이 포스트는 FastCampus에 이 강의를 보고 포스팅되었습니다.
문제가 될 시 삭제될 예정입니다.
시작하기 전에 연결리스트 특징 복습 ㄱㄱ
- 동일한 데이터 타입을 순서에 따라 관리하는 자료 구조입니다.
- 하나의 노드에는 자료와 다음 요소를 가리키는 링크가 있습니다.
- 자료가 추가 될때 노드 만큼의 메모리를 할당 받고 이전 노드의 링크로 연결합니다.
- i번째 요소를 찾는데 걸리는 시간은 요소의 개수에 비례합니다. ( O(n) )
JDK 클래스에는 LinkedList가 있습니다.
뭘 구현해볼 건데
노드 정의, 연결리스트 추가, 삭제, 조회를 구현해볼 예정입니다.
잠깐 이거 코드 여기에만 올라옴??
전편에도 말했지만 모든 코드는 깃허브에 올라갈 예정입니다.
링크
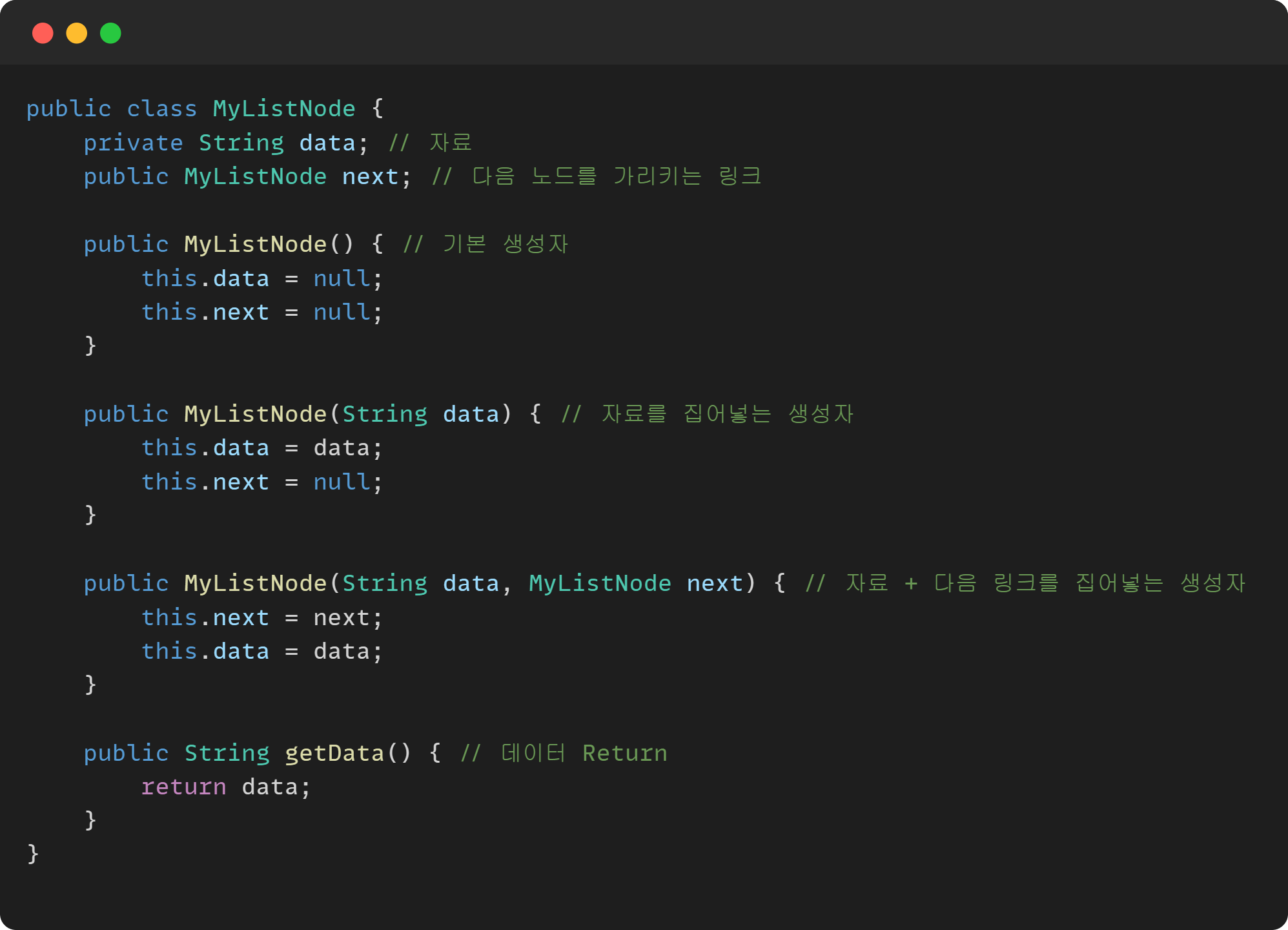
노드 정의
private String data; // 자료
public myListNode next; // 다음 노드를 가리키는 링크
public myListNode() { // 기본 생성자
this.data = null;
this.next = null;
}
public myListNode(String data) { // 자료를 집어넣는 생성자
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
public myListNode(String data, myListNode next) { // 자료 + 다음 링크를 집어넣는 생성자
this.next = next;
this.data = data;
}
public String getData() { // 데이터 Return
return data;
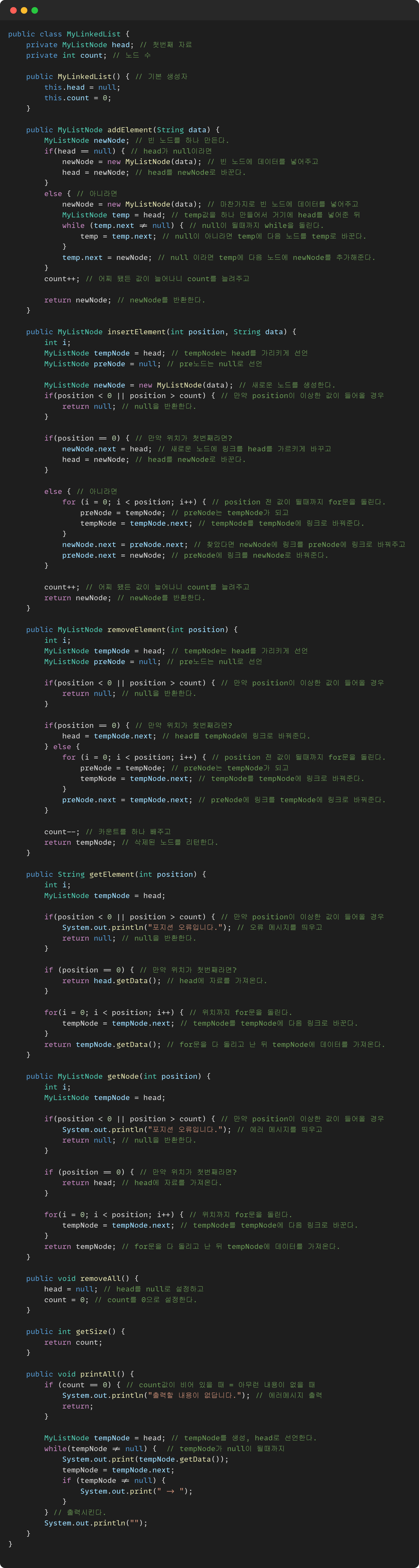
}연결리스트 정의
private myListNode head; // 첫번째 자료
private int count; // 노드 수
public myLinkedList() { // 기본 생성자
this.head = null;
this.count = 0;
}연결리스트를 정의하는 쪽에서는 두 가지 방법이 있습니다.
- Head 자체를 첫 번째 자료로 쓰는 방법
- 가장 단순하고, 쉬운 방법입니다.
- 저희가 구현할 방법이기도 합니다.
- Head 포인터를 사용하는 방법
