항상 듣기로만 했던 데이터 바인딩. 개념을 조금 더 이해하고자 글로 적게 됐다. 데이터 바인딩에 대해 검색해보니 프런트엔드의 대표 라이브러리 리액트와 프레임워크 엥귤러를 가장 많이 비교했다. 하지만... 리액트만 해본 나로서 앵귤러 시스템을 이해하기 어려웠다.
데이터 바인딩이란?
- 데이터 바인딩은 화면에 보이는 데이터와 브라우저 메모리에 있는 데이터를 일치시키는 기법
자바스크립트 웹 애플리케이션의 복잡도가 증가하면서 브라우저의 메모리에 있는 여러 개의 자바스크립트 객체와 화면에 있는 데이터를 일치시키기가 매우 어려워졌다. 이러한 어려운 작업을 쉽게 해주는 해결책이 있다면 그건 데이터 바인딩일 것이다. 데이터 바인딩 이란 두 데이터 혹은 정보의 소스를 모두 일치시키는 기법이다. 즉 화면에 보이는 데이터와 브라우저 메모리에 있는 데이터를 일치시키는 기법이다. 많은 자바스크립트 프레임워크가 이러한 데이터 바인딩 기술을 제공하고 있다.
데이터 바인딩 (Stackoverflow)
Can anyone explain the difference between Reacts one-way data binding and Angular's two-way data binding
구글링을 하던 중 7년전 stackoverflow 유익한 정보를 찾았다.
단반향 (1 way data binding)
- 리액트는 부모가 자식으로 props를 전달하는 방법을 선택한다. 부모의 state를 바꾸려면 이벤트를 걸어서, state를 자식에게 전달하고 부모와 자식이 소통을 하게 된다. 여기서 데이터가 흘러가는 방향은
부모 -> 자식
양반향 (2 ways data binding)
- 리액트에서와 달리 앵귤러에서는 이벤트가 필요 없다는 얘기인건가..? 이게 가능하구나..
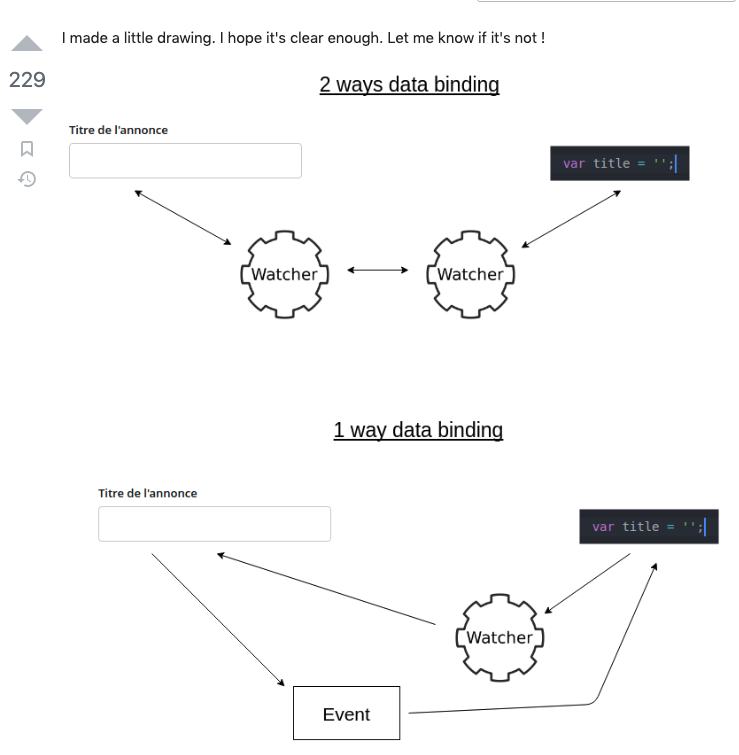
바인딩 코드로 접하기
앵귤러 뭐지..? html을 그냥 막 가져다 쓰는건가..?
