M103
Basic Cluster Administration
Chapter 1: The Mongod
The Mongod
chmod 400 <path-to-the-file>chmod 400 /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfilechown [new owner]:[group] <file name>sudo chown myuser:myuser /var/mongodb_directorymkdir [modifiers] <name of the directory>mkdir -p /db/mongodb_data/
sudo mkdir -p /var/datarm [options] [directory|file]rm -rf <directory name>ls
ls -lacd <directory>
cat <name of the file>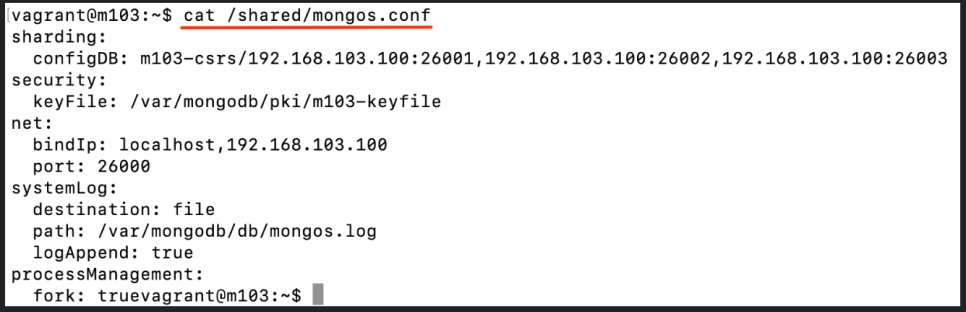
rm <file name>ps -ef | grep mongo
ps -ef | grep mongod
ps -ef | grep mongos
kill <pid>kill 13029
killall mongod
mongod
mongo
db.createCollection("employees")
use admin
db.shutdownServer()
exitWhich of these are default configurations for mongod?
- mongod listens on port 27017
- database files are stored in the directory /data/db/
mongod --helpmongod --dbpath <directory path>
mongod --port <port number>mongod --auth
mongod --bind_ip 123.123.123.123
mongod --bind_ip localhost,123.123.123.123mongod
mongod --dbpath /data/db --logpath /data/log/mongod.log
mongod --dbpath /data/db --logpath /data/log/mongod.log --fork
mongod --dbpath /data/db --logpath /data/log/mongod.log --fork --replSet "M103" --keyFile /data/keyfile --bind_ip "127.0.0.1,192.168.103.100" --tlsMode requireTLS --tlsCAFile "/etc/tls/TLSCA.pem" --tlsCertificateKeyFile "/etc/tls/tls.pem"
storage: dbPath: "/data/db" systemLog: path: "/data/log/mongod.log" destination: "file" replication: replSetName: M103 net: bindIp : "127.0.0.1,192.168.103.100" tls: mode: "requireTLS" certificateKeyFile: "/etc/tls/tls.pem" CAFile: "/etc/tls/TLSCA.pem" security: keyFile: "/data/keyfile" processManagement: fork: truemongod --dbpath /data/db --logpath /data/logs --replSet M103 --bind_ip '127.0.0.1,192.168.103.100' --keyFile /data/keyfile --forkWhich of the following represents a configuration file equivalent to the command line options?
storage:
dbPath: "/data/db"
systemLog:
destination: file
path: "/data/logs"
replication:
replSetName: "M103"
net:
bindIp: "127.0.0.1,192.168.103.100"
security:
keyFile: "/data/keyfile"
processManagement:
fork: truemongod --config mongod.conf
mongod -f mongod.confmongo admin --host localhost:27000 --eval '
db.createUser({
user: "m103-admin",
pwd: "m103-pass",
roles: [
{role: "root", db: "admin"}
]
})
'ls -l /data/db
ls -l /data/db/diagnostic.data
ls -l /data/db/journal
ls /tmp/mongodb-27017.sockWhich of the following files in the MongoDB data directory can you access to view collection data?
