- ReplicaSet 구성 및 노드 샤딩
- MongoRouter
- config 서버
- Arbiter
- ShardKey 설정
- Shard Node 추가 및 제거
- 커넥션관리를 위한 WriteConcern의 w, jounal,
- ReadPreference 의 RP_PRIMARY, RP_SECONDARY, RP_PRIMARY_PREFERRE, RP_SECONDARY_PREFERRE, RP_NEAREST 옵션
- aggregate 로 데이터 집계
- explain 을 통한 Query Plan, Index 걸기
-> Try Free -> 회원가입 -> Create a cluster Starting at FREE -> AWS / Seoul (ap-norheast-2) -> Create Cluster -> Create database user -> Add Access IP -> Connect
- Create database user and password change
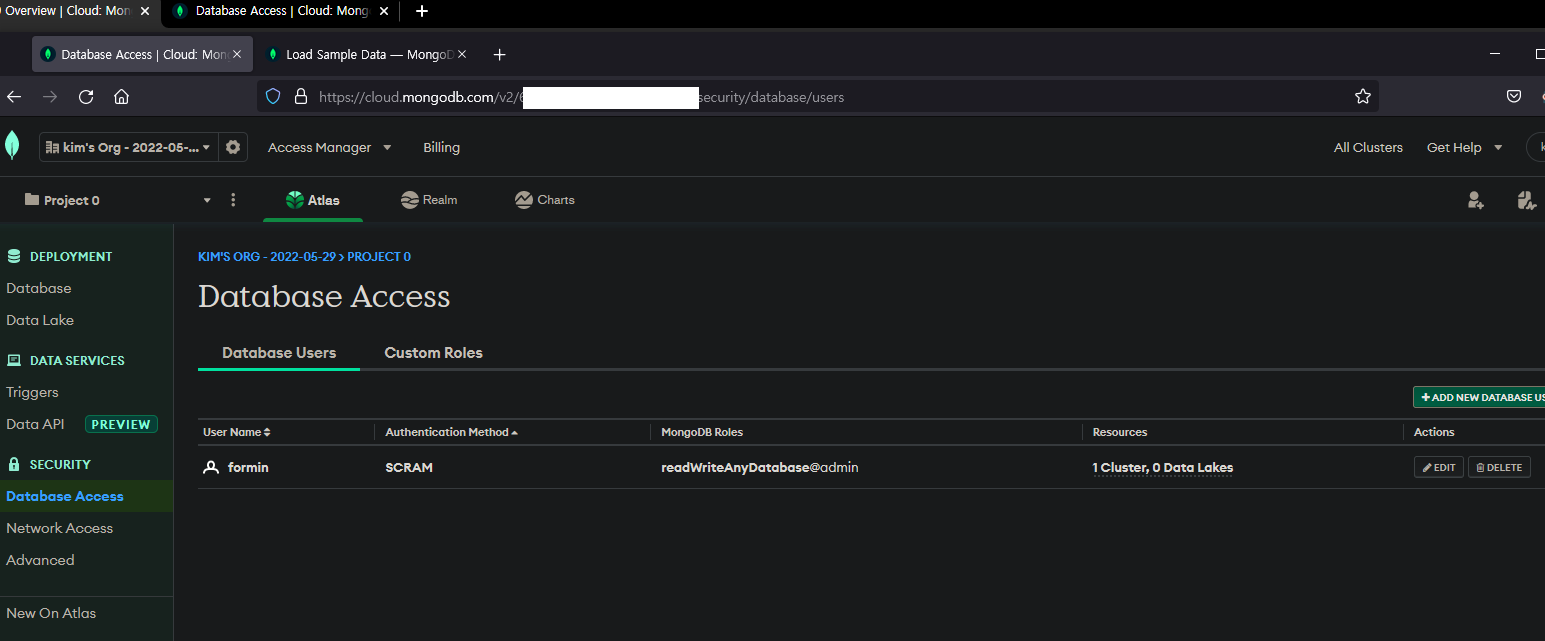
- Add Access IP
- 0.0.0.0 입력 시 어디서나 액세스 가능
- MongoDB for VS Code 설치

- Connect with Connection String Connect
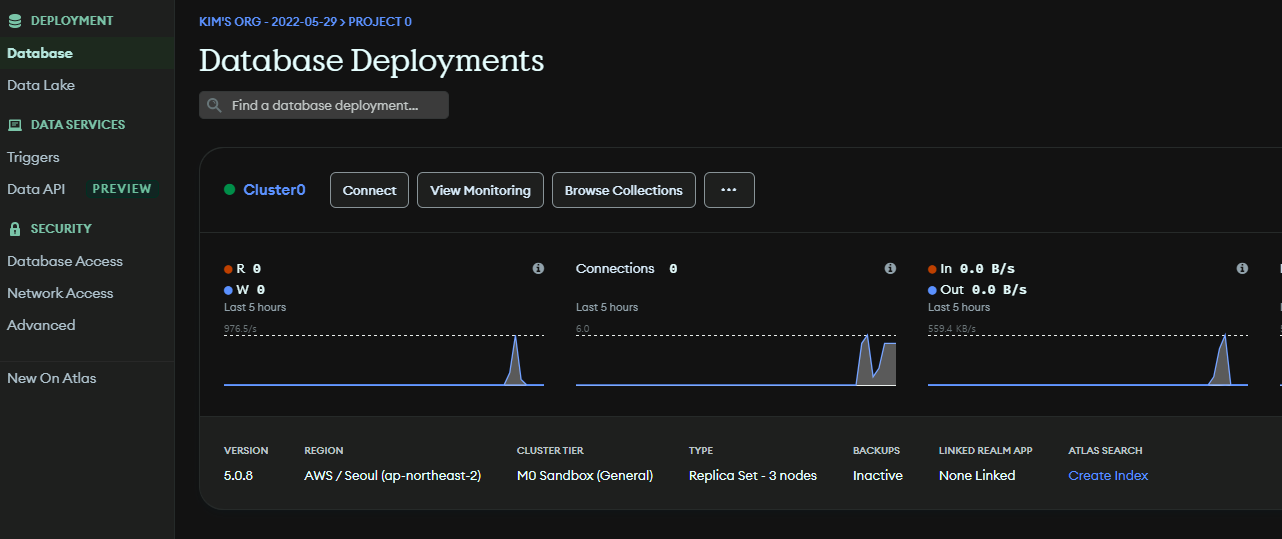
