로 사용한다는게 딱히 쉽게이해할수있는 코드는 아닌것같다고생각했다
시도3
- stackoverflow가 떴다.. 만약에 a->b->a인 경우 stackoverflow가 터질것같은데 이걸 어떻게 막아야하는지모르겠다
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Main{
static Map<Character, List<Character>> map;
static Node[] nodeArr;
static Set<String> result = new HashSet<>();
public static class Node{
PriorityQueue<Character> neighbor = new PriorityQueue<>();
Node(char c){
neighbor.add(c);
}
}
public static void solve(Node node, char start){
if(node==null || node.neighbor==null) return;
for(char c : node.neighbor){
result.add(start + " => "+ c);
solve(nodeArr[c],c);
solve(nodeArr[c],start);
}
}
public static void print(ArrayList<Character> result){
for (int i=0;i<result.size()-1;i++){
System.out.print(result.get(i) + " => ");
}
System.out.println(result.get(result.size()-1));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new HashMap<>();
nodeArr = new Node[150];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
String input[] = br.readLine().split(" => ");
for(int j=0;j<input.length;j++){
char x = input[0].charAt(0);
char neighbor = input[1].charAt(0);
if(nodeArr[x]!=null){
if(!nodeArr[x].neighbor.contains(neighbor)){
nodeArr[x].neighbor.add(neighbor);
}
}
else nodeArr[x] = new Node(neighbor);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<nodeArr.length;i++){
if(nodeArr[i]!=null) solve(nodeArr[i], (char)i);
}
bw.write(result.size()+"\n");
for(String str:result){
bw.write(str+"\n");
}
bw.close();
}
}
시도4
- 위의 코드를 chatgpt의 도움을 받아 stackoverflow를 없애봤다
하지만 오류가 뜬다. 순서가 잘못되었다.
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Main{
static Map<Character, List<Character>> map;
static Node[] nodeArr;
static Set<String> result = new HashSet<>();
static boolean[] visited;
public static class Node{
PriorityQueue<Character> neighbor = new PriorityQueue<>();
Node(char c){
neighbor.add(c);
}
}
public static void solve(Node node, char start){
if(node==null || node.neighbor==null) return;
for(char c : node.neighbor){
if (!visited[c]){
result.add(start + " => "+ c);
visited[c] = true;
solve(nodeArr[c],c);
solve(nodeArr[c],start);
visited[c] = false;
}
}
}
public static void print(ArrayList<Character> result){
for (int i=0;i<result.size()-1;i++){
System.out.print(result.get(i) + " => ");
}
System.out.println(result.get(result.size()-1));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new HashMap<>();
nodeArr = new Node[300];
visited = new boolean[300];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
String input[] = br.readLine().split(" => ");
for(int j=0;j<input.length;j++){
char x = input[0].charAt(0);
char neighbor = input[1].charAt(0);
if(nodeArr[x]!=null){
if(!nodeArr[x].neighbor.contains(neighbor)){
nodeArr[x].neighbor.add(neighbor);
}
}
else nodeArr[x] = new Node(neighbor);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<nodeArr.length;i++){
if(nodeArr[i]!=null) solve(nodeArr[i], (char)i);
}
bw.write(result.size()+"\n");
for(String str:result){
bw.write(str+"\n");
}
bw.close();
}
}
시도5
- 그래서 이번엔 정렬을 하기 위해서 Result라는 class를 도입하고, 이 class에 값을 넣고 정렬하여 마지막에 출력하도록 할려고했다 근데 오답이 뜬다. 이유를 모르겠다
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Main{
static Map<Character, List<Character>> map;
static Node[] nodeArr;
static Set<String> result = new HashSet<>();
static boolean[] visited;
static List<Result> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
public static class Node{
PriorityQueue<Character> neighbor = new PriorityQueue<>();
Node(char c){
neighbor.add(c);
}
}
public static class Result implements Comparable<Result>{
char start;
char end;
Result(char start, char end){
this.start=start;
this.end=end;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Result o) {
