스택+큐
스택(Stack)
- 나중에 넣은 데이터가 먼저 나오는 LIFO(Last In First Out) 기반의 선형 자료 구조
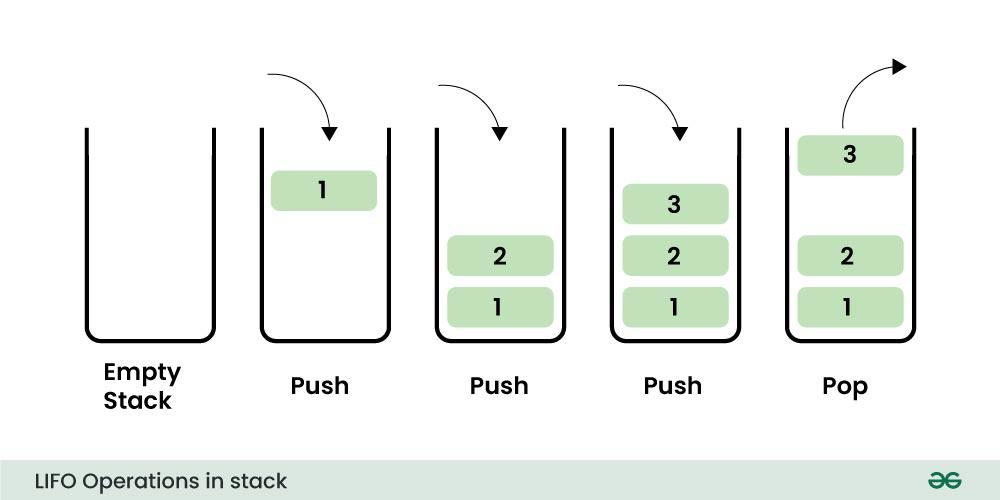
- 구현 메서드(method)
-
데이터 전체 획득 :
Stack.getBuffer() -
비어있는지 확인 :
Stack.isEmpty()// Stack() : 생성자 함수 function Stack(array) { this.array = array ? array : []; } // getBuffer() : 객체 내 데이터 셋 반환 (값만 복사) Stack.prototype.getBuffer = function () { return this.array.slice(); }; // isEmpty() : 객체 내 데이터 O/X Stack.prototype.isEmpty = function () { return this.array.length === 0; // 비어있으면 O , 데이터가 있으면 X }; let stack = new Stack([1, 2, 3]); console.log(stack); let data = stack.getBuffer(); console.log(data); console.log(data === stack.array); // ⬆️ 완벽하게 일치하였으면 true 지만 배열의 값만 복사해와서 다르므로 false console.log(stack.isEmpty()); console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(Stack.prototype)); ------------------------------------------------------------------------ OUTPUT Stack { array: [ 1, 2, 3 ] } [ 1, 2, 3 ] false ➡️ 완벽하게 일치하였으면 true 지만 배열의 값만 복사해와서 다르므로 False false { constructor: { value: [Function: Stack], writable: true, enumerable: false, configurable: true }, getBuffer: { value: [Function (anonymous)], writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true }, isEmpty: { value: [Function (anonymous)], writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true } } -
추가 :
Stack.push() -
삭제
Stack.pop() -
마지막 데이터 조회 :
Stack.peak() -
크기 확인 :
Stack.size()// Stack() : 생성자 함수 function Stack(array) { this.array = array ? array : []; } // push() : 데이터 추가 Stack.prototype.push = function (element) { return this.array.push(element); }; // pop() : 데이터 삭제 Stack.prototype.pop = function () { return this.array.pop(); }; //peak() : 가장 끝 데이터 반환 Stack.prototype.peak = function () { return this.array[this.array.length - 1]; }; // size() : 스택 내 데이터 개수 확인 Stack.prototype.size = function () { return this.array.length; }; let stack = new Stack([1, 2]); console.log(stack); stack.push(3); console.log("push : ", stack); console.log("pop : ", stack.pop()); console.log("pop : ", stack.pop()); console.log("peak : ", stack.peak()); console.log("size : ", stack.size()); console.log(stack); ------------------------------------------------------------------------ OUTPUT Stack { array: [ 1, 2 ] } push : Stack { array: [ 1, 2, 3 ] } pop : 3 pop : 2 peak : 1 size : 1 Stack { array: [ 1 ] } -
데이터 위치 :
Stack.indexOf() -
존재 여부 확인 :