- Database Deployment -> Connect
- Connect using MongoDB Compasss
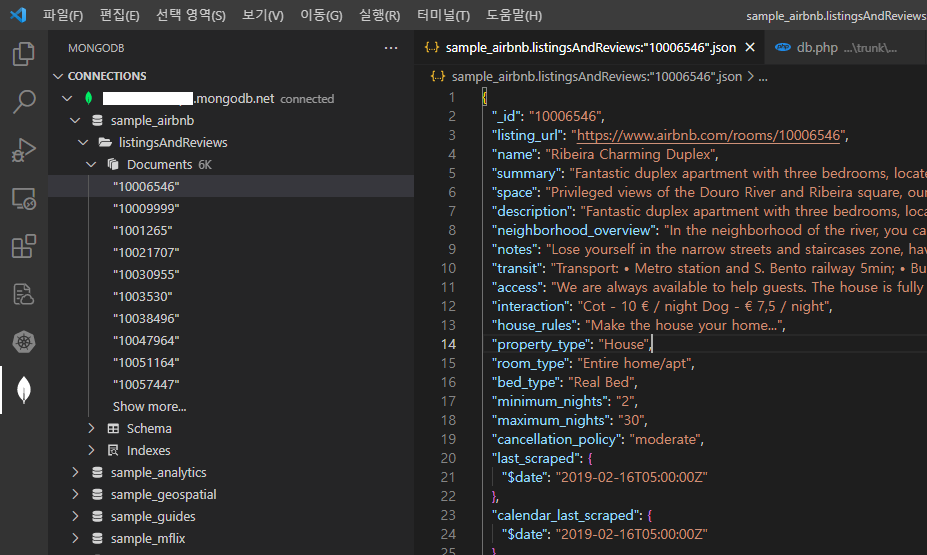
- sample data bulk insert
- install mongodbphp
https://zetcode.com/db/mongodbphp/
$ git clone https://github.com/mongodb/mongo-php-driver.git
$ cd mongo-php-driver
$ git submodule sync && git submodule update --init
$ phpize
$ ./configure
$ make
$ sudo make install- sample data select
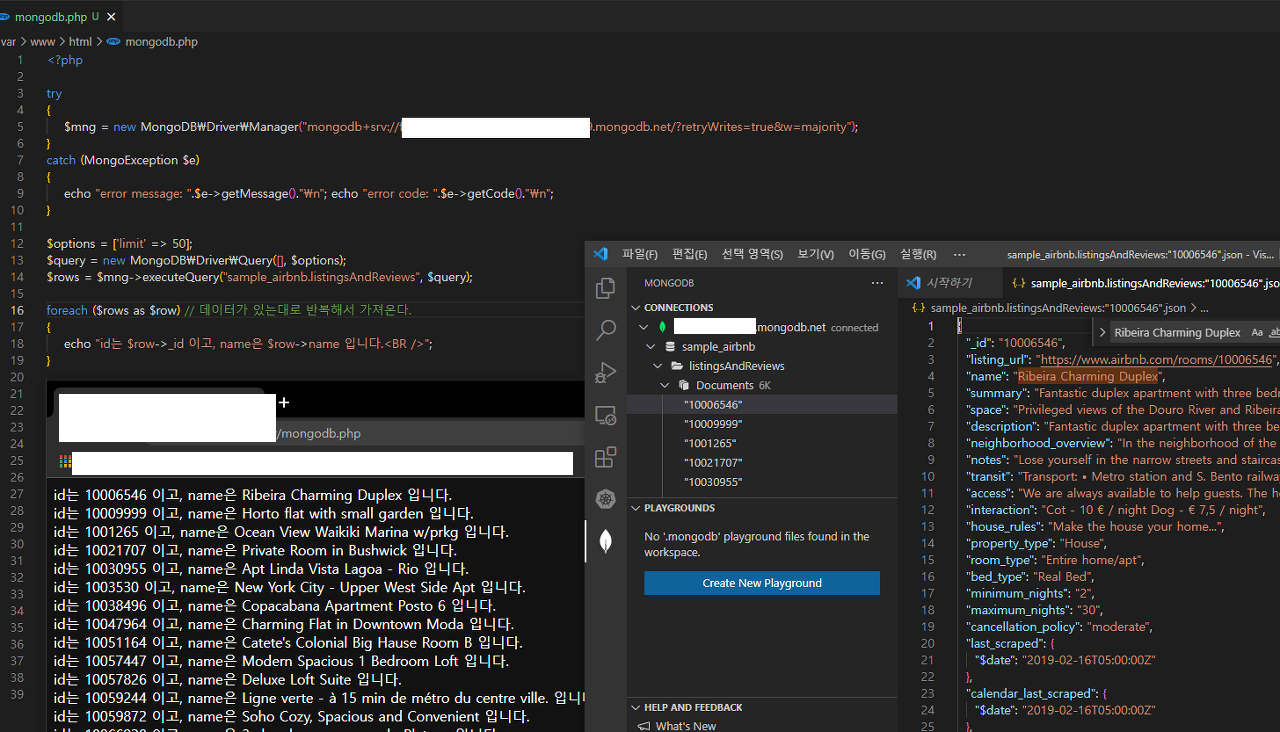
<?php
try
{
$mng = new MongoDB\Driver\Manager("mongodb+srv://id:password@XXX.mongodb.net/?retryWrites=true&w=majority");
}
catch (MongoException $e)
{
echo "error message: ".$e->getMessage()."\n"; echo "error code: ".$e->getCode()."\n";
}
$options = ['limit' => 50];
$query = new MongoDB\Driver\Query([], $options);
$rows = $mng->executeQuery("sample_airbnb.listingsAndReviews", $query);
foreach ($rows as $row) // 데이터가 있는대로 반복해서 가져온다.
{
echo "id는 $row->_id 이고, name은 $row->name 입니다.<BR />";
}
?>what is a document?
- collections consist of one or many documents.
- A field is a unique identifier for a specific datapoint.
- Each field has a value associated with it.
What is Atlas?
- They are both MongoDB products
- Atlas has many tools and services within it that are built specifically for the MongoDB Database.
- MongoDB stores data in BSON, and you can then view it in JSON.
- BSON is faster to parse and lighter to store than JSON.
- JSON supports fewer data types than BSON.
