정의
연결 리스트는 노드(Node)들이 포인터를 통해 연결된 선형 자료구조다. 각 노드는 데이터와 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터(또는 참조)로 구성된다.
현실에 비유하자면
보물찾기 게임의 단서들
- 각 장소에서 "다음 단서는 도서관에 있다"는 메모를 남김
- 특정 단서를 찾으려면 처음부터 순서대로 따라가야 한다 - O(n) 접근
- 중간에 새로운 단서를 추가하는 것은 쉽다 - O(1) 삽입
- 한 장소를 건너뛰고 싶으면 이전 장소의 메모만 바꾸면 된다
지하철 노선
- 각 역에서 "다음 역은 ○○역"이라는 안내가 있다
- 특정 역에 가려면 순서대로 지나가야 한다
- 새로운 역을 중간에 추가하는 것은 연결만 바꾸면 쉽다
- 하지만 "3번째 역이 어디지?"라고 물어보면 처음부터 세어야 한다
회사의 보고 체계
- 직원 A → 팀장 B → 부장 C → 이사 D 순으로 연결
- 새로운 중간 관리자를 추가하기 쉽다 (연결만 변경)
- 하지만 "5단계 위 상사가 누구지?"를 알려면 하나씩 올라가야 한다
구조
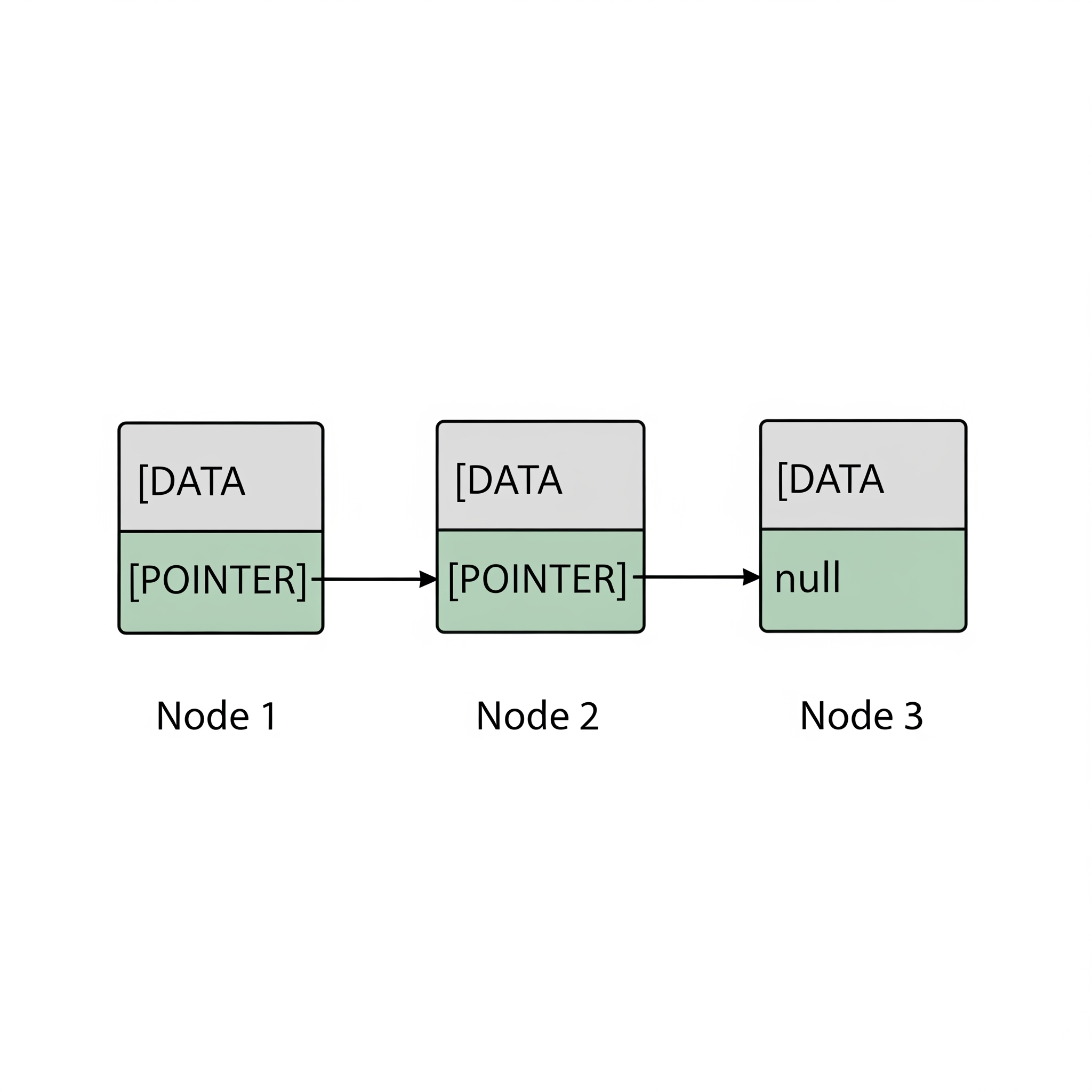
연결 리스트의 종류
단일 연결 리스트 (Singly Linked List)
각 노드가 다음 노드만을 가리키는 구조다.
이중 연결 리스트 (Doubly Linked List)
각 노드가 이전 노드와 다음 노드를 모두 가리키는 구조다.
원형 연결 리스트 (Circular Linked List)
마지막 노드가 첫 번째 노드를 가리켜 순환하는 구조다.
