https://boonsuen.com/process-scheduling-solver
Multilevel Queue
Ready queue is partitioned into separate queues.
- Foreground (interactive)
- Background (batch)
Process resides permanently in a given queue.
Each queue has its own scheduling algorithm.
- Foreground - Round Robin
- Background - FCFS
Scheduling must be done between the queues.
- Fixed priority scheduling; (i.e., serve all from foreground then from background). Possibility of starvation.
- Time slice – each queue gets a certain amount of CPU time which it can schedule amongst its processes; i.e., 80% to foreground in RR and 20% to background in FCFS.
Multilevel Queue Scheduling
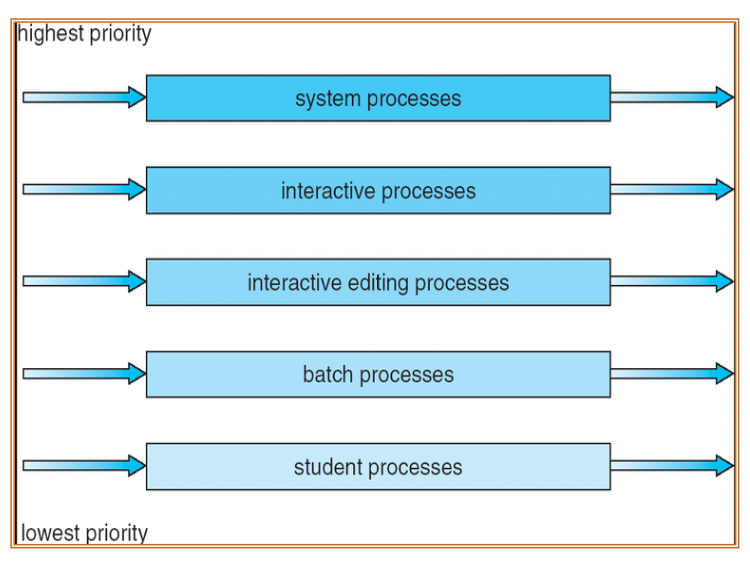
Syetem processes
Interactive processes
Interactive editing processes
Batch processes
Student processes
Multilevel Feedback Queue
A process can move between the various queues; aging can be implemented this way.
프로세스는 다양한 대기열 사이를 이동할 수 있으며 에이징은 이러한 방식으로 구현될 수 있습니다.
Multilevel-feedback-queue scheduler defined by the following parameters:
- number of queues
- scheduling algorithms for each queue
- method used to determine when to upgrade a process
- method used to determine when to demote a process
- method used to determine which queue a process will enter when that process needs service
- 대기열 수
- 각 큐에 대한 스케줄링 알고리즘
- 프로세스 업그레이드 시기를 결정하는 데 사용되는 방법
- 프로세스를 강등할 시기를 결정하는 데 사용되는 방법
- 프로세스가 서비스를 필요로 할 때 프로세스가 입력할 대기열을 결정하는 데 사용되는 메서드
Example
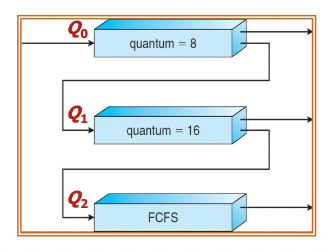
Three queues:
- Q0 – RR with time quantum 8 milliseconds
- Q1 – RR with time quantum 16 milliseconds
- Q2 – FCFS
Scheduling
- A new job enters queue Q0 which uses RR with 8 milliseconds time quantum. When it gains CPU, job receives 8 milliseconds. If it does not finish in 8 milliseconds, job is moved to queue Q1.
- At Q1 job is again served with RR (16 milliseconds time quantum) and receives 16 additional milliseconds. If it still does not complete, it is moved to queue Q2.
- Processes in Q2 run on an FCFS basis but run only when Q0 and Q1 are empty.