mongodump --uri "mongodb+srv://<your username>:<your password>@<your cluster>.mongodb.net/sample_supplies"
mongoexport --uri="mongodb+srv://<your username>:<your password>@<your cluster>.mongodb.net/sample_supplies" --collection=sales --out=sales.json
mongorestore --uri "mongodb+srv://<your username>:<your password>@<your cluster>.mongodb.net/sample_supplies" --drop dump
mongoimport --uri="mongodb+srv://<your username>:<your password>@<your cluster>.mongodb.net/sample_supplies" --drop sales.json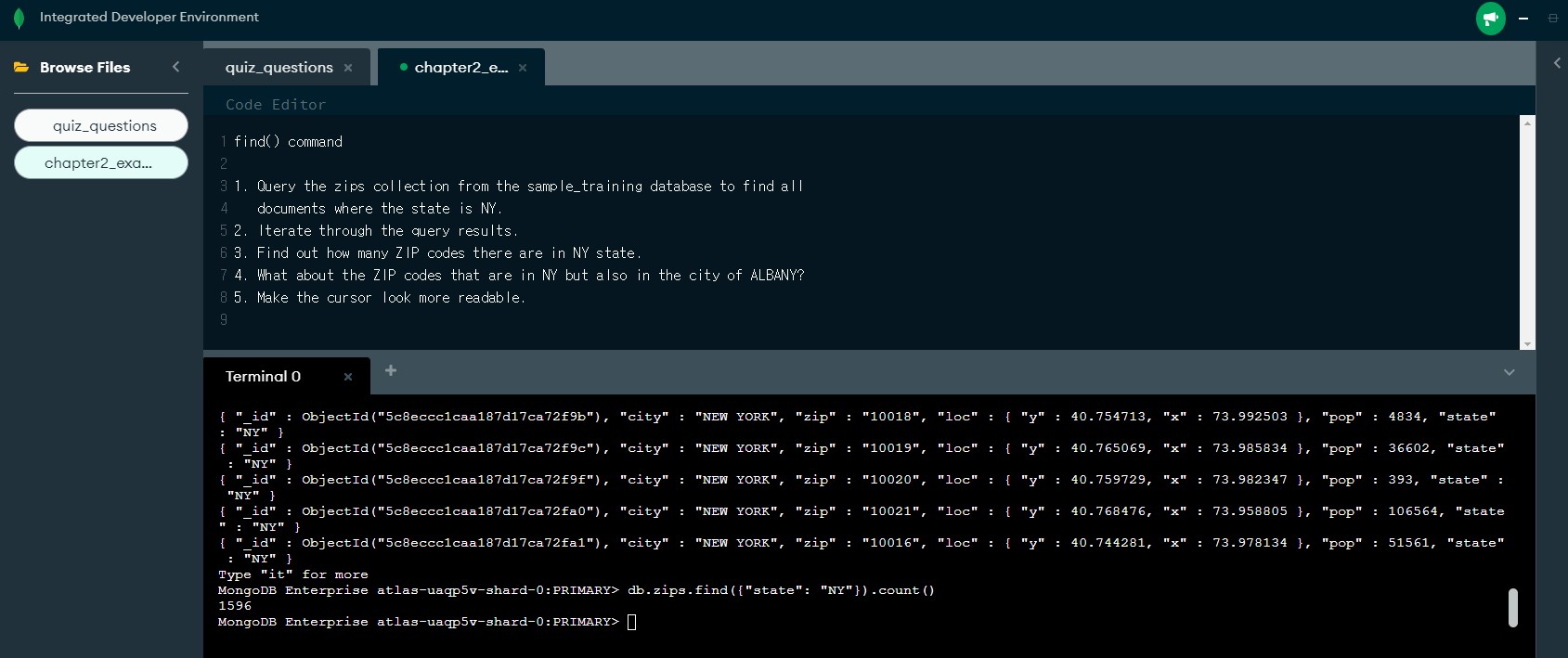
mongo "mongodb+srv://:@.mongodb.net/admin"
show dbs
use sample_training
show collections
db.zips.find({"state": "NY"})
db.zips.find({"state": "NY"}).count()
db.zips.find({"state": "NY", "city": "ALBANY"})
db.zips.find({"state": "NY", "city": "ALBANY"}).pretty()What does it do in the mongo shell?
- Iterates through the cursor results.
Which of the following the mongo shell?
- It allows you to interact with your MongoDB instance without using a Graphical User Interface
- It is a fully functioning JavaScript interpreter
How does the value of _id get assigned to a document?
- It is automatically generated as an ObjectId type value.