- The correct answer is none of the above. You should never access the data files directly.
mkdir -p /var/mongodb/dbmongo admin --host localhost:27000 --eval '
db.createUser({
user: "m103-admin",
pwd: "m103-pass",
roles: [
{role: "root", db: "admin"}
]
})
'mongod --config mongod.conf --dbpath /var/mongodb/db --port 27000db.createUser() db.dropUser()db.<collection>.renameCollection()
db.<collection>.createIndex()
db.<collection>.drop()db.dropDatabase()
db.createCollection()
db.serverStatus()db.runCommand({
"createIndexes":"<collection_name>",
"indexes":[
{
"key":{ "product": 1 },
"name": "name_index"
}
]
}
)db.<collection>.createIndex(
{ "product": 1 },
{ "name": "name_index" }
)db.<collection>.createIndexWhich of the following methods executes a database command?
- db.runCommand( { } )
mongo admin --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --eval 'db.getLogComponents()'
mongo admin --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --eval 'db.setLogLevel(0, "index")'
db.adminCommand({ "getLog": "global" })
tail -f /data/db/mongod.log
mongo admin --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --eval 'db.products.update( { "sku" : 6902667 }, { $set : { "salePrice" : 39.99} } ) '
grep -i 'update' /data/db/mongod.log Which of the following operations can be used to access the logs?
-
Running db.adminCommand({ "getLog": "global" }) from the Mongo shell
-
Running tail -f from the command line
db.runCommand({listCollections: 1})
mongo newDB --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin --eval ' db.getProfilingLevel() '
mongo newDB --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin --eval ' db.setProfilingLevel(1) '
mongo newDB --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin --eval ' db.getCollectionNames() '
mongo newDB --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin --eval ' db.setProfilingLevel( 1, { slowms: 0 } ) '
mongo newDB --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin --eval ' db.new_collection.insert( { "a": 1 } ) '
mongo newDB --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin --eval ' db.system.profile.find().pretty() ' Which of the following events are captured by the profiler?
-
Administrative operations
-
CRUD operations
-
Configuration operations
mongod --config mongod.conf --dbpath /var/mongodb/db --port 27000 --logpath /var/mongodb/logs/mongod.log --forkmongod -f mongod.conf --port 27000 --authcat /etc/mongod.confmongod -f /etc/mongod.confmongo --host 127.0.0.1:27017use admin
db.createUser({
user: "root",
pwd: "root123",
roles : [ "root" ]
})mongo --username root --password root123 --authenticationDatabase admindb.stats()
use admin
db.shutdownServer() When should you deploy a MongoDB deployment with security enabled?
-
When deploying a development environment
-
When deploying your staging environment
-
When deploying an evaluation environment
-
When deploying your production environment
mongo admin -u root -p root123db.createUser(
{ user: "security_officer",
pwd: "h3ll0th3r3",
roles: [ { db: "admin", role: "userAdmin" } ]
}
)
db.createUser(
{ user: "dba",
pwd: "c1lynd3rs",
roles: [ { db: "admin", role: "dbAdmin" } ]
}
)
db.grantRolesToUser( "dba", [ { db: "playground", role: "dbOwner" } ] )
db.runCommand( { rolesInfo: { role: "dbOwner", db: "playground" }, showPrivileges: true} ) Which of the following actions are granted to the userAdmin built-in role?
-
dropRole
-
createRole
-
viewUser
Which of the following are true about replication in MongoDB?
-
In the event of failover, the nodes vote to elect a new primary.
-
The secondary nodes replicate data from the primary node.
replica sets in MongoDB?
-
Replica set members have a fixed role assigned.
-
We should always use arbiters.
-
We can have up to 50 voting members in a replica set.
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node1
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27011
security:
authorization: enabled
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node1/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-examplesudo mkdir -p /var/mongodb/pki/
sudo chown vagrant:vagrant /var/mongodb/pki/
openssl rand -base64 741 > /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
chmod 400 /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfilemkdir -p /var/mongodb/db/node1mongod -f node1.confcp node1.conf node2.conf
cp node2.conf node3.conf
vi node2.conf
:wqstorage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node2
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27012
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node2/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-examplestorage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node3
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27013
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node3/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-examplemkdir /var/mongodb/db/{node2,node3}mongod -f node2.conf
mongod -f node3.confmongo --port 27011rs.initiate()use admin
db.createUser({
user: "m103-admin",
pwd: "m103-pass",
roles: [
{role: "root", db: "admin"}
]
})
exit mongo --host "m103-example/192.168.103.100:27011" -u "m103-admin" -p "m103-pass" --authenticationDatabase "admin"rs.status()
rs.add("m103:27012")
rs.add("m103:27013")
rs.isMaster()
rs.stepDown()
rs.isMaster() about setting up a replica set
-
rs.initiate() must be run on every node in the replica set.
