Git
Git Docs.
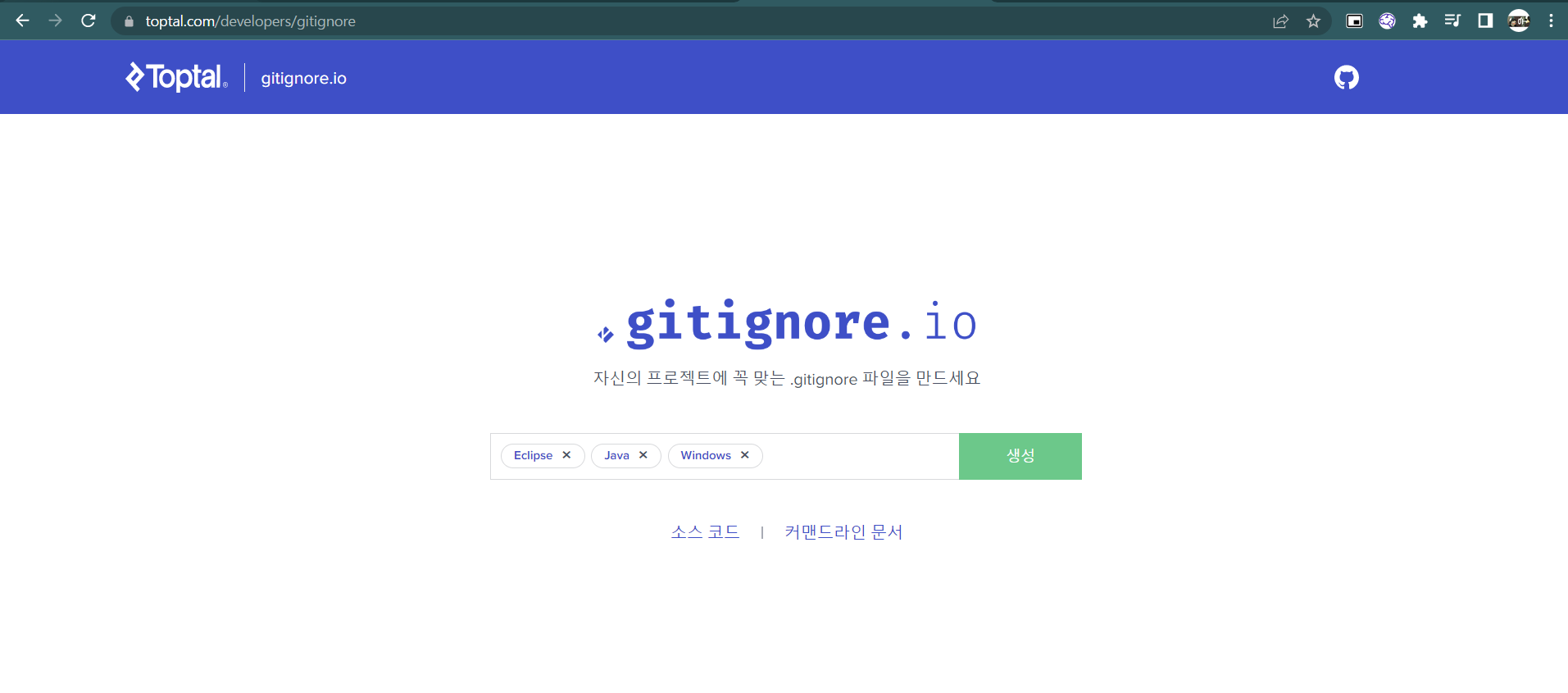
gitignore - Commit시에 자신의 컴퓨터 환경설정을 담은 .classpath와 같은 파일들 제외해주는 .gitignore에 추가를 도와줌.
Git Commands
Tutorial
$ Git help
$ Git help tutorial # redirect you to the gittutorial.htmlLinux
Linux와 동일하게 Git Bash에서도 commands가 사용가능하다.