- You can select a non ObjectId type value when inserting a new document, as long as that value is unique to this collection.
mongoimport --uri="mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@<cluster>.mongodb.net/sample_supplies" sales.json
mongo "mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@<cluster>.mongodb.net/admin"
use sample_training
db.inspections.findOne();
db.inspections.insert({
"_id" : ObjectId("56d61033a378eccde8a8354f"),
"id" : "10021-2015-ENFO",
"certificate_number" : 9278806,
"business_name" : "ATLIXCO DELI GROCERY INC.",
"date" : "Feb 20 2015",
"result" : "No Violation Issued",
"sector" : "Cigarette Retail Dealer - 127",
"address" : {
"city" : "RIDGEWOOD",
"zip" : 11385,
"street" : "MENAHAN ST",
"number" : 1712
}
})
db.inspections.insert({
"id" : "10021-2015-ENFO",
"certificate_number" : 9278806,
"business_name" : "ATLIXCO DELI GROCERY INC.",
"date" : "Feb 20 2015",
"result" : "No Violation Issued",
"sector" : "Cigarette Retail Dealer - 127",
"address" : {
"city" : "RIDGEWOOD",
"zip" : 11385,
"street" : "MENAHAN ST",
"number" : 1712
}
})
db.inspections.find({"id" : "10021-2015-ENFO", "certificate_number" : 9278806}).pretty()-
If a document is inserted without a provided _id value, then the _id field and value will be automatically generated for the inserted document before insertion.
-
MongoDB can store duplicate documents in the same collection, as long as their _id values are different.
db.inspections.insert([ { "test": 1 }, { "test": 2 }, { "test": 3 } ])
db.inspections.insert([{ "_id": 1, "test": 1 },{ "_id": 1, "test": 2 },
{ "_id": 3, "test": 3 }])
db.inspections.find({ "_id": 1 })
db.inspections.insert([{ "_id": 1, "test": 1 },{ "_id": 1, "test": 2 },
{ "_id": 3, "test": 3 }],{ "ordered": false })
db.inspection.insert([{ "_id": 1, "test": 1 },{ "_id": 3, "test": 3 }])
show collections
use training
show dbs
db.pets.insert([{ "pet": "cat" }, { "pet": "dog" }, { "pet": "fish" }])
db.pets.insert([{ "_id": 1, "pet": "cat" },
{ "_id": 1, "pet": "dog" },
{ "_id": 3, "pet": "fish" },
{ "_id": 4, "pet": "snake" }], { "ordered": false })
db.pets.insert([{ "_id": 1, "pet": "cat" },
{ "_id": 2, "pet": "dog" },
{ "_id": 3, "pet": "fish" },
{ "_id": 3, "pet": "snake" }])
mongo "mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@<cluster>.mongodb.net/admin"
use sample_training
db.zips.find({ "zip": "12534" }).pretty()
db.zips.find({ "city": "HUDSON" }).pretty()
db.zips.find({ "city": "HUDSON" }).count()
db.zips.updateMany({ "city": "HUDSON" }, { "$inc": { "pop": 10 } })
db.zips.updateOne({ "zip": "12534" }, { "$set": { "pop": 17630 } })
db.zips.updateOne({ "zip": "12534" }, { "$set": { "population": 17630 } })
db.grades.find({ "student_id": 151, "class_id": 339 }).pretty()
db.grades.find({ "student_id": 250, "class_id": 339 }).pretty()
db.grades.updateOne({ "student_id": 250, "class_id": 339 },
{ "$push": { "scores": { "type": "extra credit",
"score": 100 }
}
})
When all collections are dropped from a database, the database no longer appears in the list of databases when you run show dbs.
mongo "mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@<cluster>.mongodb.net/admin"
use sample_training
db.inspections.find({ "test": 1 }).pretty()
db.inspections.find({ "test": 3 }).pretty()
db.inspections.deleteMany({ "test": 1 })
db.inspections.deleteOne({ "test": 3 })
db.inspection.find().pretty()
show collections
db.inspection.drop()
비교 쿼리
$gt
해당 값보다 더 큰 값을 가진 필드를 찾습니다.
$lt
해당 값보다 작은 값을 가진 필드를 찾습니다
$gte
해당 값보다 크거나 같은 값을 가진 필드를 찾습니다
$lte
해당 값보다 작거나 같은 값을 가진 필드를 찾습니다
$eq
해당 값과 일치하는 값을 가진 필드를 찾습니다.
$ne
해당 값과 일치하지 않는 값을 가진 필드를 찾습니다.
$in
필드의 값이 $in 안에 들어있는 값들 중 하나인 필드를 찾습니다.
$nin
필드의 값이 $nin 안에 값들이 아닌 필드를 찾습니다.