-
Enabling internal authentication in a replica set implicitly enables client authentication.
Chapter 2: Replication
Lab: Deploy a Replica Set
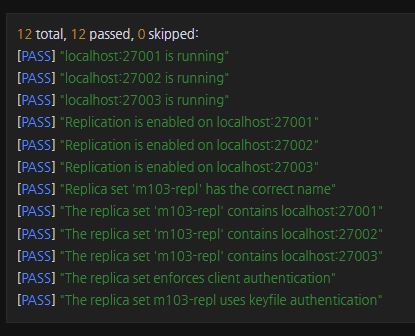
mongod --replSet m103-repl --dbpath /var/mongodb/db/1 --keyFile /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile --port 27001 --auth
mongod --replSet m103-repl --dbpath /var/mongodb/db/2 --keyFile /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile --port 27002 --auth
mongod --replSet m103-repl --dbpath /var/mongodb/db/3 --keyFile /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile --port 27003 --authrs.initiate()db.createUser({ user: "m103-admin", pwd: "m103-pass", roles: [ {role: "root", db: "admin"} ] })mongo admin -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --port 27001use admin
rs.add("localhost:27002")
rs.add("localhost:27003")Which of the following fields are included in the replica set configuration document?
-
version
-
members
-
_id
rs.status()
rs.isMaster()
db.serverStatus()['repl']
rs.printReplicationInfo() What information can be obtained from running rs.printReplicationInfo()?
-
The time of the latest entry in the oplog.
-
The time of the earliest entry in the oplog.
mkdir allbymyselfdb
mongod --dbpath allbymyselfdbmongo
show dbsuse local
show collectionsuse local
db.oplog.rs.find()var stats = db.oplog.rs.stats()
stats.capped
stats.size
stats.maxSize
rs.printReplicationInfo() Chapter 2: Replication
Local DB: Part 2
use m103
db.createCollection('messages')
use local
db.oplog.rs.find( { "o.msg": { $ne: "periodic noop" } } ).sort( { $natural: -1 } ).limit(1).pretty()
use m103
for ( i=0; i< 100; i++) { db.messages.insert( { "msg": "not yet", _id: i } ) }
db.messages.count()
use local
db.oplog.rs.find({"ns": "m103.messages"}).sort({$natural: -1})
use m103
db.messages.updateMany( {}, { $set: { author: "norberto" } } )
use local
db.oplog.rs.find( { "ns": "m103.messages" } ).sort( { $natural: -1 } ) -
The oplog.rs collection contains all operations that will be replicated.
-
The local database will not be replicated.
Chapter 2: Replication
Reconfiguring a Running Replica Set
node4.conf
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node4
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27014
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node4/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-examplearbiter.conf
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/arbiter
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 28000
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/arbiter/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-examplemongod -f node4.conf
mongod -f arbiter.confrs.add("m103:27014")
rs.addArb("m103:28000")rs.isMaster()rs.remove("m103:28000")cfg = rs.conf()
cfg.members[3].votes = 0
cfg.members[3].hidden = true
cfg.members[3].priority = 0rs.reconfig(cfg) about reconfiguring a replica set with rs.reconfig()?
-
It does not require any of the nodes to restarted.
