Intensive Reading : https://developer.android.com/kotlin/flow?hl=en
suspend 함수가 단일의 값을 반환시키는 반면,
코루틴에서 flow 는 여러 값들을 순차적으로 방출 시킬 수 있다.
예를들면 flow를 사용하여 데이터베이스의 실시간 업데이트를 받을 수 있다.
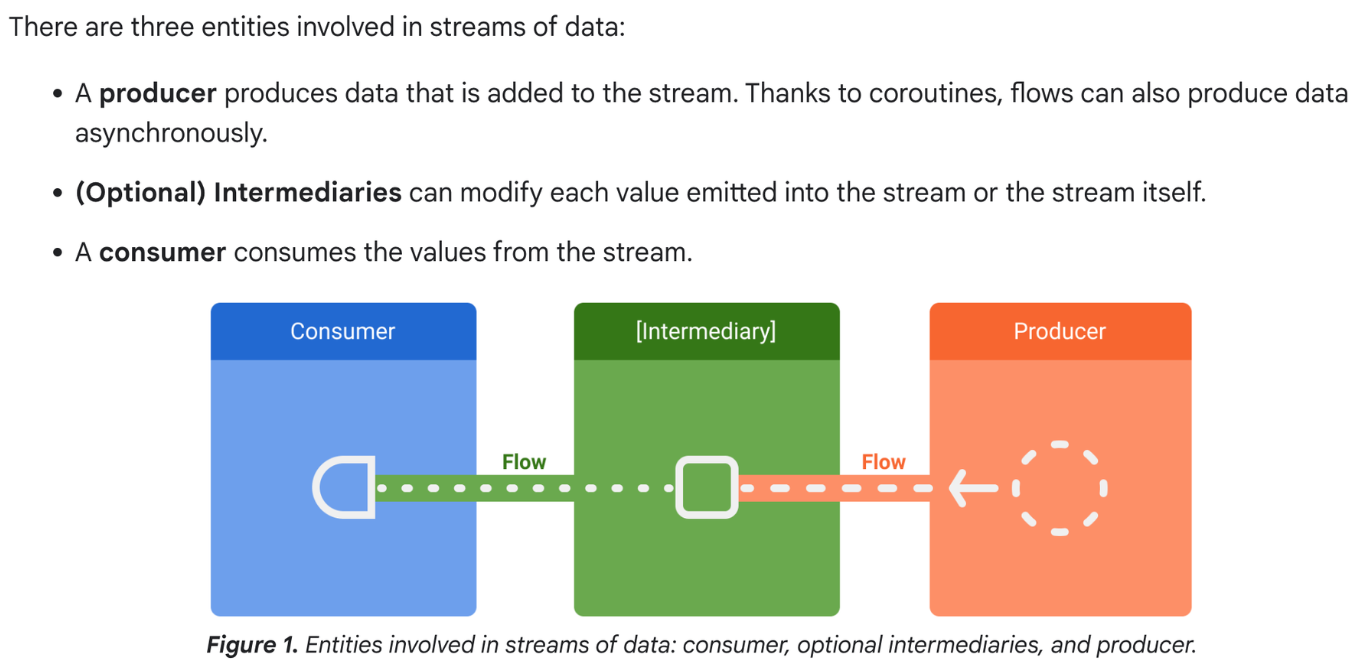
데이터 스트림의 세가지 엔티티
- producer
- 스트림에 추가되는 데이터를 생성.
- 코루틴을 이용하여 비동기적으로 데이터를 생성할 수도 있다.
- 중개자(optional)
- 스트림의 방출된 값을 수정할 수 있다.
- 소비자
- 스트림의 값을 소비합니다.
repository : UI 데이터의 생산자. → UI : 데이터를 표시하는 소비자
UI 계층 : 사용자 입력 이벤트의 생성자 → 다른 계층이 이를 소비
생산자와 소비자 사이의 계층은 일반적으로 중개자 역할을 합니다.
Creating a flow
flow builder 함수는 emit 함수를 사용하여 데이터 스트림에 새로운 값들을 수동으로 방출할 수 있는 새 흐름을 생성합니다.
Example) DataSource가 생산자 역할을 하는 경우.
- while 문과 delay 를 이용하여 고정된 간격으로 최신 뉴스를 자동으로 가져옵니다.
class NewsRemoteDataSource(
private val newsApi: NewsApi,
private val refreshIntervalMs: Long = 5000
) {
val latestNews: Flow<List<ArticleHeadline>> = flow {
while(true) {
val latestNews = newsApi.fetchLatestNews()
emit(latestNews) // Emits the result of the request to the flow
delay(refreshIntervalMs) // Suspends the coroutine for some time
}
}
}
// Interface that provides a way to make network requests with suspend functions
interface NewsApi {
suspend fun fetchLatestNews(): List<ArticleHeadline>
}flow builder는 코루틴 내에 실행이 된다. → 동일한 비동기 API 의 이점을 누릴 수 있음.