How many documents in the sample_training.zips collection have fewer than 1000 people listed in the pop field?
db.zips.find({ "pop": { "$lt": 1000 }}).count()What is the difference between the number of people born in 1998 and the number of people born after 1998 in the sample_training.trips collection?
db.trips.find({ "birth year": { "$gt": 1998 }}).count()
db.trips.find({ "birth year": 1998 }).count()Using the sample_training.routes collection find out which of the following statements will return all routes that have at least one stop in them?
db.routes.find({ "stops": { "$gt": 0 }}).pretty()The given query looks for strict equality where the stops field has to be greater than zero, thus excluding all zero stops.
db.routes.find({ "stops": { "$ne": 0 }}).pretty()This query will also work, given that there are no non-negative or non- numeric values in this collection. It returns all documents where the stops field is not equal to 0.
논리 쿼리
$or
여러 개의 조건 중에 적어도 하나를 만족하는 다큐먼트를 찾습니다.
$and
여러 개의 조건을 모두 만족하는 다큐먼트를 찾습니다.
$nor
여러 개의 조건을 모두 만족하지 않는 다큐먼트를 찾습니다.
$not
뒤의 조건을 만족하지 않는 필드를 찾습니다.
mongo "mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@<cluster>.mongodb.net/admin"
use sample_training
db.routes.find({ "$and": [ { "$or" :[ { "dst_airport": "KZN" },
{ "src_airport": "KZN" }
] },
{ "$or" :[ { "airplane": "CR2" },
{ "airplane": "A81" } ] }
]}).pretty()
How many businesses in the sample_training.inspections dataset have the inspection result "Out of Business" and belong to the "Home Improvement Contractor - 100" sector?
db.inspections.find({ "result": "Out of Business", "sector": "Home Improvement Contractor - 100" }).count()Which is the most succinct query to return all documents from the sample_training.inspections collection where the inspection date is either "Feb 20 2015", or "Feb 21 2015" and the company is not part of the "Cigarette Retail Dealer - 127" sector?
db.inspections.find(
{ "$or": [ { "date": "Feb 20 2015" },
{ "date": "Feb 21 2015" } ],
"sector": { "$ne": "Cigarette Retail Dealer - 127" }}).pretty() How many zips in the sample_training.zips dataset are neither over-populated nor under-populated?
In this case, we consider population of more than 1,000,000 to be over- populated and less than 5,000 to be under-populated.
db.zips.find({ "pop": { "$gte": 5000, "$lte": 1000000 }}).count()
db.zips.find({ "$nor": [ { "pop": { "$lt":5000 } },
{ "pop": { "$gt": 1000000 } } ] } ).count()How many companies in the sample_training.companies dataset were
either founded in 2004
[and] either have the social category_code [or] web category_code,
[or] were founded in the month of October
[and] also either have the social category_code [or] web category_code?
db.companies.find({ "$and": [
{ "$or": [ { "founded_year": 2004 },
{ "founded_month": 10 } ] },
{ "$or": [ { "category_code": "web" },
{ "category_code": "social" }]}]}).count()
mongo "mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@<cluster>.mongodb.net/admin"
use sample_training
db.trips.find({ "$expr": { "$eq": [ "$end station id", "$start station id"] }
}).count()
db.trips.find({ "$expr": { "$and": [ { "$gt": [ "$tripduration", 1200 ]},
{ "$eq": [ "$end station id", "$start station id" ]}
]}}).count()
What are some of the uses for the $ sign in MQL?
- $ signifies that you are looking at the value of that field rather than the field name.
- $ denotes an operator.
Which of the following statements will find all the companies that have more employees than the year in which they were founded?
db.companies.find(
{ "$expr": { "$gt": [ "$number_of_employees", "$founded_year" ]} }
).count()
db.companies.find(
{ "$expr": { "$lt": [ "$founded_year", "$number_of_employees" ] } }
).count()How many companies in the sample_training.companies collection have the same permalink as their twitter_username?
db.companies.find({ "$expr": { "$eq": [ "$permalink", "$twitter_username"] } }).count()mongo "mongodb+srv://:@.mongodb.net/admin"
use sample_airbnb
db.listingsAndReviews.find({ "amenities": {
"$size": 20,
"$all": [ "Internet", "Wifi", "Kitchen",
"Heating", "Family/kid friendly",
"Washer", "Dryer", "Essentials",
"Shampoo", "Hangers",
"Hair dryer", "Iron",
"Laptop friendly workspace" ]
}
}).pretty()What is the name of the listing in the sample_airbnb.listingsAndReviews dataset that accommodates more than 6 people and has exactly 50 reviews?
db.listingsAndReviews.find({ "reviews": { "$size":50 }, "accommodates": { "$gt":6 }})Using the sample_airbnb.listingsAndReviews collection find out how many documents have the "property_type" "House", and include "Changing table" as one of the "amenities"?
