질문(1)
let animal = {
eat() {
this.full = true;
}
};
let rabbit = {
__proto__: animal
};
rabbit.eat();- 이코드를 실행할때 full프로퍼티는 rabbit에 생긴대요
근데 이해가 안돼요 eat method는 animal에 있잖아요
rabbit.eat()이니까.. 즉, . 앞에가 rabbit이니까 this가 rabbit이 되나요?
-> rabbit이 반환한 객체에 대해 eat()을 호출하는것이다. 그러면 this가 rabbit이라는것을 알 수 있다
질문(2)
let hamster = {
stomach: [],
eat(food) {
this.stomach.push(food);
}
};
let speedy = {
__proto__: hamster
};
let lazy = {
__proto__: hamster
};
// 햄스터 speedy가 음식을 먹습니다.
speedy.eat("apple");
alert( speedy.stomach ); // apple
// 햄스터 lazy는 음식을 먹지 않았는데 배에 apple이 있다고 나오네요. 왜 그럴까요? lazy는 배가 비어있도록 고쳐주세요.
alert( lazy.stomach ); // apple- 메서드 speedy.eat은 프로토타입 hamster에서 발견되는데, 점 앞엔 객체 speedy가 있으므로 this엔 speedy가 할당되어 메서드가 실행됩니다.
- this.stomach.push()를 실행하려면 프로퍼티 stomach을 찾아서 여기에 push를 호출해야 합니다. 그런데 this인 speedy엔 프로퍼티 stomach이 없습니다.
- stomach을 찾기위해 프로토타입 체인을 거슬러 올라가보니 hamster에 stomach이 있는것을 발견합니다.
왜 hamster에 stomach가 있는거죠? speedy의 stomach에 "apple"이 추가되어있어야하는거아닌가요?
-> this는 일단 자식꺼가 들어가는게 맞는데 stomach라는 변수가 없으니까 그걸 찾으러 올라가다 보니 부모꺼가 있었고 그거에다가 push를 했다
prototype : 객체를 생성할 때 사용하는 패턴
프로토타입 패턴은 객체를 효율적으로 생성하는 방법을 다루는 패턴 중 하나인데, 주로 객체를 생성하는 비용이 클 때 이를 회피하기 위해 사용된다.
객체를 생성할 때의 비용이 크다는 말은, 말 그대로 객체를 생성할 때마다 뭔가 일을 많이 해야한다는 뜻이다.
// Player.java
class Weapon {}
class Armor {}
class BasicSward extends Weapon {}
class BasicArmor extends Armor {}
class Player {
public Weapon weapon;
public Armor armor;
public Player() {
this.weapon = new BasicSward(); // 초심자의 목도
this.armor = new BasicArmor(); // 초보자용 갑주
}
}- Player 객체는 자신이 생성될 때 BasicSward 객체와 BasicArmor 객체까지 함께 생성해야한다.
이런 경우 그냥 Player 객체만 생성하는 상황보다는 객체의 생성 비용이 높다고 할 수 있다
비용이 높은 Player객체를 딱 한번만 생성하고 그 다음부터는 생성된 객체를 복사해서 사용해도 되지 않을까?
// 이건 너무 객체 생성 비용이 높으니까...
Player evan = new Player();
Player john = new Player();
Player wilson = new Player();
// 이런 방법으로 접근해보는 것은 어떨까?
Player player = new Player();
Player evan = player.clone();
Player john = player.clone();
Player wilson = player.clone();- 프로토타입, 즉 원본 객체가 존재하고 그 객체를 복제해서 새로운 객체를 생성하는 방법인 것이다. (참조한다)
js가 객체를 생성하는 방법
- js는 class라는 개념이 없는데 어떻게 객체를 만들어내는 것일까?
- 답은 "함수"이다
지금까지 알아낸 것을 정리해보자
- 프로토타입 패턴이란 객체를 생성할 때 원본 객체를 복제하여 생성하는 방법이다.
- 자바스크립트는 객체를 생성할 때 프로토타입 패턴을 사용한다.
- 자바스크립트는 객체를 생성할 때 함수를 사용한다.
그렇다는 것은 자바스크립트가 함수를 사용하여 객체를 생성할 때 뭔가를 참조하고 복제해서 객체를 생성한다는 말이다.
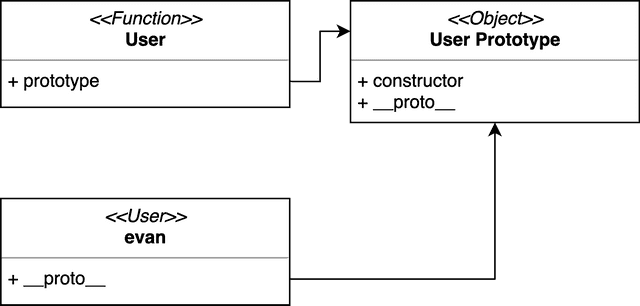
function User () {}
const evan = new User();
console.log(evan);
console.log(typeof evan);User { __proto__: Object }
object
-> User 함수의 프로토타입 객체를 복제한 것이다.(User를 복제한게 아니라)
만약 객체를 생성하면서 함수를 복제했다면 생성된 객체는 object 타입이 아니라 function 타입이어야 하지 않겠는가?