if(this.start==o.start){
return this.end - o.end;
}else return this.start-o.start;
}
}
public static void solve(Node node, char start){
if(node==null || node.neighbor==null) return;
for(char c : node.neighbor){
if (!visited[c]){
result.add(start + " " + c);
visited[c] = true;
solve(nodeArr[c],c);
solve(nodeArr[c],start);
visited[c] = false;
}
}
}
public static void print(ArrayList<Character> result){
for (int i=0;i<result.size()-1;i++){
System.out.print(result.get(i) + " => ");
}
System.out.println(result.get(result.size()-1));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new HashMap<>();
nodeArr = new Node[300];
visited = new boolean[300];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
String input[] = br.readLine().split(" => ");
for(int j=0;j<input.length;j++){
char x = input[0].charAt(0);
char neighbor = input[1].charAt(0);
if(nodeArr[x]!=null){
if(!nodeArr[x].neighbor.contains(neighbor)){
nodeArr[x].neighbor.add(neighbor);
}
}
else nodeArr[x] = new Node(neighbor);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<nodeArr.length;i++){
if(nodeArr[i]!=null) solve(nodeArr[i], (char)i);
}
bw.write(result.size()+"\n");
for (String str:result) {
String input[] = str.split(" ");
char c1 = input[0].charAt(0);
char c2 = input[1].charAt(0);
resultList.add(new Result(c1, c2));
}
resultList = resultList.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
for (Result result:resultList) {
bw.write(result.start+" => "+result.end+"\n");
}
bw.close();
}
}
시도6
- 생각해보니 a=>a 일경우에 출력하지 않는것을 빼먹었다. 그래서 다시작성했다
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Main{
static Map<Character, List<Character>> map;
static Node[] nodeArr;
static Set<String> result = new HashSet<>();
static boolean[] visited;
static List<Result> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
public static class Node{
PriorityQueue<Character> neighbor = new PriorityQueue<>();
Node(char c){
neighbor.add(c);
}
}
public static class Result implements Comparable<Result>{
char start;
char end;
Result(char start, char end){
this.start=start;
this.end=end;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Result o) {
if(this.start==o.start){
return this.end - o.end;
}else return this.start-o.start;
}
}
public static void solve(Node node, char start){
if(node==null || node.neighbor==null) return;
for(char c : node.neighbor){
if (!visited[c]){
result.add(start + " " + c);
visited[c] = true;
solve(nodeArr[c],c);
solve(nodeArr[c],start);
visited[c] = false;
}
}
}
public static void print(ArrayList<Character> result){
for (int i=0;i<result.size()-1;i++){
System.out.print(result.get(i) + " => ");
}
System.out.println(result.get(result.size()-1));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new HashMap<>();
nodeArr = new Node[300];
visited = new boolean[300];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
String input[] = br.readLine().split(" => ");
for(int j=0;j<input.length;j++){
char x = input[0].charAt(0);
char neighbor = input[1].charAt(0);
if(nodeArr[x]!=null){
if(!nodeArr[x].neighbor.contains(neighbor)){
nodeArr[x].neighbor.add(neighbor);
}
}
else nodeArr[x] = new Node(neighbor);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<nodeArr.length;i++){
if(nodeArr[i]!=null) solve(nodeArr[i], (char)i);
}
bw.write(result.size()+"\n");
for (String str:result) {
String input[] = str.split(" ");
char c1 = input[0].charAt(0);
char c2 = input[1].charAt(0);
if(c1!=c2) resultList.add(new Result(c1, c2));
}
resultList = resultList.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
for (Result result:resultList) {
bw.write(result.start+" => "+result.end+"\n");
}
bw.close();
}
}
- 하지만 그래도 오답이 뜬다
- 그래서 chatgpt를 통해 자문을 구했다.
