🏷️문제 88. Merge Sorted Array
1. 문제 설명
-
두 개의 정수 배열 nums1과 nums2가 주어지며, 이 배열들은 비내림차순으로 정렬되어 있습니다. 또한 m과 n이라는 두 개의 정수가 주어지는데, 이는 각각 nums1과 nums2의 요소의 개수를 나타냅니다.
-
nums1과 nums2를 비내림차순으로 정렬된 하나의 배열로 병합하세요.
-
최종 정렬된 배열은 함수에 의해 반환되지 않고, 대신 배열 nums1에 저장되어야 합니다. 이를 위해 nums1의 길이는 m + n이며, 처음 m개의 요소는 병합되어야 할 요소를 나타내고, 마지막 n개의 요소는 0으로 설정되어 무시되어야 합니다. nums2의 길이는 n입니다.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [1,2,3] and [2,5,6].
The result of the merge is [1,2,2,3,5,6] with the underlined elements coming from nums1.Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0
Output: [1]
Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [1] and [].
The result of the merge is [1].Example 3:
Input: nums1 = [0], m = 0, nums2 = [1], n = 1
Output: [1]
Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [] and [1].
The result of the merge is [1].
Note that because m = 0, there are no elements in nums1. The 0 is only there to ensure the merge result can fit in nums1.2. 접근 방식
num1.length-m만큼(남은 자리수 만큼)num2를 복사할 수 있도록 반복문으로num2를 복사합니다.n == 0인 경우 복사를break합니다.m == 0인 경우n값이 0인 아닌 것(데이터 존재)을 확인 후num1의 길이만큼 복사합니다.Arrays.sort()를 사용하여 오름차순 정렬 (import 필요)
3. 의사 코드
for (m부터 num1.length만큼 반복){
num1[m부터 유효한 자리까지 복사] = num2[처음부터 끝까지];
num1 오름차순 정렬;
num1 출력;
} 4. 구현 코드
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int index = 0;
for(int i = m; i < nums1.length; i++){
if(index == n)
break;
nums1[i] = nums2[index++];
}
Arrays.sort(nums1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums1));
}
}- 시간 복잡도: O(n)
- 공간 복잡도: O(1)
5. 개선 사항
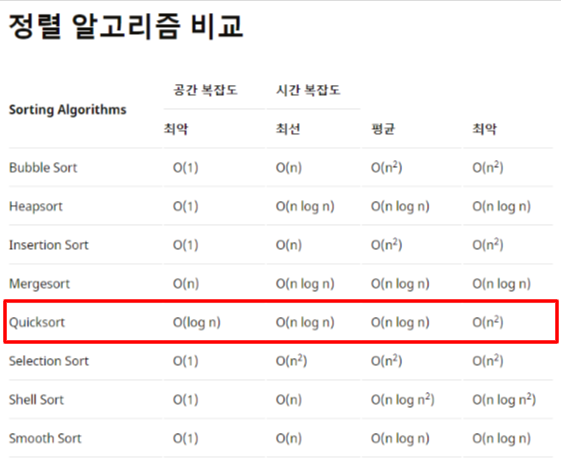
Arrays.sort() vs Collections.sort()
Arrays.sort()과Collections.sort()정렬 방식과 시간 복잡도가 궁금하여 확인을 해보았습니다.
Arrays.sort()- Arrays.sort()는 내부적으로 DualPivotQuicksort.sort()를 호출하며 큌 정렬 방식을 사용합니다.
- 일반적인 (one-pivot)퀵 정렬과 다르게 two-pivot을 사용하여 성능이 더 좋지만 함수 내부에서 배열의 크기에 따라 MergeSort, QuickSort, InsertionSort, CountingSort가 사용됩니다. (참조 설명)
- 시간 복잡도는 일반적으로 최선의 경우 O(nlog(n))을 가지고, 최악의 경우 O(n^2)를 가집니다.
Collections.sort()- Collections.sort()는 삽입정렬과 합병정렬을 결합한 TimeSort을 사용합니다.
- 시간 복잡도는 평균과 최악의 경우 O(nlog(n))으로 더 효율적인 정렬을 할 수 있습니다.
6. 최종 회고
- Java의 함수를 사용하더라도 구현코드에 더 적합한 함수를 사용하도록 더 알아보고 사용하도록 하는 것이 효율적인 방법이라고 생각이 들었습니다.
- 백준 문제를 풀 때는 최대한 문제를 이해하고 풀려고 합니다. LeetCode 문제를 영문으로 풀면서 똑같이 최대한 문제를 이해하는데 있어 영문을 잘못 해석하게 되어 시간이 걸렸습니다. 다음에는 조금 더 정확하게 해석하는 것이 시간을 줄이는 방법이 될 것 같습니다.
7. 참고
[Java] Arrays.sort()와 Collections.sort()의 시간복잡도 비교
[Java] 자바 내장 정렬 함수 - Arrays.sort()
[JAVA] 정렬에 대한 고찰 (Arrays.sort() 와 Collections.sort())
복잡도와 빅오 표기법 정리