-
It does not require any of the configuration files to be updated.
mongo admin -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --port 27001cfg = rs.conf()
cfg.members[3].votes = 0
cfg.members[3].hidden = true
cfg.members[3].priority = 0
rs.reconfig(cfg) 3 total, 3 passed, 0 skipped:
[PASS] "localhost:27004 has zero (0) votes"
[PASS] "localhost:27004 is hidden"
[PASS] "localhost:27004 has priority zero (0)"
Chapter 2: Replication
Reads and Writes on a Replica Set
mongo --host "m103-example/m103:27011" -u "m103-admin" -p "m103-pass" --authenticationDatabase "admin"rs.isMaster()
use newDB
db.new_collection.insert( { "student": "Matt Javaly", "grade": "A+" } )
mongo --host "m103:27012" -u "m103-admin" -p "m103-pass" --authenticationDatabase "admin"show dbs
rs.slaveOk()
use newDB
db.new_collection.find()
db.new_collection.insert( { "student": "Norberto Leite", "grade": "B+" } )
use admin
db.shutdownServer()mongo --host "m103:27011" -u "m103-admin" -p "m103-pass" --authenticationDatabase "admin"rs.isMaster() about reading and writing from secondaries?
- We have to run rs.slaveOk() before we can read from secondary nodes.
Chapter 2: Replication
Failover and Elections
cfg = rs.conf()
cfg.members[2].priority = 0
rs.reconfig(cfg)
rs.isMaster()
rs.stepDown()
rs.isMaster() Which of the following is true about elections?
-
Nodes with priority 0 cannot be elected primary.
-
Nodes with higher priority are more likely to be elected primary.
Chapter 2: Replication
Write Concerns: Part 1
Write Concerns: Part 2
Consider a 3-member replica set, where one secondary is offline. Which of the following write concern levels can still return successfully?
- majority
Chapter 2: Replication
Lab - Writes with Failovers
Problem:
Evaluate the effect of using a write concern with a replica set where one node has failed.
Consider a 3-node replica set with only 2 healthy nodes, that receives the following insert() operation:
use payroll
db.employees.insert(
{ "name": "Aditya", "salary_USD": 50000 },
{ "writeConcern": { "w": 3, "wtimeout": 1000 } }
) Which of the following is true about this write operation?
-
The unhealthy node will receive the new document when it is brought back online.
-
If a writeConcernError occurs, the document is still written to the healthy nodes.
Chapter 2: Replication
Read Concerns
Chapter 2: Replication
Read Concerns
Which of the following read concerns only return data from write operations that have been committed to a majority of nodes?
-
linearizable
-
majority
Chapter 2: Replication
Read Preferences
Which of the following read preference options may result in stale data?
-
secondary
-
nearest
-
primaryPreferred
-
secondaryPreferred
Chapter 2: Replication
Lab: Read Preferences
Consider a 3-node replica set that experiences a network outage.
Two of the three nodes were unreachable during the outage, leaving one node remaining.
Which of these readPreferences will allow you to read data from this node?
-
primaryPreferred
-
secondaryPreferred
-
nearest
-
secondary
Chapter 3: Sharding
When to Shard
We should consider sharding when:
-
we are holding more than 5TB per server and operational costs increase dramatically.
-
government regulations require data to be located in a specific geography.
-
our organization outgrows the most powerful servers available, limiting our vertical scaling options.
Chapter 3: Sharding
Sharding Architecture
In a sharded cluster, collection metadata is stored in:
- the configuration servers.
