단절선
문제 분석 및 풀이
설계 분석
처음 생각
- 간선 (u,v)를 포함하는 사이클이 있다면 간선 (u,v)는 단절선이 아니다.
- 모든 노드에 대해서 (u,v) 로 시작하는 경로를 DFS로 탐색. u로 돌아 오는 경로가 있으면 (u,v)는 단절선 아님
- 아이디어 자체는 맞는 듯 하지만 구현에서 시간초과
- https://testcase.ac/problems/11400 기준으로 틀린 케이스 없음
찾아본 풀이
-
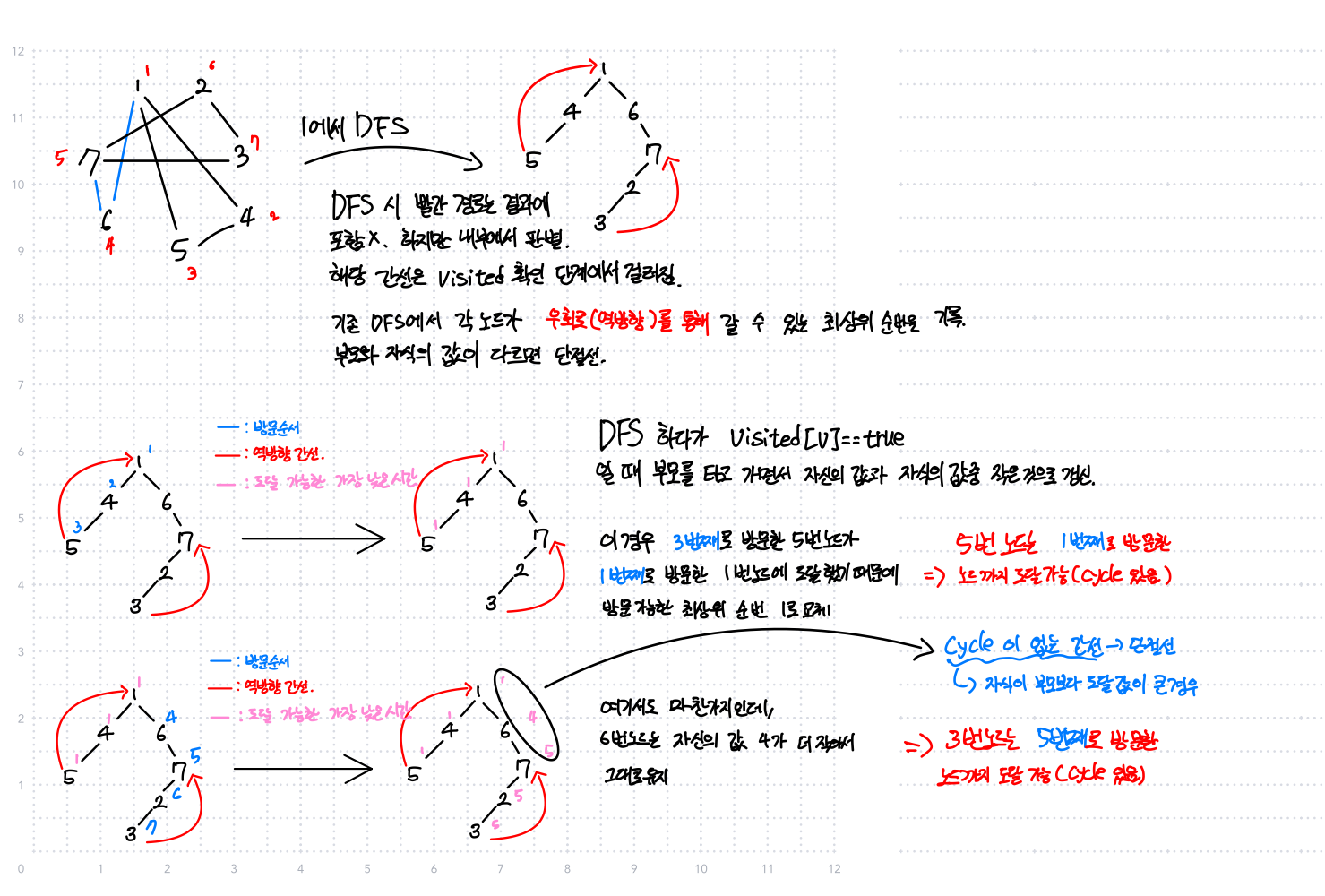
DFS 스패닝 트리를 생성
- DFS를 어떤 노드 대해서 실행 했을 때 생기는 그래프를 루트가 해당 노드인 트리로 해석
- 간선 (u,v)이 절단선이려면 v가 루트인 서브트리에서 v를 거치지 않고 u로 도달하는 경로가 없어야함
- 위에서 말한 간선 (u,v)를 포함하는 사이클이 있다면 간선 (u,v)는 단절선이 아니다. 적용
-
스패닝 트리를 생성하는 과정에서 방문 순서 기록
- 이미 방문한 노드를 방문하는 경우 (사이클)
- 부모를 타고 가면서 자신의 방문 순서와, 방문한 노드의 방문순서 중 작은 값으로 갱신 후 경로는 포함 x
-
문제에서 그래프는 항상 연결되어 있다고 했으니까 DFS 1회 진행하면 답을 찾을 수 있음
풀이
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int V,E;
unordered_map<int ,vector<int>> graph;
vector<int> visited;
set<pair<int, int>> bridges;
int time_count=1;
int dfs(int curent, int parent)
{
// 방문 여부 + 방문 시간 기록
visited[curent] = time_count++;
// 현재 서브트리에서 도달 가능한 가장 낮은 방문 시간
// 모든 노드는 초기에 자기 자신까지만 도달 가능
int low_node_value = visited[curent];
// 이웃 노드를 자식으로 취급
for (auto child : graph[curent])
{
// 바로 되돌아가는 역방향 간선은 차단
if (child == parent) continue;
// 이미 방문한 경우 (사이클이 있는 경우)
if (visited[child] != 0)
{
// 자신의 방문 순서와 도달 가능한 가장 낮은 방문 시간 중 작은 값으로 갱신
low_node_value = min(low_node_value, visited[child]);
continue;
}
// 재귀를 통해서 서브트리를 탐색
// 여기서 서브트리가 도달 가능한 가장 낮은 방문 시간 값 나옴
int subtree = dfs(child, curent);
// 서브트리 값이랑, 내 방문 순서랑 비교해서 작은걸로 갱신
low_node_value = min(low_node_value, subtree);
// 서브 트리의 순번이 부모보다 큰 경우 브릿지임
if (subtree > visited[curent])
{
bridges.insert({min(curent,child), max(curent,child)});
}
}
return low_node_value;
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> V >> E;
for (int i=0; i<E; i++)
{
int u,v;
cin >> u >> v;
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
visited.resize(V+1,0);
dfs(1, 0);
cout << bridges.size() << "\n";
for (auto p : bridges)
cout << p.first << " " << p.second << "\n";
return 0;
}