시간 복잡도
| 연산 | 시간 복잡도 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| 접근 (Access) | O(n) | 처음부터 순차적으로 탐색 |
| 검색 (Search) | O(n) | 선형 검색 필요 |
| 삽입 (Insert) | O(1) | 위치를 알고 있다면 |
| 삭제 (Delete) | O(1) | 위치를 알고 있다면 |
공간 복잡도
- O(n): n개의 노드와 각 노드마다 추가 포인터 저장 공간
JavaScript/TypeScript 구현
노드 클래스 정의
class ListNode<T> {
data: T;
next: ListNode<T> | null;
constructor(data: T) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}단일 연결 리스트 구현
class SinglyLinkedList<T> {
private head: ListNode<T> | null;
private size: number;
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.size = 0;
}
// 리스트 맨 앞에 삽입
prepend(data: T): void {
const newNode = new ListNode(data);
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
this.size++;
}
// 리스트 맨 뒤에 삽입
append(data: T): void {
const newNode = new ListNode(data);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
// 특정 인덱스에 삽입
insertAt(index: number, data: T): void {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) {
throw new Error('Index out of bounds');
}
if (index === 0) {
this.prepend(data);
return;
}
const newNode = new ListNode(data);
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
this.size++;
}
// 데이터로 검색
find(data: T): ListNode<T> | null {
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
if (current.data === data) {
return current;
}
current = current.next;
}
return null;
}
// 인덱스로 삭제
removeAt(index: number): T | null {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size || !this.head) {
return null;
}
if (index === 0) {
const data = this.head.data;
this.head = this.head.next;
this.size--;
return data;
}
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
const nodeToRemove = current.next;
const data = nodeToRemove.data;
current.next = nodeToRemove.next;
this.size--;
return data;
}
// 배열로 변환
toArray(): T[] {
const result: T[] = [];
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
result.push(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
return result;
}
getSize(): number {
return this.size;
}
}이중 연결 리스트 노드
class DoublyListNode<T> {
data: T;
next: DoublyListNode<T> | null;
prev: DoublyListNode<T> | null;
constructor(data: T) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList<T> {
private head: DoublyListNode<T> | null;
private tail: DoublyListNode<T> | null;
private size: number;
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
// 앞에 삽입
prepend(data: T): void {
const newNode = new DoublyListNode(data);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = this.tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
// 뒤에 삽입
append(data: T): void {
const newNode = new DoublyListNode(data);
if (!this.tail) {
this.head = this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
}장점
- 동적 크기: 런타임에 크기를 자유롭게 변경할 수 있다
- 효율적 삽입/삭제: 위치를 알고 있다면 O(1) 시간에 수행
- 메모리 효율성: 필요한 만큼만 메모리를 사용한다
단점
- 순차 접근: 특정 위치 접근에 O(n) 시간 필요
- 추가 메모리: 포인터 저장을 위한 추가 공간 필요
- 캐시 성능: 메모리가 연속적이지 않아 캐시 미스 발생 가능
- 포인터 관리: 포인터 조작 실수 시 메모리 누수나 오류 발생
활용 사례
일반적인 사례
- 실행 취소/다시 실행: 편집기의 히스토리 관리
- 음악/동영상 플레이리스트: 순차적 재생과 추가/제거
- 브라우저 히스토리: 뒤로/앞으로 가기 기능
다른 자료구조의 기반
- 스택 구현: 단일 연결 리스트로 구현 가능
- 큐 구현: 이중 연결 리스트로 효율적 구현
- 해시 테이블: 충돌 해결을 위한 체이닝
프론트엔드에서의 활용
React 컴포넌트 체인
// 컴포넌트 간 연결 관리
interface ComponentNode {
id: string;
component: React.ComponentType;
next: ComponentNode | null;
}
class ComponentChain {
private head: ComponentNode | null = null;
addComponent(id: string, component: React.ComponentType): void {
const newNode: ComponentNode = {
id,
component,
next: this.head
};
this.head = newNode;
}
renderChain(): React.ReactElement[] {
const components: React.ReactElement[] = [];
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
const Component = current.component;
components.push(<Component key={current.id} />);
current = current.next;
}
return components;
}
}무한 스크롤 구현
interface DataNode<T> {
data: T;
next: DataNode<T> | null;
}
class InfiniteScrollList<T> {
private head: DataNode<T> | null = null;
private tail: DataNode<T> | null = null;
append(data: T): void {
const newNode: DataNode<T> = { data, next: null };
if (!this.head) {
this.head = this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail!.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
}
getPage(startIndex: number, pageSize: number): T[] {
const result: T[] = [];
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
// startIndex까지 이동
while (current && index < startIndex) {
current = current.next;
index++;
}
// pageSize만큼 데이터 수집
while (current && result.length < pageSize) {
result.push(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
return result;
}
}배열과의 비교
| 특성 | 배열 | 연결 리스트 |
|---|---|---|
| 접근 시간 | O(1) | O(n) |
| 삽입/삭제 | O(n) | O(1)* |
| 메모리 사용 | 연속적 | 비연속적 |
| 캐시 성능 | 좋음 | 나쁨 |
| 구현 복잡도 | 낮음 | 높음 |
*위치를 알고 있을 때
최적화 팁
- 더미 헤드 노드: 삽입/삭제 로직을 단순화
- 꼬리 포인터 유지: 리스트 끝 삽입을 O(1)로 최적화
- 크기 추적: 별도 변수로 리스트 크기 관리
- 메모리 풀링: 노드 재사용으로 메모리 할당/해제 비용 절약