그러나, 제한 사항
- flow 는 순차적이다. 생산자가 코루틴에 있기에 suspend function 을 호출할 경우, 생산자는 suspend 함수가 리턴될때까지 멈춘다.
- ex) 생산자는 fetchLatestNews 네트워크 요청이 완료될때까지 중지된다. 완료되어야 그 결과가 스트림으로 내보내진다.
- flow builder 사용시 생산자는 다른 CoroutineContext로부터 값을 emit 할 수가 없다. 그러므로 새로운 coroutines을 생성하거나, withContext 코드 블록을 사용하여 emit 하지 말기
- 이러한 경우,
[callbackFlow](https://kotlinlang.org/api/kotlinx.coroutines/kotlinx-coroutines-core/kotlinx.coroutines.flow/callback-flow.html)사용하기.
- 이러한 경우,
Modifying the stream
중개자는 중간 연산자를 사용하여 값을 소비하지 않고 데이터 스트림을 수정 할 수 있다.
- 중간연산자 (https://kotlinlang.org/api/kotlinx.coroutines/kotlinx-coroutines-core/kotlinx.coroutines.flow/-flow/)
class NewsRepository(
private val newsRemoteDataSource: NewsRemoteDataSource,
private val userData: UserData
) {
/**
* Returns the favorite latest news applying transformations on the flow.
* These operations are lazy and don't trigger the flow. They just transform
* the current value emitted by the flow at that point in time.
*/
val favoriteLatestNews: Flow<List<ArticleHeadline>> =
newsRemoteDataSource.latestNews
// Intermediate operation to filter the list of favorite topics
.map { news -> news.filter { userData.isFavoriteTopic(it) } }
// Intermediate operation to save the latest news in the cache
.onEach { news -> saveInCache(news) }
}Collecting from a flow
값을 수신하기위해 terminal operator 를 사용하여 flow를 트리거 시킵니다.
방출되는 스트림으 모든 값을 얻기위해 collect 를 사용합니다.
(https://kotlinlang.org/api/kotlinx.coroutines/kotlinx-coroutines-core/kotlinx.coroutines.flow/-flow/)
class LatestNewsViewModel(
private val newsRepository: NewsRepository
) : ViewModel() {
init {
viewModelScope.launch {
// Trigger the flow and consume its elements using collect
newsRepository.favoriteLatestNews.collect { favoriteNews ->
// Update View with the latest favorite news
}
}
}
}Collecting the flow 은 생산자(최신 뉴스를 새로고침하고, 고정 간격으로 네트워크 요청 결과를 내보내는)를 트리거 시킨다.
생산자는 While(true) 루프로 항상 활성상태로 유지되므로, 데이터 스트림은 뷰모델이 지워지고, viewModelScope 이 취소될때 닫히게 될것이다.
flow collection 은 아래와 같은 이유로 멈출 수 있다.
- 위와 같은 예시와 같이 수집하는 코루틴은 취소되어집니다. 이것은 또한 생산자를 중지시킵니다.
- 생산자는 아이템 방출을 완료합니다. 이 경우, 데이터 스트림은 닫힙니다. 그리고 collect 를 호출한 코루틴이 실행을 재개합니다.
terminal operator 가 흐름에서 호출될때 마다 생산자 코드가 실행된다.
여러 소비자가 동시에 수집할 때 흐름을 최적화하고 공유하려면 shareIn 연산자를 사용하기.
Catching unexpected exception
class LatestNewsViewModel(
private val newsRepository: NewsRepository
) : ViewModel() {
init {
viewModelScope.launch {
newsRepository.favoriteLatestNews
// Intermediate catch operator. If an exception is thrown,
// catch and update the UI
.catch { exception -> notifyError(exception) }
.collect { favoriteNews ->
// Update View with the latest favorite news
}
}
}
}- 예외 발생시 collect 람다는 울리지 않을 것이다.
class NewsRepository(...) {
val favoriteLatestNews: Flow<List<ArticleHeadline>> =
newsRemoteDataSource.latestNews
.map { news -> news.filter { userData.isFavoriteTopic(it) } }
.onEach { news -> saveInCache(news) }
// If an error happens, emit the last cached values
.catch { exception -> emit(lastCachedNews()) }
}- 예외 발생시 collect 람다는 울릴 것이다. 예외로 인해 새 아이템들이 스트림에 방출되었기 때문이다.
