문제 이해
[ 입력형태 / 조건 ]
n
전체 학생의 수 | 5 | 2명 이상 30명 이하
lost
체육복을 도난당한 학생들의 번호가 담긴 배열 | [2, 4] | 1명 이상 n명 이하이고 중복되는 번호는 없음
reserve
여벌의 체육복을 가져온 학생들의 번호가 담긴 배열 | [1, 3, 5] | 여벌 체육복을 가져온 학생이 체육복을 도난당했을 수 있습니다. 이때 이 학생은 체육복을 하나만 도난당했다고 가정하며, 남은 체육복이 하나이기에 다른 학생에게는 체육복을 빌려줄 수 없음
[ 문제 ]
체육수업을 들을 수 있는 학생의 최댓값을 return
[ 풀이 ]
도난당한 학생들은 set으로 저장하고, 여벌의 체육복을 가져온 학생들은 최소힙으로 관리하여 작은 번호부터 빌려줌(그리디)
코드
> [실패] 1차 시도 : Set, PriorityQueue
- 생각한 풀이 그대로 구현
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int[] lost, int[] reserve) {
Set<Integer> set_lost = new HashSet<>();
for(int l : lost){
set_lost.add(l);
}
PriorityQueue<Integer> rev = new PriorityQueue<>();
for(int r : reserve){
rev.add(r);
}
int ans = n-lost.length;
while(!rev.isEmpty()){
int stu = rev.poll();
if(set_lost.contains(stu-1)){
ans++;
set_lost.remove(stu-1);
continue;
}
if(set_lost.contains(stu)){
ans++;
set_lost.remove(stu);
continue;
}
if(set_lost.contains(stu+1)){
ans++;
set_lost.remove(stu+1);
continue;
}
}
return ans;
}
}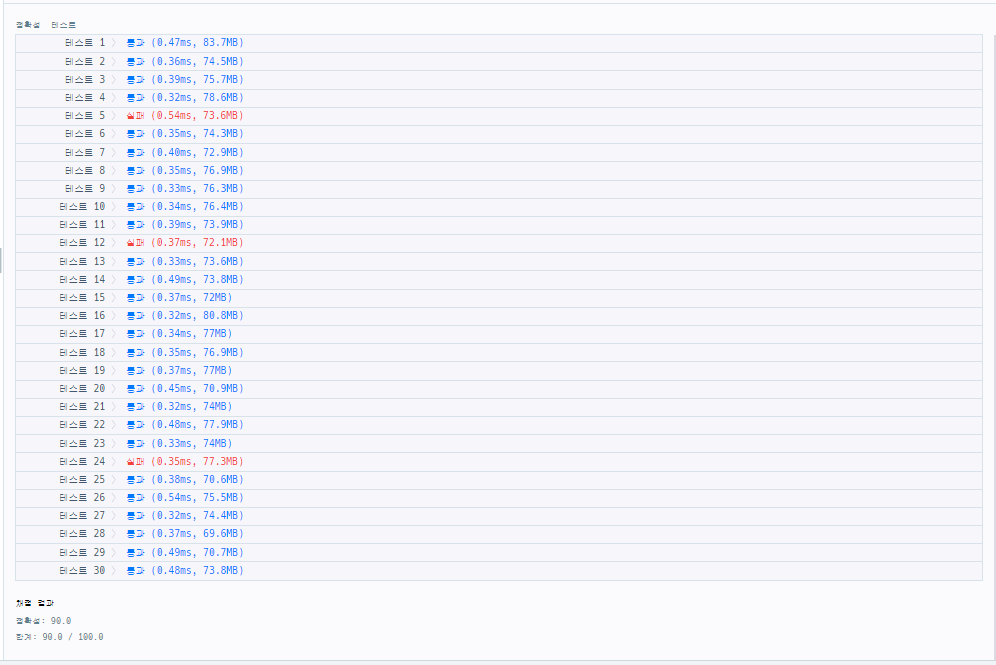
=> lost와 reverse에 같은 번호가 있다면 우선적으로 빌릴수 없는 상태로 만들어야함
> [성공] 2차 시도 : Set, PriorityQueue
- 잃어버렸고, 여분을 가진 상태라면 빌려줄수 없는 상태로 만들어야하므로 pq에 넣을때 if문으로 이를 분리했음
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int[] lost, int[] reserve) {
Set<Integer> set_lost = new HashSet<>();
for(int l : lost){
set_lost.add(l);
}
PriorityQueue<Integer> rev = new PriorityQueue<>();
for(int r : reserve){
if(set_lost.contains(r)){
set_lost.remove(r);
continue;
}
rev.add(r);
}
int ans = n-set_lost.size();
while(!rev.isEmpty()){
int stu = rev.poll();
if(set_lost.contains(stu-1)){
ans++;
set_lost.remove(stu-1);
continue;
}
if(set_lost.contains(stu)){
ans++;
set_lost.remove(stu);
continue;
}
if(set_lost.contains(stu+1)){
ans++;
set_lost.remove(stu+1);
continue;
}
}
return ans;
}
}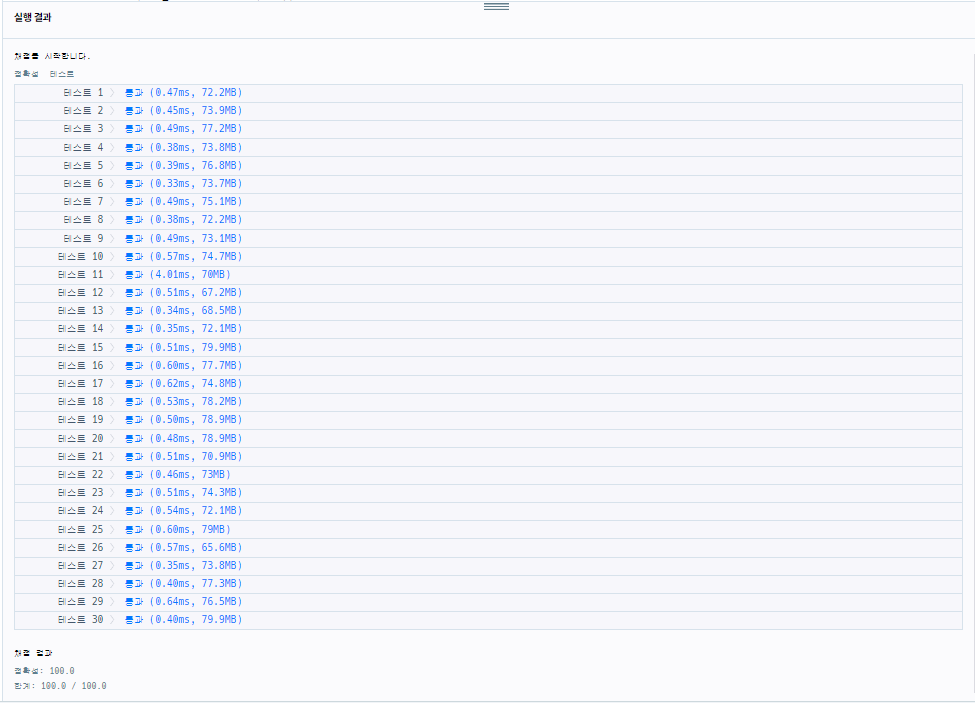
Tip : 문제에서 따로 기재된 조건을 분석해보면 반례를 좀 더 빠르게 찾을 수 있다.