- Head를 더미로 놔두고, 더미가 첫 번째 자료를 가리키는 방식입니다.
- 위 방법을 Head 포인터라고 하죠.
연결리스트 추가
public myListNode addElement(String data) {
myListNode newNode; // 빈 노드를 하나 만든다.
if(head == null) { // head가 null이라면
newNode = new myListNode(data); // 빈 노드에 데이터를 넣어주고
head = newNode; // head를 newNode로 바꾼다.
}
else { // 아니라면
newNode = new myListNode(data); // 마찬가지로 빈 노드에 데이터를 넣어주고
myListNode temp = head; // temp값을 하나 만들어서 거기에 head를 넣어준 뒤
while (temp.next != null) { // null이 될때까지 while을 돌린다.
temp = temp.next; // null이 아니라면 temp에 다음 노드를 temp로 바꾼다.
}
temp.next = newNode; // null 이라면 temp에 다음 노드에 newNode를 추가해준다.
}
count++; // 어찌됬든 값이 늘어나니 count를 늘려주고
return newNode; // newNode를 반환한다.
}연결리스트 삽입
public myListNode insertElement(int position, String data) {
int i;
myListNode tempNode = head; // tempNode는 head를 가리키게 선언
myListNode preNode = null; // pre노드는 null로 선언
myListNode newNode = new myListNode(data); // 새로운 노드를 생성한다.
if(position < 0 || position > count) { // 만약 position이 이상한 값이 들어올 경우
return null; // null을 반환한다.
}
if(position == 0) { // 만약 위치가 첫번째라면?
newNode.next = head; // 새로운 노드에 링크를 head를 가르키게 바꾸고
head = newNode; // head를 newNode로 바꾼다.