Chapter 3: Sharding
Setting Up a Sharded Cluster
Configuration file for first config server
csrs_1.conf
sharding:
clusterRole: configsvr
replication:
replSetName: m103-csrs
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
net:
bindIp: localhost,192.168.103.100
port: 26001
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/csrs1.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/csrs1csrs_2.conf
sharding:
clusterRole: configsvr
replication:
replSetName: m103-csrs
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
net:
bindIp: localhost,192.168.103.100
port: 26002
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/csrs2.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/csrs2csrs_3.conf
sharding:
clusterRole: configsvr
replication:
replSetName: m103-csrs
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
net:
bindIp: localhost,192.168.103.100
port: 26003
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/csrs3.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/csrs3 Starting the three config servers:
mongod -f csrs_1.conf
mongod -f csrs_2.conf
mongod -f csrs_3.confConnect to one of the config servers:
mongo --port 26001Initiating the CSRS:
rs.initiate()Creating super user on CSRS:
use admin
db.createUser({
user: "m103-admin",
pwd: "m103-pass",
roles: [
{role: "root", db: "admin"}
]
})Authenticating as the super user:
db.auth("m103-admin", "m103-pass")Add the second and third node to the CSRS:
rs.add("192.168.103.100:26002")
rs.add("192.168.103.100:26003")Mongos config (mongos.conf):
sharding:
configDB: m103-csrs/192.168.103.100:26001,192.168.103.100:26002,192.168.103.100:26003
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
net:
bindIp: localhost,192.168.103.100
port: 26000
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/mongos.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: trueStart the mongos server:
mongos -f mongos.confConnect to mongos:
vagrant@m103:~$ mongo --port 26000 --username m103-admin --password m103-pass --authenticationDatabase adminCheck sharding status:
MongoDB Enterprise mongos> sh.status()Updated configuration for node1.conf:
sharding:
clusterRole: shardsvr
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node1
wiredTiger:
engineConfig:
cacheSizeGB: .1
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27011
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node1/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-replUpdated configuration for node2.conf:
sharding:
clusterRole: shardsvr
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node2
wiredTiger:
engineConfig:
cacheSizeGB: .1
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27012
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node2/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-replUpdated configuration for node3.conf:
sharding:
clusterRole: shardsvr
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node3
wiredTiger:
engineConfig:
cacheSizeGB: .1
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27013
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node3/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-replConnecting directly to secondary node (note that if an election has taken place in your replica set, the specified node may have become primary):
mongo --port 27012 -u "m103-admin" -p "m103-pass" --authenticationDatabase "admin"Shutting down node:
use admin
db.shutdownServer()Restarting node with new configuration:
mongod -f node2.confStepping down current primary:
rs.stepDown()Adding new shard to cluster from mongos:
sh.addShard("m103-repl/192.168.103.100:27012") What is true about the mongos?
-
The mongos configuration file doesn't need to have a dbpath.
-
The mongos configuration file needs to specify the config servers.
Chapter 3: Sharding
Lab: Deploy a Sharded Cluster
mongod --replSet m103-csrs --dbpath /var/mongodb/db/csrs1 --keyFile /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile --port 26001 --auth
mongod --replSet m103-csrs --dbpath /var/mongodb/db/csrs2 --keyFile /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile --port 26002 --auth
mongod --replSet m103-csrs --dbpath /var/mongodb/db/csrs3 --keyFile /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile --port 26003 --auth Chapter 3: Sharding
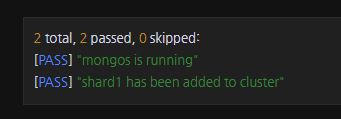
Lab: Deploy a Sharded Cluster
mongo --port 26000 -u "m103-admin" -p "m103-pass" --authenticationDatabase "admin"
sh.addShard("shard1/localhost:27001") Chapter 3: Sharding
Config DB
use config
db.databases.find().pretty()
db.collections.find().pretty()
db.shards.find().pretty()
db.chunks.find().pretty()
db.mongos.find().pretty() When should you manually write data to the Config DB?
- When directed to by MongoDB documentation or Support Engineers
Chapter 3: Sharding
Shard Keys
use m103
show collections
sh.enableSharding("m103")
db.products.findOne()
db.products.createIndex( { "sku": 1 } )
sh.shardCollection( "m103.products", { "sku": 1 } )
sh.status() Which of the following statements is true about shard keys?
-
Shard keys are used to route queries to specific shards
-
Shard keys must be supported by an index
Chapter 3: Sharding
Picking a Good Shard Key
Which of the following are indicators that a field or fields are a good shard key choice?
-
Low Frequency
-
High Cardinality
-
Non-monotonic change
Chapter 3: Sharding
Hashed Shard Keys
Which of the following functions does Hashed Sharding support?
