
6-4.NumberOfDiscIntersections
We draw N discs on a plane. The discs are numbered from 0 to N − 1. An array A of N non-negative integers, specifying the radiuses of the discs, is given. The J-th disc is drawn with its center at (J, 0) and radius A[J].
We say that the J-th disc and K-th disc intersect if J ≠ K and the J-th and K-th discs have at least one common point (assuming that the discs contain their borders).
The figure below shows discs drawn for N = 6 and A as follows:
A[0] = 1
A[1] = 5
A[2] = 2
A[3] = 1
A[4] = 4
A[5] = 0
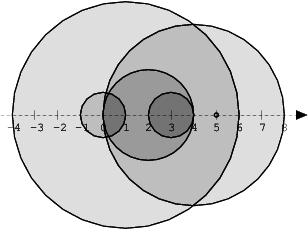
There are eleven (unordered) pairs of discs that intersect, namely:
discs 1 and 4 intersect, and both intersect with all the other discs;
disc 2 also intersects with discs 0 and 3.
Write a function:
class Solution { public int solution(int[] A); }
that, given an array A describing N discs as explained above, returns the number of (unordered) pairs of intersecting discs. The function should return −1 if the number of intersecting pairs exceeds 10,000,000.
Given array A shown above, the function should return 11, as explained above.
Write an efficient algorithm for the following assumptions:
N is an integer within the range [0..100,000];
each element of array A is an integer within the range [0..2,147,483,647].
우리는 평면에 N개의 원을 그립니다. 원은 0부터 N-1까지 번호가 매겨져 있습니다. N개의 비음수 정수로 구성된 배열 A가 주어지며, 이는 원의 반지름을 나타냅니다. J번째 원은 중심이 (J, 0)이고 반지름이 A[J]입니다.
J번째 원과 K번째 원이 서로 다른 경우(J ≠ K) 두 원이 적어도 하나의 공통점을 가지면 두 원이 교차한다고 합니다(원의 경계가 포함된다고 가정합니다).
다음 그림은 N = 6이고 배열 A가 다음과 같은 경우 그려진 원을 보여줍니다:
A[0] = 1 A[1] = 5 A[2] = 2 A[3] = 1 A[4] = 4 A[5] = 0
교차하는 원의 쌍은 총 11개입니다:
원 1과 원 4가 교차하며, 둘 다 다른 모든 원과 교차합니다.
원 2도 원 0과 원 3과 교차합니다.
위에서 설명한 대로 배열 A가 주어졌을 때 교차하는 원의 (순서 없는) 쌍의 수를 반환합니다. 교차하는 쌍의 수가 10,000,000을 초과하면 함수는 -1을 반환해야 합니다.
위에서 주어진 배열 A의 경우 함수는 11을 반환해야 합니다.
다음 가정을 만족하는 효율적인 알고리즘을 작성하세요:
N은 [0…100,000] 범위 내의 정수입니다.
배열 A의 각 요소는 [0…2,147,483,647] 범위 내의 정수입니다.
문제풀이
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(int[] A) {
int N = A.length;
if (N < 2) return 0;
// 시작 지점과 끝 지점을 저장할 배열
long[] start = new long[N];
long[] end = new long[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
start[i] = (long)i - A[i];
end[i] = (long)i + A[i];
}
// 시작 지점과 끝 지점을 정렬
Arrays.sort(start);
Arrays.sort(end);
int intersections = 0;
int activeDiscs = 0;
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
while (j < N && end[j] < start[i]) {
activeDiscs--;
j++;
}
intersections += activeDiscs;
if (intersections > 10000000) return -1;
activeDiscs++;
}
return intersections;
}
}N이 2보다 작으면 교차하는 원이 없으므로 0을 반환합니다.
원의 시작 지점은 (long)i - A[i] start에,
끝 지점은 (long)i + A[i] end에
배열로 저장 후
start와 end 배열을 각각 오름차순으로 정렬
intersections 변수 : 교차하는 원의 쌍의 수
activeDiscs 변수 : 현재 교차하는 원의 수
start 배열을 순회하면서 각 원의 시작 지점을 확인
while 루프를 사용하여 현재 원의 시작 지점보다 작은 끝 지점을 가진 원의 수를 감소
intersections에 현재 교차하는 원의 수를 더합니다.
교차하는 원의 쌍의 수가 10,000,000을 초과하면 -1을 반환합니다.
현재 원을 교차하는 원으로 추가
제출결과
문제풀어보기 -> https://app.codility.com/programmers/lessons/6-sorting/number_of_disc_intersections/