하지만 evan 객체는 object 타입을 가지고 있다. 즉, 이 함수 자체가 아니라 다른 객체 타입의 무언가를 복제했다는 것이고, 그 원본 객체가 User 함수의 프로토타입 객체인 것이다.
필자는 User 함수의 프로토타입을 명시적으로 선언하지 않았지만, 자바스크립트는 함수가 생성될 때 자동으로 그 함수의 프로토타입 객체(Prototype Object)도 함께 생성하고 해당 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티에 연결해둔다.
그리고 이 프로토타입 객체는 함수를 사용해서 새로운 객체를 생성할 때 원본 객체 역할을 해줄 객체를 의미한다.
즉, new User()라는 문법을 사용하여 새로운 객체를 만들게 되면 User 함수 자체가 아니라 User 함수가 생성될 때 함께 생성된 User 함수의 프로토타입 객체를 복제해서 새로운 객체를 만든다는 것이다.
총 정리
- 프로토타입 패턴이란 객체를 생성할 때 원본 객체를 복제하여 생성하는 방법이다.
- 자바스크립트는 객체를 생성할 때 프로토타입 패턴을 사용한다.
- 자바스크립트는 객체를 생성할 때 함수를 사용한다.
const newUser = new User();에서
newUser객체는 User함수의 프로토타입 객체를 복제한 것이다- 함수가 생성되며 함께 생성된 프로토타입 객체는 모두
constructor라는 프로퍼티를 가지고 있고
이 프로퍼티에는 프로토토 타입객체가 생성될때 선언했던 함수가 들어있다
-> 함수를 선언하면 함수 + 해당 함수의 프로토타입객체 << 가 함께 생성되고 생성자가 이 둘을 연결한다
함수.prototype을 통해 해당 함수의 프로토 타입객체에 접근할 수 있고,함수.prototype.constuctor을 이용해 원래 함수에 접근할 수 있다
->.__proto__를 통해 생성된 객체 ~ 원본 객체와의 연결을 할 수 있다
prototype은함수.prototype인거고.__proto__는 함수로부터 생성된 객체뒤에 붙이는 프로퍼티이다
프로퍼티와 상속
- 프로퍼티와 메서드는 원본 객체를 통해 공유될 수 있다
프로퍼티와 메서드를 정의하는 방법
1. this를 사용하여 생성자 함수 내에 정의
function User (name) {
'use strict';
this.say = function () {
console.log('Hello, World!');
};
}
const evan = new User();
console.log(evan.say());2. 프로토타입 객체에 정의
function User (name) {}
User.prototype.say = function () {
console.log('Hello, World!');
}
const evan = new User();
console.log(evan.say());- 각 객체마다 고유한 프로퍼티를 부여하고 싶다면 원본 객체에 정의하는 것이 아니라, 생성자 함수 내에서 this를 사용하여 정의해야한다. 다시 말하지만 원본 객체에 정의한 프로퍼티나 메소드는 생성된 객체들 끼리 공유된다.
프로토타입을 활용한 상속
- Object.Create를 사용하자!
- 첫 번째 인자로 생성할 객체의 원본 객체가 될 객체, 두 번째 인자로 새로 생성할 객체에 추가할 프로퍼티를 객체 타입으로 받는다
Object.create(User.prototype, {
foo: {
configurable: false,
enumerable: true,
value: 'I am Foo!',
}
});상속 이해하기
function SuperClass (name) {
this.name = name;
}
SuperClass.prototype.say = function () {
console.log(`I am ${this.name}`);
}
function SubClass (name) {
SuperClass.call(this, name);
}
SubClass.prototype = Object.create(SuperClass.prototype);
SubClass.prototype.constructor = SubClass;
SubClass.prototype.run = function () {
console.log(`${this.name} is running`);
}질문3
위의 코드
SubClass.prototype.constructor = SubClass;는 왜 필요한가요?
Object.create를 사용하면 인자로 들어온 프로토타입을 상속받는 또다른 프로토타입을 만들어줍니다
subClass의 prototype은 Superclass.prototype을 상속받는 또다른 프로토타입인 subclassPrototype이 됩니다.
근데 이 subclass의 protytype 객체는 superclass ptototype(!= superclass method) 을 그대로 복제한것이기때문에 이의 constuctor도
superclass method를 가리킵니다
이 경우 subclass method 를 가리키도록 해주어야합니다. 왜냐하면 이렇게 하는 것이
js의 프로토타입 체이닝 원칙이기 때문이다
subclass.prototype의 constructor을 subclass method로 바꿔줍니다
함수 정의
- 익명 함수
var add = function (x, y) {
return x + y;
};
var plus = add;
console.log(add(3,7)); // 10
console.log(plus(3,7)); // 10- 기명 함수
var add = function sum(x, y) {
return x + y;
};
console.log(add(3,7)); // 10
console.log(sum(3, 7)); // Error 외부에서 접근 못함