- Even distribution of a monotonically changing shard key field
Chapter 3: Sharding
Lab: Shard a Collection
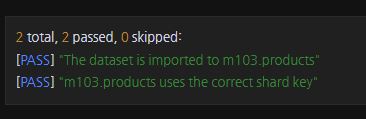
mongoimport /dataset/products.json -d m103 -c products --drop --port 26000 --username m103-admin --password m103-pass --authenticationDatabase adminsh.enableSharding("m103") db.products.createIndex({"name": 1})
db.adminCommand( { shardCollection: "m103.products", key: { name: 1 } } )
sh.status()validate_lab_shard_collectionsh.addShard("m103-repl-2/localhost:27004") Chapter 3: Sharding
Chunks
use config
show collectionsdb.chunks.findOne()use config
db.settings.save({_id: "chunksize", value: 2})sh.status()mongoimport /dataset/products.part2.json --port 26000 -u "m103-admin" -p "m103-pass" --authenticationDatabase "admin" --db m103 --collection products Which of the following is true about chunks?
- Chunk ranges have an inclusive minimum and an exclusive maximum.
Chapter 3: Sharding
Lab: Documents in Chunks
Consider the following document:
{
"_id" : ObjectId("573f7197f29313caab89b3a4"),
"sku" : 20005012,
"name" : "Complete Hit Singles A's & B's - CD",
"type" : "Music",
"regularPrice" : 14.99,
"salePrice" : 14.99,
"shippingWeight" : "0.25"
} Which of the following chunks would contain this document?
{"_id" : "m103.products-sku_20000000", "shard" : "shard2", "min" : { "sku" : 20000000 }, "max" : { "sku" : 25000000 } } Chapter 3: Sharding
Balancing
sh.startBalancer(timeout, interval)
sh.stopBalancer(timeout, interval)
sh.setBalancerState(boolean) Given a sharded cluster running MongoDB 3.6, which of the shard components is responsible for running the Balancer process?
- Primary node of the Config Server Replica Set
Chapter 3: Sharding
Queries in a Sharded Cluster
For a find() operation, which cluster component is responsible for merging the query results?
- The mongos that issued the query
Chapter 3: Sharding
Targeted Queries vs Scatter Gather: Part 1
db.products.find( { "sku": 20009151 } )db.products.find( { "type": "movie" } ){ "sku": 1, "type": 1, "name": 1 }db.products.find( { "sku": ... } )
db.products.find( { "sku": ... , "type": ... } )
db.products.find( { "sku": ... , "type": ... , "name": ... } )db.products.find( { "type": ... } )
db.products.find( { "name": ... } ) Chapter 3: Sharding
Targeted Queries vs Scatter Gather: Part 2
use m103
show collections
db.products.find({"sku" : 1000000749 }).explain()
db.products.find( {
"name" : "Gods And Heroes: Rome Rising - Windows [Digital Download]" }
).explain() Given a collection that is sharded on the following shard key:
{ "sku" : 1, "name" : 1 }
Which of the following queries results in a targeted query?
-
db.products.find( { "name" : "MongoHacker", "sku" : 1337 } )
-
db.products.find( { "sku" : 1337, "name" : "MongoHacker" } )
-
db.products.find( { "sku" : 1337 } )
Chapter 3: Sharding
Lab: Detect Scatter Gather Queries
Which of the following is required in order for a query to be targeted to a subset of shards?
-
An index exists on the shard key
-
The query uses the shard key
Final Exam
Final: Question 1
Which of the following are valid command line instructions to start a mongod? You may assume that all specified files already exist.
mongod -f /etc/mongod.conf
mongod --logpath/var/log/mongo/mongod.log--dbpath/data/db--fork Final Exam
Final: Question 2
storage:
dbPath: /data/db
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/log/mongod.log
net:
bindIp: localhost,192.168.0.100
security:
keyFile: /var/pki/keyfile
processManagement:
fork: true Select all the directories that MongoDB must have access to. Disregard the path to the configuration file itself, and the /tmp/ directory.