단반향 (1 way data binding)
리액트는 HTML을 건드리지 않는다. 렌더링에 의존한다. 데이터를 바꾸려면 이벤트가 필요하다.
React doesn't have a mechanism to allow the HTML to change the component. The HTML can only raise events that the component responds to. The typical example is by using onChange.
//js
render() {
return <input value={this.state.value} onChange={this.handleChange} />
}
handleChange(e) {
this.setState({value: e.target.value});
}
/*
The value of the `<input />` is controlled entirely by the render function.
The only way to update this value is from the component itself,
which is done by attaching an onChange event to the `<input />`
which sets this.state.value to with the React component method setState.
The `<input />` does not have direct access to the components state,
and so it cannot make changes. This is one-way binding.
*/양반향 (2 ways data binding)
내가 느낀 엥귤러 양방향 데이터 바인딩은, 가상 DOM이 아닌 오리지널 DOM을 건드리는 것 같다. $scope.name 같은 변수를 직접적으로 건드려서 watcher 기능으로 변화가 있을 때마다 코드를 자동으로 바꿔주는 것 같다.
Changes to the
<input />are reflected in the $scope.name property automatically, since ng-model sets up watches the input and notifies $scope of the changes. Changes from the code and changes from the HTML are two-way binding. (Check out this fiddle)
//js
$scope.name = 'test';
$timeout(function() { $scope.name = 'another' }, 1000);
$timeout(function() { console.log($scope.name); }, 5000);
<!-- html --->
<input ng-model="name" />
/*
The input will start out with test, then update to another in 1000ms.
Any changes to $scope.name,
either from controller code or by changing the input,
will be reflected in the console log 4000ms later.
*/장단점/특징
* 단방향
장점 : 데이터 변화에 따른 성능 저하 없이 DOM 객체 갱신 가능, 데이터 흐름이 단방향(부모->하위 컴포넌트)이라, 코드를 이해하기 쉽고 데이터 추적과 디버깅이 쉬움
단점: 변화를 감지하고 화면을 업데이트 하는 코드를 매번 작성해야 함
-
컴포넌트 내에서 '단방향 데이터 바인딩'은 Javascript(Model)에서 HTML(View)로 한 방향으로만 데이터를 동기화하는 것을 의미함.
[JS(Model) -> HTML(View)] -
💡 단방향 데이터 바인딩이기에 역으로 HTML(View)에서 JS(Model)로의 직접적인 데이터 갱신은 불가능.
이벤트 함수(onClick, onChange,...)를 주고 함수를 호출한 뒤 Javascript에서 HTML로 데이터를 변경해야 함.[HTML(View) -> JS(Model)] -
💡 컴포넌트 간에서 단방향 데이터 바인딩은 부모 컴포넌트에서 자식 컴포넌트로만 데이터가 전달되는 구조.
* 양방향
장점 : 코드의 사용면에서 코드량을 크게 줄여줌
단점 : 변화에 따라 DOM 객체 전체를 렌더링해주거나 데이터를 바꿔주므로, 성능이 감소되는 경우가 있음
- 💡 컴포넌트 내에서 '양방향 데이터 바인딩'은 Javascript(Model)와 HTML(View) 사이에 ViewModel이 존재하여 하나로 묶여서(Binding) 되어서 둘 중 하나만 변경되어도 함께 변경되는 것을 의미.
[HTML(View) <-> ViewModel <-> Javascript(Model)] - 💡 컴포넌트 간에서는 부모 컴포넌트에서 자식 컴포넌트로는 Props를 통해 데이터를 전달하고, 자식 컴포넌트에서 부모 컴포넌트로는 Emit Event를 통해서 데이터를 전달하는 구조.
느낀점
솔직히.. 엥귤러를 직접 코드로 짜보지 않아서 아직까지는 100% 와닿지 않는다. 하지만, 컴포넌트 내부에서 혹은 컴포넌트 간에 데이터 바인딩을 이해한다면 보는 시야가 넓어지지 않을까