db.listingsAndReviews.find( {
"$and": [
{ "$expr": { "$eq": [ "$property_type", "House"] } },
{ "amenities": { "$all": [ "Changing table" ] } }
]
}
).count()
db.listingsAndReviews.find({ "property_type": "House",
"amenities": "Changing table" }).count()
{"property_type": "House","amenities": "Changing table"}Which of the following queries will return all listings that have "Free parking on premises", "Air conditioning", and "Wifi" as part of their amenities, and have at least 2 bedrooms in the sample_airbnb.listingsAndReviews collection?
db.listingsAndReviews.find(
{ "amenities":
{ "$all": [ "Free parking on premises", "Wifi", "Air
conditioning" ] }, "bedrooms": { "$gte": 2 } } ).pretty()Projection Syntax
mongo "mongodb+srv://:@.mongodb.net/admin"
use sample_airbnb
db.listingsAndReviews.find({ "amenities":
{ "$size": 20, "$all": [ "Internet", "Wifi", "Kitchen", "Heating",
"Family/kid friendly", "Washer", "Dryer",
"Essentials", "Shampoo", "Hangers",
"Hair dryer", "Iron",
"Laptop friendly workspace" ] } },
{"price": 1, "address": 1}).pretty()
db.listingsAndReviews.find({ "amenities": "Wifi" },
{ "price": 1, "address": 1, "_id": 0 }).pretty()
db.listingsAndReviews.find({ "amenities": "Wifi" },
{ "price": 1, "address": 1,
"_id": 0, "maximum_nights":0 }).pretty()
use sample_training
db.grades.findOne()
db.grades.find({ "class_id": 431 },
{ "scores": { "$elemMatch": { "score": { "$gt": 85 } } }
}).pretty()
db.grades.find({ "scores": { "$elemMatch": { "type": "extra credit" } }
}).pretty()How many companies in the sample_training.companies collection have offices in the city of Seattle?
db.companies.find({ "offices": { "$elemMatch": { "city": "Seattle" } } }).count()Which of the following queries will return only the names of companies from the sample_training.companies collection that had exactly 8 funding rounds?
db.companies.find({ "funding_rounds": { "$size": 8 } }, { "name": 1, "_id": 0 })mongo "mongodb+srv://:@.mongodb.net/admin"
use sample_training
db.trips.findOne({ "start station location.type": "Point" })
db.companies.find({ "relationships.0.person.last_name": "Zuckerberg" },
{ "name": 1 }).pretty()
db.companies.find({ "relationships.0.person.first_name": "Mark",
"relationships.0.title": { "$regex": "CEO" } },
{ "name": 1 }).count()
db.companies.find({ "relationships.0.person.first_name": "Mark",
"relationships.0.title": {"$regex": "CEO" } },
{ "name": 1 }).pretty()
db.companies.find({ "relationships":
{ "$elemMatch": { "is_past": true,
"person.first_name": "Mark" } } },
{ "name": 1 }).pretty()
db.companies.find({ "relationships":
{ "$elemMatch": { "is_past": true,
"person.first_name": "Mark" } } },
{ "name": 1 }).count()How many trips in the sample_training.trips collection started at stations that are to the west of the -74 longitude coordinate?
Longitude decreases in value as you move west.
Note: We always list the longitude first and then latitude in the coordinate pairs; i.e.
<field_name>: [ , ]
db.trips.find({ "start station location.coordinates.0": { "$lt": -74 }}).count()How many inspections from the sample_training.inspections collection were conducted in the city of NEW YORK?
db.inspections.find({ "address.city": "NEW YORK" }).count() Which of the following queries will return the names and addresses of all listings from the sample_airbnb.listingsAndReviews collection where the first amenity in the list is "Internet"?
db.listingsAndReviews.find({ "amenities.0": "Internet" }, { "name": 1, "address": 1 }).pretty()mongo "mongodb+srv://:@.mongodb.net/admin"
use sample_airbnb
db.listingsAndReviews.find({ "amenities": "Wifi" },
{ "price": 1, "address": 1, "_id": 0 }).pretty()
db.listingsAndReviews.aggregate([
{ "$match": { "amenities": "Wifi" } },
{ "$project": { "price": 1,
"address": 1,
"_id": 0 }}]).pretty()
db.listingsAndReviews.findOne({ },{ "address": 1, "_id": 0 })
db.listingsAndReviews.aggregate([ { "$project": { "address": 1, "_id": 0 }},
{ "$group": { "_id": "$address.country" }}])
db.listingsAndReviews.aggregate([
{ "$project": { "address": 1, "_id": 0 }},
{ "$group": { "_id": "$address.country",
"count": { "$sum": 1 } } }
])
What room types are present in the sample_airbnb.listingsAndReviews collection?