-
/var/log/
-
/var/pki/
-
/data/db/
Final Exam
Final: Question 3
Given the following output from rs.status().members:
[
{
"_id": 0,
"name": "localhost:27017",
"health": 1,
"state": 1,
"stateStr": "PRIMARY",
"uptime": 548,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"electionTime": Timestamp(1521038358, 2),
"electionDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:39:18Z"),
"configVersion": 2,
"self": true
},
{
"_id": 1,
"name": "localhost:27018",
"health": 1,
"state": 2,
"stateStr": "SECONDARY",
"uptime": 289,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDurable": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"optimeDurableDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.558Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.517Z"),
"pingMs": NumberLong("0"),
"syncingTo": "localhost:27022",
"configVersion": 2
},
{
"_id": 2,
"name": "localhost:27019",
"health": 1,
"state": 2,
"stateStr": "SECONDARY",
"uptime": 289,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDurable": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"optimeDurableDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.558Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.654Z"),
"pingMs": NumberLong("0"),
"syncingTo": "localhost:27022",
"configVersion": 2
},
{
"_id": 3,
"name": "localhost:27020",
"health": 1,
"state": 2,
"stateStr": "SECONDARY",
"uptime": 289,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDurable": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"optimeDurableDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.558Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.726Z"),
"pingMs": NumberLong("0"),
"syncingTo": "localhost:27022",
"configVersion": 2
},
{
"_id": 4,
"name": "localhost:27021",
"health": 0,
"state": 8,
"stateStr": "(not reachable/healthy)",
"uptime": 0,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(0, 0),
"t": NumberLong("-1")
},
"optimeDurable": {
"ts": Timestamp(0, 0),
"t": NumberLong("-1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("1970-01-01T00:00:00Z"),
"optimeDurableDate": ISODate("1970-01-01T00:00:00Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.656Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:12.668Z"),
"pingMs": NumberLong("0"),
"lastHeartbeatMessage": "Connection refused",
"configVersion": -1
},
{
"_id": 5,
"name": "localhost:27022",
"health": 1,
"state": 2,
"stateStr": "SECONDARY",
"uptime": 289,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDurable": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"optimeDurableDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.558Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:55.974Z"),
"pingMs": NumberLong("0"),
"syncingTo": "localhost:27017",
"configVersion": 2
},
{
"_id": 6,
"name": "localhost:27023",
"health": 1,
"state": 2,
"stateStr": "SECONDARY",
"uptime": 289,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDurable": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"optimeDurableDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.558Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.801Z"),
"pingMs": NumberLong("0"),
"syncingTo": "localhost:27022",
"configVersion": 2
}
] At this moment, how many replica set members are eligible to become primary in the event of the current Primary crashing or stepping down?
- 5
Final Exam
Final: Question 4
Given the following replica set configuration:
conf = {
"_id": "replset",
"version": 1,
"protocolVersion": 1,
"members": [
{
"_id": 0,
"host": "192.168.103.100:27017",
"priority": 2,
"votes": 1
},
{
"_id": 0,
"host": "192.168.103.100:27018",
"priority": 1,
"votes": 1
},
{
"_id": 2,
"host": "192.168.103.100:27018",
"priority": 1,
"votes": 1
}
]
} What errors are present in the above replica set configuration?
-
You cannot specify the same host information among multiple members.
-
You cannot specify two members with the same _id.
Final Exam
Final: Question 5
Given the following replica set configuration:
conf = {
"_id": "replset",
"version": 1,
"protocolVersion": 1,
"members": [
{
"_id": 0,
"host": "localhost:27017",
"priority": 1,
"votes": 1
},
{
"_id": 1,
"host": "localhost:27018",
"priority": 1,
"votes": 1
},
{
"_id": 2,
"host": "localhost:27019",
"priority": 1,
"votes": 1
},
{
"_id": 3,
"host": "localhost:27020",
"priority": 0,
"votes": 0,
"slaveDelay": 3600
}
]
} What is the most likely role served by the node with "_id": 3?
- It serves as a "hot" backup of data in case of accidental data loss on the other members, like a DBA accidentally dropping the database.
Final Exam
Final: Question 6
Given the following shard key:
{ "country": 1, "_id": 1 } Which of the following queries will be routed (targeted)? Remember that queries may be routed to more than one shard.
db.customers.find({"country": "Norway", "_id": 54})
db.customers.find({"country": { $gte: "Portugal", $lte: "Spain" }})
db.customers.find({"_id": 914, "country": "Sweden"})