Ctrl + C, q = exit
Ctrl + Insert : Copy / Shift + Insert : Paste
pwd, ls, cd, mkdir, cat, ...Userame
$ git config --global user.name "beaver"
$ git config --global user.email "beaver@beaver.com"$ git config --global --list # view the user info
> user.name=beaver
> user.name=beaver@beaver.comGitHub Docs : getting started with git
Environment
Auto-Completion
$ curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/git/git/master/contrib/completion/git-prompt.shBash
$ vi .bashrc
아래의 코드 copy & paste하기.. ~/git-prompt.sh
export GIT_PS1_SHOWDIRTYSTATE=1
export PS1='[\u@\h \W$(__git_ps1 " (%s)")]$ '
종료 : esc -> :xInit
$ git init
# .git 파일이 생성되며 git이 initialize
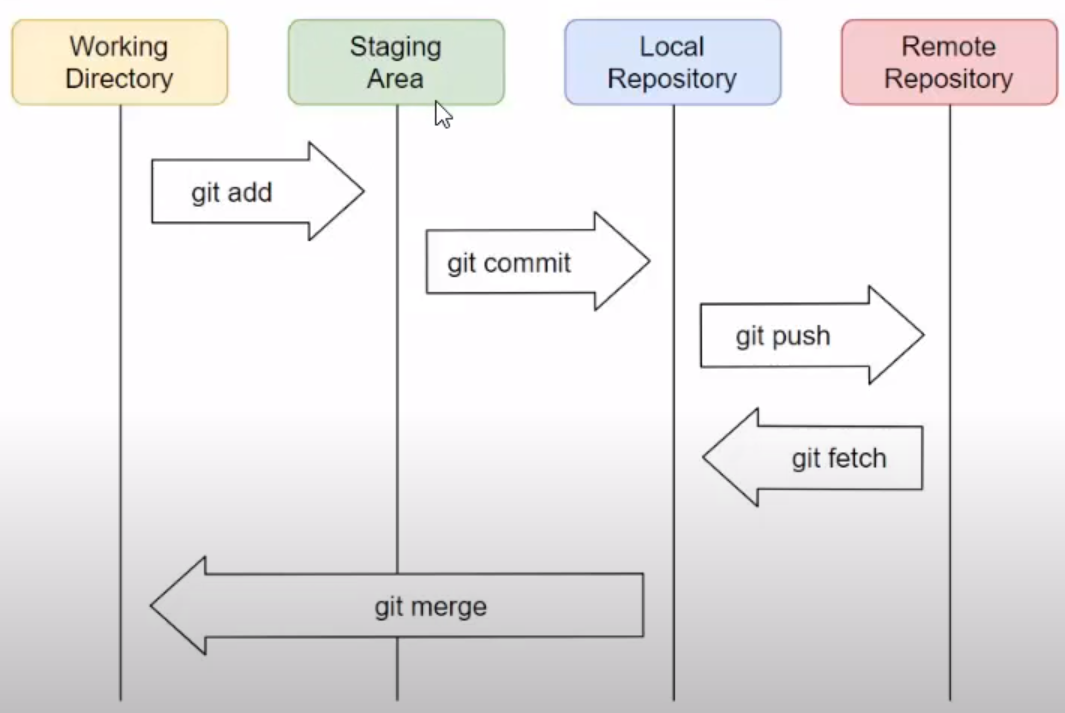
Add
$ git add .
# 해당 작업 디렉토리 내의 모든 변경 사항을 스테이징.
$ git add -A
작업 디렉토리 내의 어디에 위치하든 항상 동일히 모든 변경 내용을 스테이징.git add .는 명령어를 실행한 디렉토리 이하에서 발생한 변경 내용만 포함하고, 해당 디렉토리 기준으로 상위 디렉토리의 변경 내용을 포함하지 않는다.
git add .텍스트를 프로젝트 최상위 디렉토리에서 실행하면 git add -A와 같다.
Commit
$ git commit -m "메시지"
$ git commit -m -a "메시지" # add & commit 한번에Status
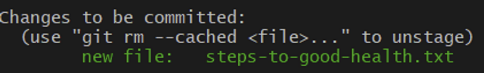
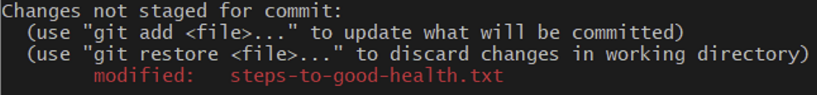
$ git status
# untracked files는 red로, git add한 (tracked files)는 green으로 표시됨.
# git add한 file이 modified됬을 경우에 또한 red로 표시됨.Ex)

Restore
$ git restore file # 해당 file 작업 내용 초기화
$ git restore . # working directory 파일 초기화Reset
$ git reset HEAD~2 # 특정 commit으로 모든 히스토리 초기화
$ git reset --mixed # 히스토리에서 삭제된 commit의 작업들은 working directory로 이동
$ git reset HEAD file.txt # staging area의 파일들 working directory로 옮기기
$ git reset --soft HEAD~1 # 특정 commit으로 초기화 후, 변경된 작업을 staging area로 이동
$ git reset --hard HEAD~2 # 특정 commit으로 초기화 후, 변경된 작업 삭제Log
$ git log
$ git log -n 3 # check the latest 3 commits
$ git log -oneline -n 3 # show in oneline
$ git log file # shows the 1st commit for the fileBranch
$ git branch
$ git branch “~” # make “~” branch
$ git checkout “~” # change to “~” branch
$ git branch -d "~" # delete "~" branchEx) 생성한 branch(ex-branch)에서 commit한 것은 master branch(master)에서 확인되지 않는다. merge후에 확인 가능하다.
(master)]$ git merge ex-branch