}
else { // 아니라면
for (i = 0; i < position; i++) { // position 전 값이 될때까지 for문을 돌린다.
preNode = tempNode; // preNode는 tempNode가 되고
tempNode = tempNode.next; // tempNode를 tempNode에 링크로 바꿔준다.
}
newNode.next = preNode.next; // 찾았다면 newNode에 링크를 preNode에 링크로 바꿔주고
preNode.next = newNode; // preNode에 링크를 newNode로 바꿔준다.
}
count++; // 어찌 됐든 값이 늘어나니 count를 늘려주고
return newNode; // newNode를 반환한다.
}연결리스트 삭제
public myListNode removeElement(int position) {
int i;
myListNode tempNode = head; // tempNode는 head를 가리키게 선언
myListNode preNode = null; // pre노드는 null로 선언
if(position < 0 || position > count) { // 만약 position이 이상한 값이 들어올 경우
return null; // null을 반환한다.
}
if(position == 0) { // 만약 위치가 첫번째라면?
head = tempNode.next; // head를 tempNode에 링크로 바꿔준다.
} else {
for (i = 0; i < position; i++) { // position 전 값이 될때까지 for문을 돌린다.
preNode = tempNode; // preNode는 tempNode가 되고
tempNode = tempNode.next; // tempNode를 tempNode에 링크로 바꿔준다.
}
preNode.next = tempNode.next; // preNode에 링크를 tempNode에 링크로 바꿔준다.
}
count--; // 카운트를 하나 빼주고
return tempNode; // 삭제된 노드를 리턴한다.
}연결리스트 조회( 1개, 자료 )
public String getElement(int position) {
int i;
myListNode tempNode = head;
if(position < 0 || position > count) { // 만약 position이 이상한 값이 들어올 경우
System.out.println("포지션 오류입니다."); // 오류 메시지를 띄우고
return null; // null을 반환한다.
}
if (position == 0) { // 만약 위치가 첫번째라면?
return head.getData(); // head에 자료를 가져온다.
}
for(i = 0; i < position; i++) { // 위치까지 for문을 돌린다.
tempNode = tempNode.next; // tempNode를 tempNode에 다음 링크로 바꾼다.
}
return tempNode.getData(); // for문을 다 돌리고 난 뒤 tempNode에 데이터를 가져온다.
}연결리스트 조회( 1개, 노드 )
public myListNode getNode(int position) {
int i;
myListNode tempNode = head;
if(position < 0 || position > count) { // 만약 position이 이상한 값이 들어올 경우
System.out.println("포지션 오류입니다."); // 오류 메시지를 띄우고
return null; // null을 반환한다.
}
if (position == 0) { // 만약 위치가 첫번째라면?
return head; // head에 자료를 가져온다.
}
for(i = 0; i < position; i++) { // 위치까지 for문을 돌린다.
tempNode = tempNode.next; // tempNode를 tempNode에 다음 링크로 바꾼다.
}
return tempNode; // for문을 다 돌리고 난 뒤 tempNode에 데이터를 가져온다.
}연결리스트 조회( 모두 )
public void printAll() {
if (count == 0) { // count값이 비어 있을 때 = 아무런 내용이 없을 때
System.out.println("출력할 내용이 없답니다."); // 에러메시지 출력
return;
}
myListNode tempNode = head; // tempNode를 생성, head로 선언한다.
while(tempNode.next != null) { // tempNode가 null이 될때까지
System.out.print(tempNode.getData());
tempNode = tempNode.next;
if (tempNode != null) {
System.out.print(" -> ");
}
} // 출력시킨다.
System.out.println("");
}연결리스트 조회( Count )
public int getCount() {
return count;
}연결리스트 전체 삭제
public void removeAll() {
head = null; // head를 null로 설정하고
count = 0; // count를 0으로 설정한다.
}+ 테스트 코드
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList();
list.addElement("A");
list.addElement("B");
list.addElement("C");
list.printAll();
list.insertElement(3, "D");
list.printAll();
list.removeElement(0);
list.printAll();
list.removeElement(1);
list.printAll();
list.insertElement(0, "A-1");
list.printAll();
System.out.println(list.getSize());
list.removeElement(0);
list.printAll();
System.out.println(list.getSize());
list.removeAll();
list.printAll();
list.addElement("A");
list.printAll();
System.out.println(list.getElement(0));
list.removeElement(0);
}위 코드는 여기서 가져왔습니다.
전체 구현 코드좀 줘바
노드 구현 코드
연결리스트 구현 코드
전체 구현 코드는 여기서도 확인 가능합니다.
마치며
연결리스트에 대한 구현은 여기까지입니다.
다음 시간에는 스택을 구현해보도록 하겠습니다.
수고하셨습니다.
