
풀이
1. DP 테이블 정의
dp[i][j] : i번째 파이프까지 고려했을 때 길이가 j인 파이프의 용량
2. 점화식 찾기
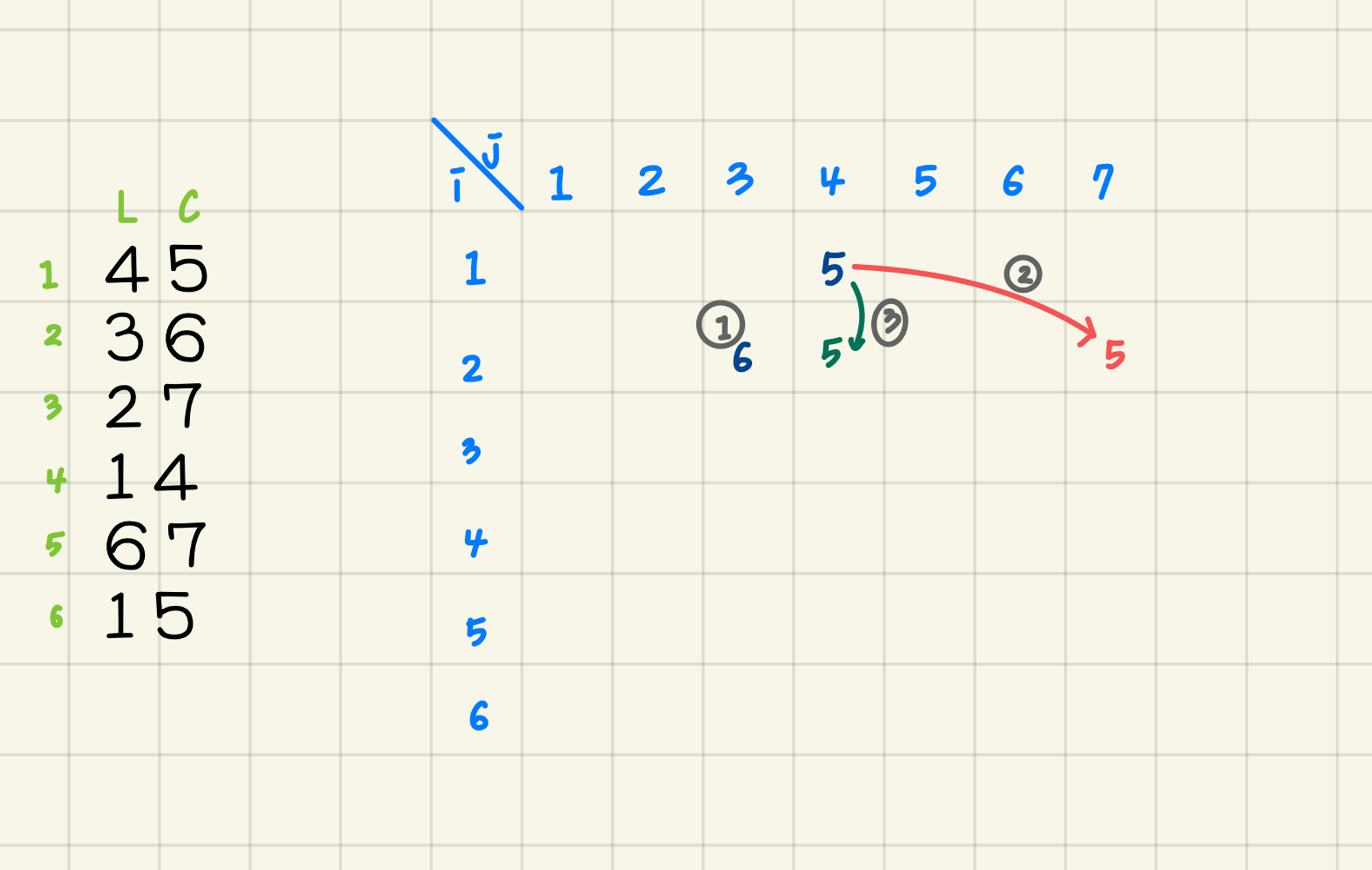
- pipes[i][0] : L (길이)
- pipes[i][1] : C (용량)
-
i번째 파이프의 길이에서의 용량을 갱신한다
dp[i][pipes[i][0]] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][pipes[i][0]], pipes[i][1]); -
dp[i - 1][j]을 탐색하며, i-1번째 파이프까지 고려한 경우에서 i번째 파이프까지 고려하게 되었을 때의 용량을 갱신한다.
for (int j = 1; j <= D; j++) { // 아직 갱신되지 않은 길이 j인 경우, 해당 j에서 i번째 파이프를 더하면 D를 초과하는 경우 => 패스! if (dp[i - 1][j] == -1 || j + pipes[i][0] > D) continue; int newValue = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], pipes[i][1]); // 기존 파이프에 i번째 파이프를 더한 경우의 용량 dp[i][j + pipes[i][0]] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j + pipes[i][0]], newValue); } -
dp[i-1][j]를 활용하여 dp[i][j]를 채운다.
for (int j = 1; j <= D; j++) dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j]);
3. 초기값
최댓값 비교를 진행하고 갱신되지 않은 상태를 명시하기 위해 dp 테이블을 -1로 채운다.
for (int i = 0; i <= P; i++) Arrays.fill(dp[i], -1);전체 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
// 백준 2073번: 수도배관공사
public class BOJ_2073 {
static int D, P;
static int[][] pipes;
static int[][] dp;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
D = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
P = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
pipes = new int[P + 1][2];
dp = new int[P + 1][D + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= P; i++) Arrays.fill(dp[i], -1);
for (int i = 1; i <= P; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
pipes[i][0] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 길이
pipes[i][1] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 용량
}
for (int i = 1; i <= P; i++) {
dp[i][pipes[i][0]] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][pipes[i][0]], pipes[i][1]);
for (int j = 1; j <= D; j++) {
if (dp[i - 1][j] == -1 || j + pipes[i][0] > D) continue;
int newValue = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], pipes[i][1]);
dp[i][j + pipes[i][0]] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j + pipes[i][0]], newValue);
}
for (int j = 1; j <= D; j++) dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j]);
}
System.out.println(dp[P][D]);
}
}