db.listingsAndReviews.aggregate([ { "$group": { "_id": "$room_type" } }])
db.listingsAndReviews.aggregate([{ "$project": { "room_type": 1, "_id": 0 }}, { "$group": { "_id": "$room_type" } } ])What are the differences between using aggregate() and find()?
aggregate() can do what find() can and more.Any find() query can be translated into an aggregation pipeline equivalent, but not every aggregation pipeline can be translated into a find() query.
aggregate() allows us to compute and reshape data in the cursor.The aggregation framework allows us to compute and reshape data via using stages like $group, $sum, and others.
mongo "mongodb+srv://:@.mongodb.net/admin"
use sample_training
db.zips.find().sort({ "pop": 1 }).limit(1)
db.zips.find({ "pop": 0 }).count()
db.zips.find().sort({ "pop": -1 }).limit(1)
db.zips.find().sort({ "pop": -1 }).limit(10)
db.zips.find().sort({ "pop": 1, "city": -1 })Which of the following commands will return the name and founding year for the 5 oldest companies in the sample_training.companies collection?
db.companies.find({ "founded_year": { "$ne": null }},
{ "name": 1, "founded_year": 1 }
).sort({ "founded_year": 1 }).limit(5)
db.companies.find({ "founded_year": { "$ne": null }},
{ "name": 1, "founded_year": 1 }
).limit(5).sort({ "founded_year": 1 })In what year was the youngest bike rider from the sample_training.trips collection born?
db.trips.find({ "birth year": { "$ne":"" } }, { "birth year": 1 }).sort({ "birth year": -1 }).limit(1)mongo "mongodb+srv://:@.mongodb.net/admin"
use sample_training
db.trips.find({ "birth year": 1989 })
db.trips.find({ "start station id": 476 }).sort( { "birth year": 1 } )
db.trips.createIndex({ "birth year": 1 })
db.trips.createIndex({ "start station id": 1, "birth year": 1 })Jameela often queries the sample_training.routes collection by the src_airport field like this:
db.routes.find({ "src_airport": "MUC" }).pretty()Which command will create an index that will support this query?
db.routes.createIndex({ "src_airport": -1 })building-with-patterns-a-summary
What is data modeling?
a way to organize fields in a document to support your application performance and querying capabilities
Data modeling is a way to organize your data, which includes making decisions about fields, collections, and datatypes that will be used in each collection.
Upsert - Update or Insert
db.iot.updateOne({ "sensor": r.sensor, "date": r.date,
"valcount": { "$lt": 48 } },
{ "$push": { "readings": { "v": r.value, "t": r.time } },
"$inc": { "valcount": 1, "total": r.value } },
{ "upsert": true })How does the upsert option work?
By default upsert is set to false.
If the upsert option is not specified, then it will have the value of false by default.
When upsert is set to true and the query predicate returns an empty cursor, the update operation creates a new document using the directive from the query predicate and the update predicate.
When upsert is set to true it can perform an insert if the query predicate doesn't return a matching document.
When upsert is set to false and the query predicate returns an empty cursor then there will be no updated documents as a result of this operation.
When upsert is set to false an update will happen only when the query predicate is matched with a document from the collection.
What actions are available to you via the Aggregation Builder in the Atlas Data Explorer?
Export pipeline to a programming language.
You can choose to export the pipeline to one of four programming languages, and select to view the import statements that are needed in the application for this pipeline to work.
Syntax for each selected aggregation stage.
When you select a stage the space to enter stage instructions has a syntax outline to help you recall what information the stage requires and in what format.
A preview of the data in the pipeline at each selected stage.
There is a sample of data, or the whole result set to the right of every stage that uses correct syntax in the aggregation pipeline builder in Atlas.
What is MongoDB Charts?
product that helps you build visualizations of the data stored in your Atlas Cluster.
Charts is available for all MongoDB Atlas Clusters and allows you to build visualizations of your data using the aggregation pipeline or even the MQL to filter data before creating charts.
What is MongoDB Compass?
MongoDB's Graphical User Interface Product
Compass is a Graphical User Interface that provides a lot of support in querying, visualizing, and analyzing your data.
