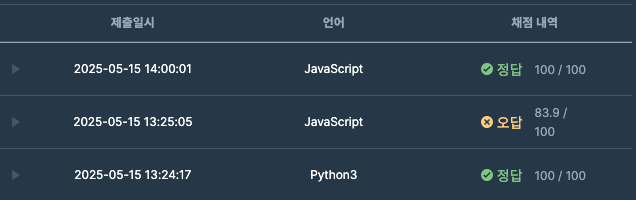
아래 프로그래머스 로고를 클릭하면 해당 문제로 이동합니다 😀
풀이과정
이럴때 보면 진짜 파이썬이 알고리즘푸는데 최강자가 아닐까?하는 생각이 든다 ,,,
이 문제는, 최소 힙 Min Heap을 이용해서 모든 음식의 스코빌 지수가 K 이상일 때 까지 가장 작은 두 값을 O(log n)으로 찾고 삽입하는 과정을 반복하면 된다.
파이썬은 heapq로 후딱 구현이 되는데,, js로는 직접 구현을 해야해서 배열 + 정렬로 MinHeap을 살짝 흉내냈는데 효율성검사에서 탈락 ~.. 그래서 직접 구현했다 ..
function solution(scoville, K) {
let count = 0;
scoville.sort((a, b) => a - b); // 초기 정렬
while (scoville[0] < K) {
if (scoville.length < 2) return -1;
const first = scoville.shift();
const second = scoville.shift();
const mixed = first + second * 2;
scoville.push(mixed);
scoville.sort((a, b) => a - b); // 다시 정렬
count++;
}
return count;
}
코드
1. Python
import heapq
def solution(scoville, K):
heapq.heapify(scoville)
mix_count = 0
while scoville[0] < K:
if len(scoville) < 2:
return -1
first = heapq.heappop(scoville)
second = heapq.heappop(scoville)
heapq.heappush(scoville, first + second * 2)
mix_count += 1
return mix_count2. JS
배열 + 정렬로 MinHeap을 살짝 흉내내어봤는데 효율성검사에서 탈락한다 ..
그래서 악으로 깡으로 클래스 구현해서 풀었다 ..
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [];
}
push(val) {
this.heap.push(val);
let i = this.heap.length - 1;
while (i > 0) {
let parent = Math.floor((i - 1) / 2);
if (this.heap[i] >= this.heap[parent]) break;
[this.heap[i], this.heap[parent]] = [this.heap[parent], this.heap[i]];
i = parent;
}
}
pop() {
if (this.heap.length === 1) return this.heap.pop();
const top = this.heap[0];
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
let i = 0;
while (true) {
let left = 2 * i + 1;
let right = 2 * i + 2;
let smallest = i;
if (left < this.heap.length && this.heap[left] < this.heap[smallest]) smallest = left;
if (right < this.heap.length && this.heap[right] < this.heap[smallest]) smallest = right;
if (smallest === i) break;
[this.heap[i], this.heap[smallest]] = [this.heap[smallest], this.heap[i]];
i = smallest;
}
return top;
}
peek() {
return this.heap[0];
}
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
}
function solution(scoville, K) {
const heap = new MinHeap();
scoville.forEach(s => heap.push(s));
let count = 0;
while (heap.peek() < K) {
if (heap.size() < 2) return -1;
const first = heap.pop();
const second = heap.pop();
heap.push(first + second * 2);
count++;
}
return count;
}결과