문제 이해
[ 입력형태 / 조건 ]
array
정수 배열 | [1, 5, 2, 6, 3, 7, 4]
commands
[i, j, k]라 할때 i~j까지를 추출해 정렬한 뒤 k번째를 가져오라는 묶음 | [[2, 5, 3], [4, 4, 1], [1, 7, 3]]
[ 문제 ]
=> commands를 만족시키는 값들을 answer에 담아 return
[ 풀이 ]
PriorityQueue로 추출해야할 구간을 넣고 poll을 함
(5-2+1)-3+1 = (j-i+1)-k+1 => pq.poll()할 횟수임
코드
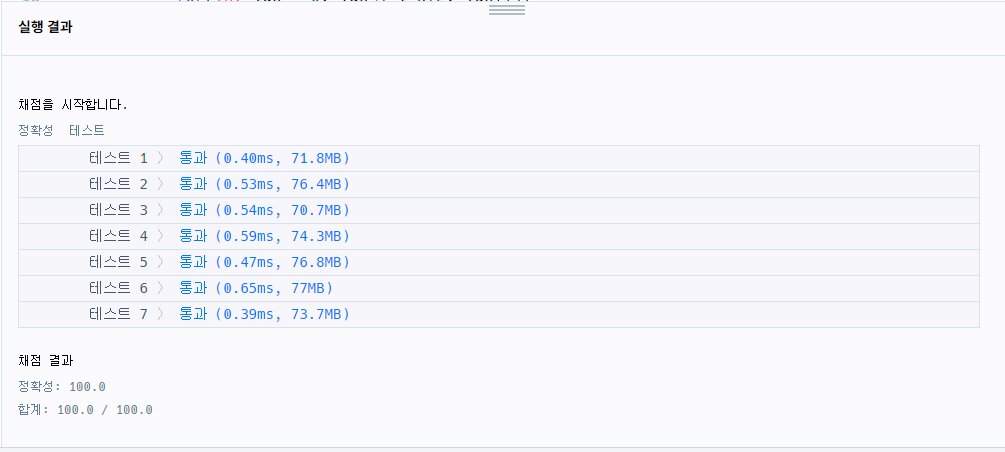
> [성공] 1차 시도 : PriorityQueue
- 생각한 풀이 그대로 구현
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] array, int[][] commands) {
int[] answer = new int[commands.length];
int point = 0;
for(int[] com : commands){
int i = com[0], j= com[1], k = com[2];
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
for(int idx=i-1; idx<j; idx++){
pq.add(array[idx]);
}
int ans = 0;
for(int idx = 0; idx<j-i-k+2; idx++){
ans = pq.poll();
}
answer[point++] = ans;
}
return answer;
}
}
=> 생각해보니 전체범위에서 최댓값 혹은 최솟값을 추출해야하면 최대힙 최소힙 구현 유무에 상관없이 전체를 넣고 빼야하는 경우가 생길 수 있음..
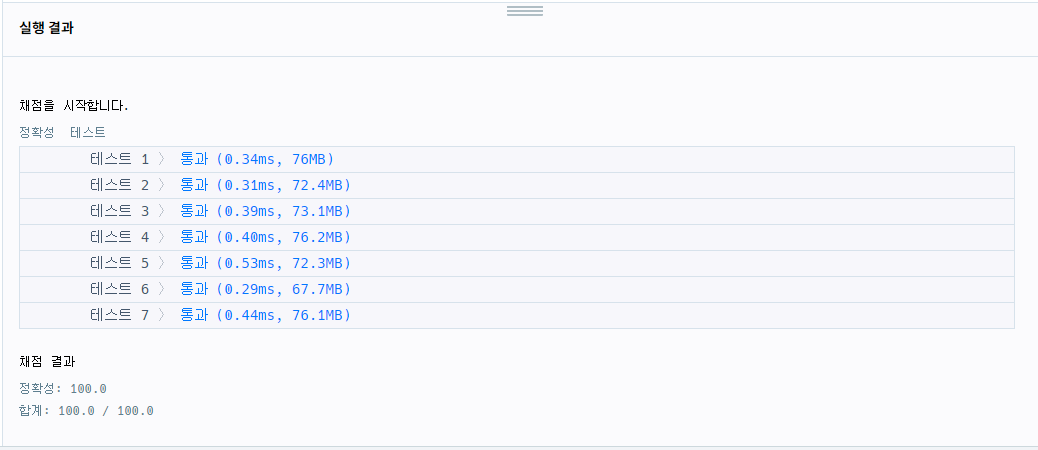
> [성공] 2차 시도 : int[] 정렬 및 인덱싱
- 좀 더 단순하게 풀어봄
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] array, int[][] commands) {
int[] answer = new int[commands.length];
int point = 0;
for(int[] com : commands){
int i = com[0], j= com[1], k = com[2];
int[] get_arr = new int[j-i+1];
for(int idx=i-1; idx<j; idx++){
get_arr[idx-i+1] = array[idx];
}
Arrays.sort(get_arr);
answer[point++] = get_arr[k-1];
}
return answer;
}
}
=> 단순 int[]배열로 관리하면 넣는 작업까지는 해당 길이만큼 진행해야 하지만, 추출은 빠르게 가능해서 좀더 효율적인 코드로 짤 수 있었음
TIP : 자료구조를 선택할 때 해당 문제에서 최적인지 검증하는 습관이 필요하다