Stack.includes(// Stack() : 생성자 함수 function Stack(array) { this.array = array ? array : []; } // indexOf() : 매개변수로 넘어온 element 위치 확인 Stack.prototype.indexOf = function (element, position = 0) { for (let i = position; i < this.array.length; i++) { if (element === this.array[i]) return i; } return -1; // return this.array.indexOf(element, position); }; // includes() : 데이터 존재 여부 확인 Stack.prototype.includes = function (element, position = 0) { for (let i = position; i < this.array.length; i++) { if (element === this.array[i]) return true; } return false; }; let stack = new Stack([1, 2, 3]); console.log("indexOf : ", stack.indexOf(1)); console.log("indexOf : ", stack.indexOf(1, 2)); console.log("includes : ", stack.includes(1)); console.log("includes : ", stack.includes(1, 2)); console.log("includes : ", stack.includes(5)); // 없는 값 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ OUTPUT indexOf : 0 indexOf : -1 includes : true includes : false includes : false
-
큐(Queue)
-
먼저 넣은 데이터가 먼저 나오는 FIFO(First In First Out) 기반의 선형 자료 구조
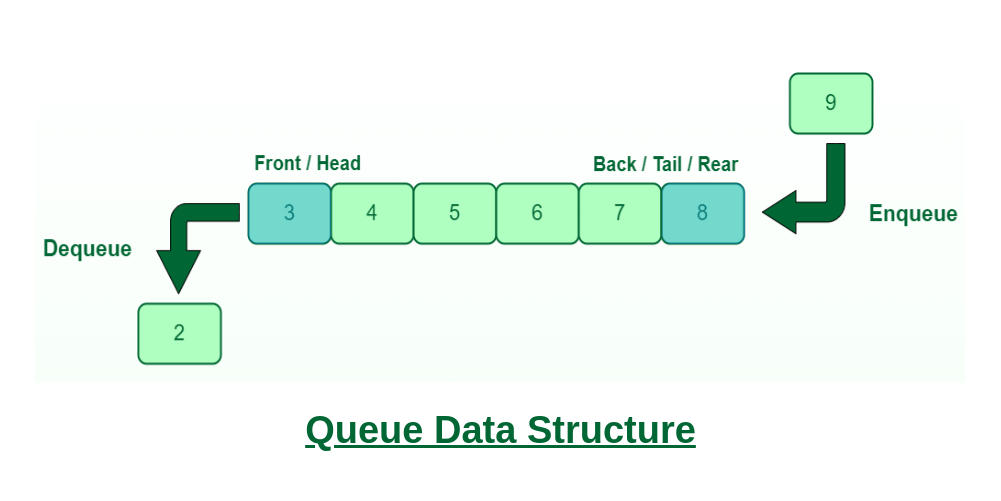
-
구현 메서드(method)
-
데이터 전체 획득 :
Queue.getBuffer() -
데이터 비어 있는지 확인 :
Queue.isEmpty()// Queue() : 생섬자 함수로 초기 데이터 설정 function Queue(array) { this.array = array ? array : []; } // getBuffer() : 객체 내 데이터 셋 반환 Queue.prototype.getBuffer = function () { return this.array.slice(); }; // isEmpty() : 객체 내 데이터 O/X Queue.prototype.isEmpty = function () { return this.array.length === 0; }; let queue = new Queue([1, 2, 3]); console.log(queue); let data = queue.getBuffer(); console.log(data); console.log(data === queue.array); console.log(queue.isEmpty()); console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(Queue.prototype)); ------------------------------------------------------------------------ OUTPUT Queue { array: [ 1, 2, 3 ] } [ 1, 2, 3 ] false false { constructor: { value: [Function: Queue], writable: true, enumerable: false, configurable: true }, getBuffer: { value: [Function (anonymous)], writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true }, isEmpty: { value: [Function (anonymous)], writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true } } -
데이터 추가 :
Queue.enqueue() -
데이터 삭제 :