Executing in a different CoroutineContext
CoroutineContext 를 바꾸기 위해 중간연산자 flowOn 를 사용합니다. flowOn 은 upstream flow 의 CoroutineContext를 변경합니다. 이는 flowOn 이전에 적용된 생산자와 중간 연산자를 의미한다.
downstream flow (flowOn 이후의 중간 연산자) 는 영향을 받지 않는다. 그리고 flow 로부터 수집하는데 사용되는 CoroutineContext 에서 실행된다.
flowOn 연산자가 여러 개인 경우 각 연산자는 해당 위치로부터 upstream 을 변경합니다.
class NewsRepository(
private val newsRemoteDataSource: NewsRemoteDataSource,
private val userData: UserData,
private val defaultDispatcher: CoroutineDispatcher
) {
val favoriteLatestNews: Flow<List<ArticleHeadline>> =
newsRemoteDataSource.latestNews
.map { news -> // Executes on the default dispatcher
news.filter { userData.isFavoriteTopic(it) }
}
.onEach { news -> // Executes on the default dispatcher
saveInCache(news)
}
// flowOn affects the upstream flow ↑
.flowOn(defaultDispatcher)
// the downstream flow ↓ is not affected
.catch { exception -> // Executes in the consumer's context
emit(lastCachedNews())
}
}- map, onEach 연산자는 defaultDispatcher 를 사용중이다
- 반면 catch 연산자와 소비자는 viewModelScope에서 사용하는 Dispatchers.Main에서 실행됩니다.
- 데이터 소스 게층은 I/O 작업을 수행하므로 I/O 작업에 최적화된 dispatcher 를 사용해야 한다.
class NewsRemoteDataSource(
...,
private val ioDispatcher: CoroutineDispatcher
) {
val latestNews: Flow<List<ArticleHeadline>> = flow {
// Executes on the IO dispatcher
...
}
.flowOn(ioDispatcher)
}Flows in Jetpack libraries
Flow with Room 을 사용하여 데이터베이스 변경 사항에 대해 알림을 받을 수 있다. data access object(DAO) 를 사용하는 경우 Flow type 을 반환하여 실시간 업데이트를 받자.
@Dao
abstract class ExampleDao {
@Query("SELECT * FROM Example")
abstract fun getExamples(): Flow<List<Example>>
}- example 목록이 변경될 때마다 데이터베이스의 새 항목이 포함된 새 목록이 생성된다.
Convert callback-based APIs to flows
callbackFlow 는 콜백 기반 API를 흐름으로 변환할 수 있는 flow builder 이다.
class FirestoreUserEventsDataSource(
private val firestore: FirebaseFirestore
) {
// Method to get user events from the Firestore database
fun getUserEvents(): Flow<UserEvents> = callbackFlow {
// Reference to use in Firestore
var eventsCollection: CollectionReference? = null
try {
eventsCollection = FirebaseFirestore.getInstance()
.collection("collection")
.document("app")
} catch (e: Throwable) {
// If Firebase cannot be initialized, close the stream of data
// flow consumers will stop collecting and the coroutine will resume
close(e)
}
// Registers callback to firestore, which will be called on new events
val subscription = eventsCollection?.addSnapshotListener { snapshot, _ ->
if (snapshot == null) { return@addSnapshotListener }
// Sends events to the flow! Consumers will get the new events
try {
offer(snapshot.getEvents())
} catch (e: Throwable) {
// Event couldn't be sent to the flow
}
}
// The callback inside awaitClose will be executed when the flow is
// either closed or cancelled.
// In this case, remove the callback from Firestore
awaitClose { subscription?.remove() }
}
}- flow builder 와는 달리,
callbackFlow사용시 send 함수를 사용하여 다른 CoroutineContext 으로 부터 혹은 trySend 함수 사용하여 코루틴 밖에서 값을 내보낼 수 있습니다. - 내부적으로
callbackFlow는 blocking queue 와 개념적으로 매우 유사한 채널을 사용한다. 채널은 버퍼링할 수 있는 최대의 요소 수량인 용량으로 구성된다.callbackFlow에서 생성된 채널의 기본 용량은 64 elements 이다. - 가득찬 채널에 새로운 요소를 추가 할때,
send는 새로운 공간이 생길떄까지 생산자를 일시 중지하는 반면,offer는 채널에 요소를 추가하지 않고 즉시 false 를 반환한다.
