문제 이해
[ 입력형태 / 조건 ]
N
스테이지의 개수 | 5 | 1 이상 500 이하의 자연수
stages
범위 | [2, 1, 2, 6, 2, 4, 3, 3] | 길이는 1 이상 200,000 이하, 1 이상 N + 1 이하의 자연수가 담겨있음
[ 문제 ]
=> 실패율이 높은 스테이지부터 내림차순으로 스테이지의 번호가 담겨있는 배열을 return
[ 풀이 ]
해당 스테이지에 도달한 사람들의 총 인원을 먼저 구해주고, map에 문제에서 요구한 실패율 계산값을 넣어준 뒤 정렬
코드
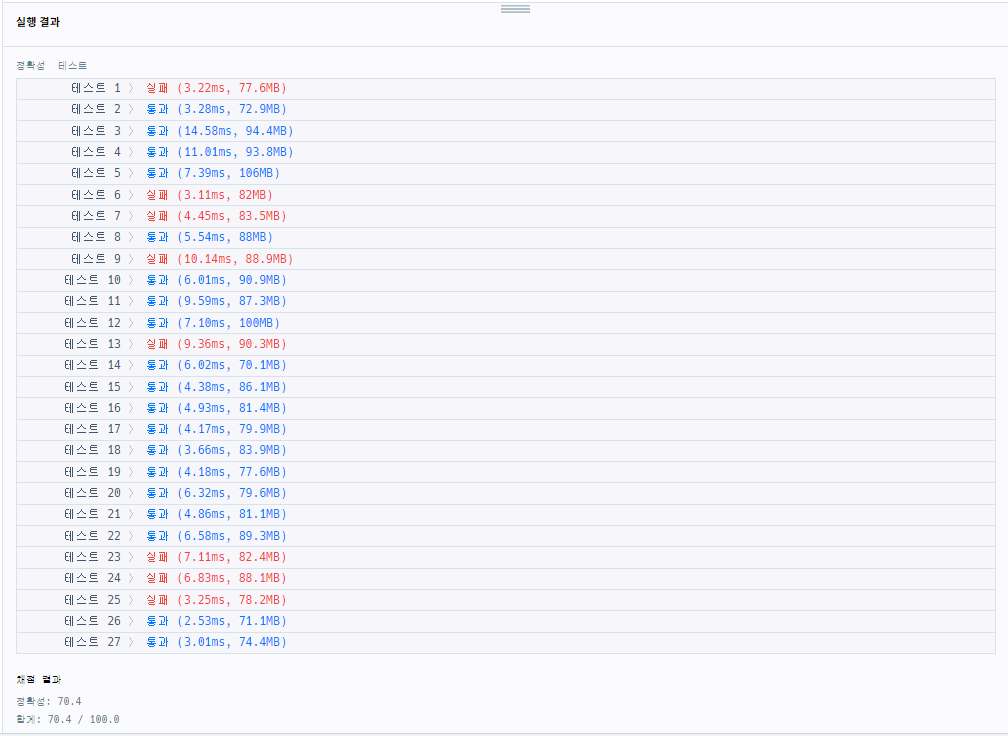
> [실패] 1차 시도 : Map 이용
- 생각한 풀이 그대로 구현
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int N, int[] stages) {
Map<Integer, Double> map = new HashMap<>();
int[] cnt = new int[N+2];
for(int stage : stages){
cnt[stage]++;
}
int total = stages.length;
for(int n=1; n<N+1; n++){
map.put(n, (double)cnt[n]/total);
total -= cnt[n];
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(map.keySet());
Collections.sort(list, (o1,o2) -> Double.compare(map.get(o2), map.get(o1)));
return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
}
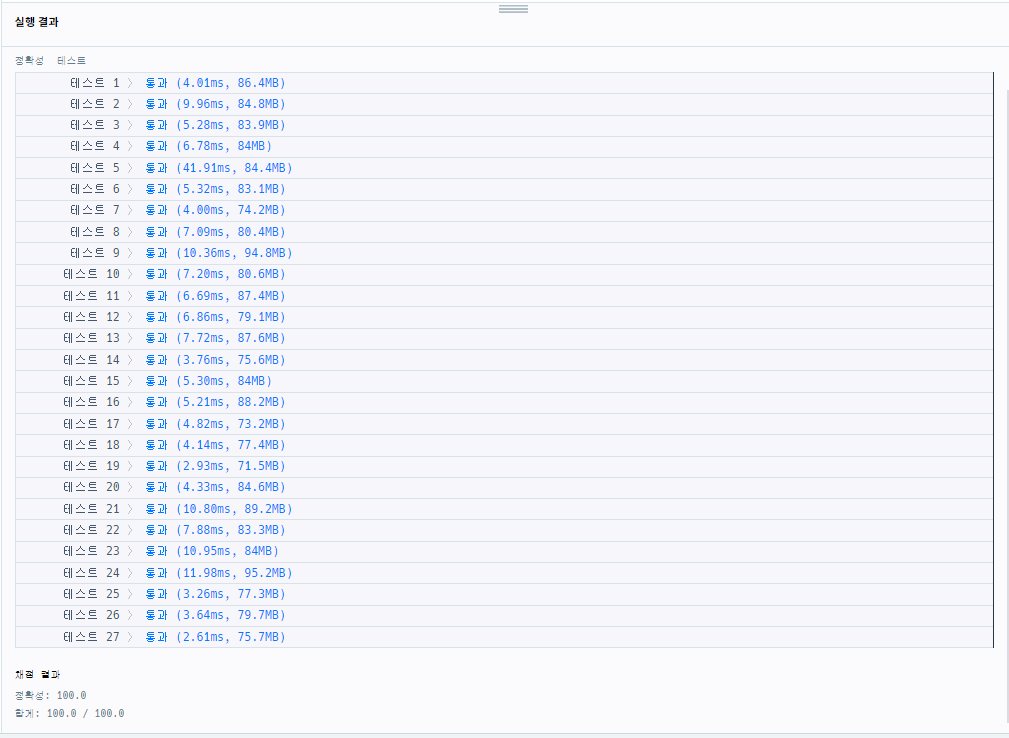
> [성공] 2차 시도 : 1차시도 개선
- 스테이지에 도달한 유저가 없는 경우 해당 스테이지의 실패율은 0 으로 정의한다.
해당 조건문을 생각하지 않았음 - 가장 큰 스테이지 번호보다 현재 n이 더 크다면 스테이지에 도달한 사람이 없는 것
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int N, int[] stages) {
Map<Integer, Double> map = new HashMap<>();
int max_depart = 0;
int[] cnt = new int[N+2];
for(int stage : stages){
cnt[stage]++;
max_depart = Math.max(max_depart, stage);
}
int total = stages.length;
for(int n=1; n<N+1; n++){
if(cnt[n]==total && max_depart < n){
map.put(n, 0.0);
}else{
map.put(n, (double)cnt[n]/total);
}
total -= cnt[n];
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(map.keySet());
Collections.sort(list, (o1,o2) -> Double.compare(map.get(o2), map.get(o1)));
return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
}
=> Stream때문일까 굉장히 느린 연산이었음
TIP : 반례를 찾을 때 문제 조건들을 자세히 따져보는 것이 중요하다