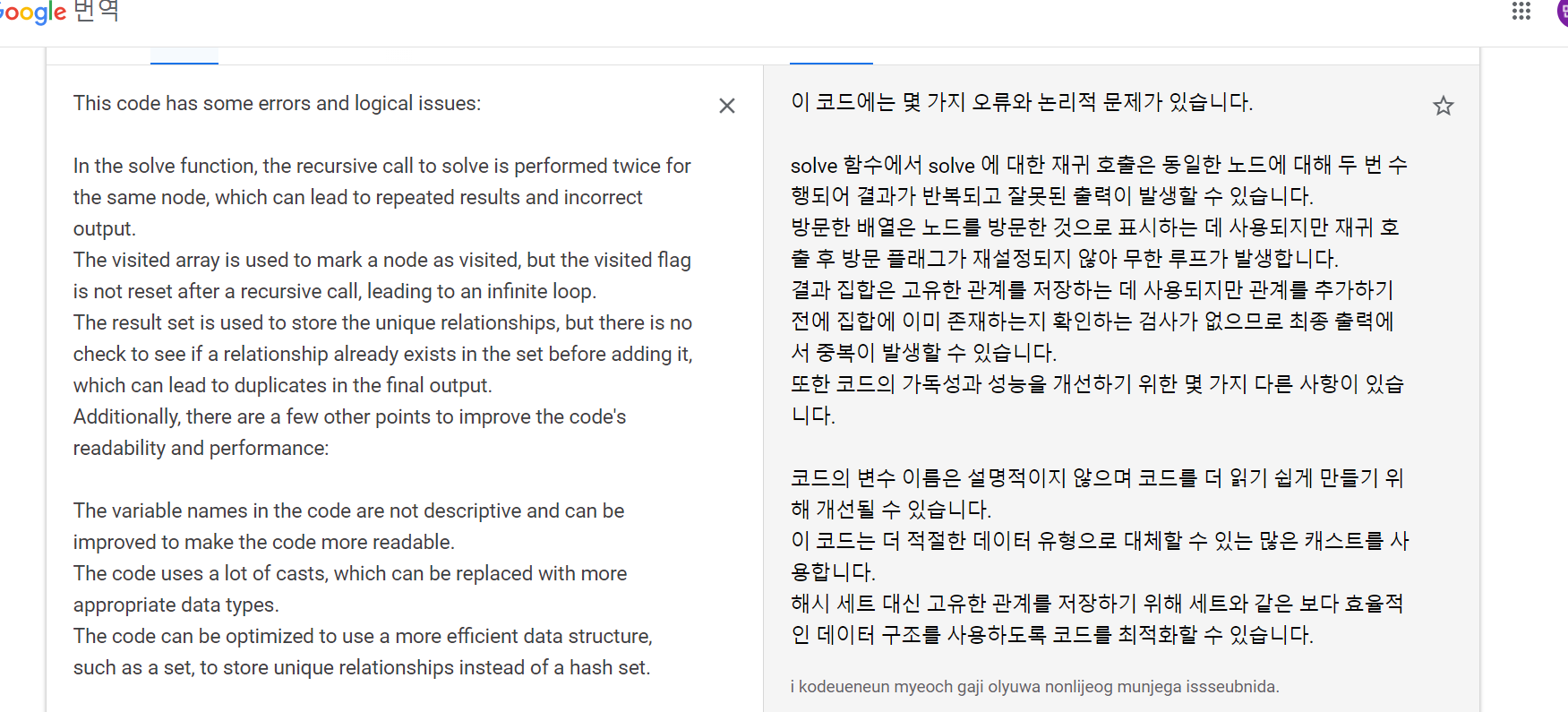
- 그래서 이것저것 고쳐봤지만 계속 오답을 내고 chatgpt는 내말을 못알아듣길래 일단여기까지 하고 답안지를 보기로했다.
답지
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Main{
static boolean arr[][];
static final int MAX = 150;
public static void solve(){
for(int k=0;k<arr.length;k++){
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<arr.length;j++){
if(arr[i][k] && arr[k][j]) arr[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
arr = new boolean[MAX][MAX];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
String input[] = br.readLine().split(" => ");
char c1 = input[0].charAt(0);
char c2 = input[1].charAt(0);
arr[c1][c2] = true;
}
solve();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int count=0;
for(int k=0;k<arr.length;k++){
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(arr[k][i]){
if(i!=k) {
count++;
sb.append((char)(k) + " => "+ (char)i+"\n");
}
}
}
}
bw.write(count+"\n");
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
}