Queue.dequeue()// Queue() : 생섬자 함수로 초기 데이터 설정 function Queue(array) { this.array = array ? array : []; } // enqueue() : 데이터 추가 Queue.prototype.enqueue = function (element) { return this.array.push(element); }; // dequeue() : 데이터 삭제 Queue.prototype.dequeue = function () { return this.array.shift(); }; let queue = new Queue([1, 2, 3]); console.log(queue); queue.enqueue(3); queue.enqueue(4); console.log("enqueue : ", queue); queue.dequeue(); console.log("dequeue : ", queue); ------------------------------------------------------------------------ OUTPUT Queue { array: [ 1, 2, 3 ] } enqueue : Queue { array: [ 1, 2, 3, 3, 4 ] } dequeue : Queue { array: [ 2, 3, 3, 4 ] } -
첫번째 데이터 :
Queue.front() -
데이터 사이즈 :
Queue.size() -
전체 삭제 :
Queue.clear()// Queue() : 생섬자 함수로 초기 데이터 설정 function Queue(array) { this.array = array ? array : []; } // front() : 가장 첫 데이터 반환 Queue.prototype.front = function () { return this.array.length === 0 ? undefined : this.array[0]; }; // size() : 큐 내 데이터 개수 확인 Queue.prototype.size = function () { return this.array.length; }; // clear() : 큐 초기화 Queue.prototype.clear = function () { return (this.array = []); }; let queue = new Queue([1, 2, 3, 4]); queue.dequeue(); console.log("front : ", queue.front()); console.log(queue); // 첫번째 데이터를 반환을 하고 배열 내에 삭제되지는 않음 console.log("size : ", queue.size()); queue.clear(); console.log(queue); ------------------------------------------------------------------------ OUTPUT front : 2 Queue { array: [ 2, 3, 4 ] } size : 3 Queue { array: [] }
-
큐 최적화
- 방식 개선 : enqueue/dequeue 방식을 push/shift 에서 index 로 변경(shift는 O(n), index는 O(1))
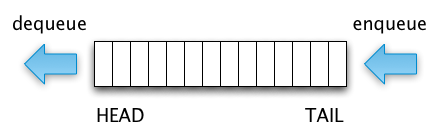
// Queue() : 생섬자 함수로 초기 데이터 설정
function Queue(array) {
this.array = array ? array : [];
this.tail = array ? array.length : [];
this.head = 0;
}
// enqueue() : 데이터 추가
Queue.prototype.enqueue = function (element) {
// return this.array.push(element);
return (this.array[this.tail++] = element);
};
// dequeue() : 데이터 삭제
Queue.prototype.dequeue = function () {
if (this.tail === this.head) return undefined;
let element = this.array[this.head];
delete this.array[this.head++];
return element;
};
let queue = new Queue([1, 2]);
console.log(queue);
queue.enqueue(3);
queue.enqueue(4);
console.log("enqueue : ", queue);
console.log(queue.dequeue());
console.log(queue.dequeue());
console.log("dequeue : ", queue);
------------------------------------------------------------------------
OUTPUT
Queue { array: [ 1, 2 ], tail: 2, head: 0 }
enqueue : Queue { array: [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ], tail: 4, head: 0 }
1
2
dequeue : Queue { array: [ <2 empty items>, 3, 4 ], tail: 4, head: 2 }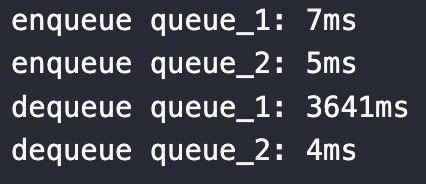
- 처음 작성한 enqueue, dequeue 보다 최적화된 코드가 수행이 더 빠르다.
