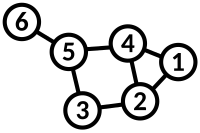
1.그래프란?
정점(Vertex)과 간선(edge)로 구성된 비선형 자료구조.
2. 주요 용어
- 정점 : 그래프의 기본 구성요소
- 간선 : 정점과 정점을 연결하는 선
- 방향/무방향 : 간선의 방향이 있다면 그 방향으로만 이동 가능. 방향이 없다면 양 방향으로 이동 간,ㅇ
- 가중치 : 간선에 값을 부여할 수 있음. (거리, 비용 등)
- 연결 : 그래프의 모든 노드들 사이의 경로가 존재하면 연결 그래프
- 차수 : 무방향에서는 인접한 노드의 수, 방향에서는 진입 차수와 진출 차수로 나눔.
- Cycle : 한 노드에서 시작에서 자기 자신으로 돌아오는 경로가 있는경우 이 경로를 Cycle이라 부른다.
3. 그래프의 구현
1) 인접 행렬 (Adjacency Matrix)
- 그래프를 2차원 배열을 사용해서 표현한다.
- matrix[from][to] = weight(or bool)
- from에서 to로 가는 경로의 가중치는 weight이다 (혹은 경로가 존재한다.)
- 대각선의 경우(from = to)를 잘 처리할 것.
- 무방향 그래프인 경우 반대의 경우도 추가.
- 메모리를 많이 차지한다. 정점은 많지만 간선이 적은 경우 낭비.
- 탐색에 유리하다
2) 인접 리스트 (Adjacency List)
- 그래프를 리스트를 사용해서 표현
- List[from].push_back(to)
- from에의 인접노드를 리스트로 관리
- 가중치는 map, pair등 다양한 방법으로 추가 가능
- 무방향 그래프인 경우 반대의 경우도 추가.
- 메모리를 적게 먹지만, 탐색은 .
3) 발생 행렬 (Incidence matrix)
- 2차원 배열을 이용해서 표현하지만 조금 독특하다.
- 행은 정점 리스트, 열은 간선 리스트
- 열을 순회하면서 간선과 연결된 정점은 1 아니면 0
- 방향 그래프인 경우 들어가면 1 나가면 -1
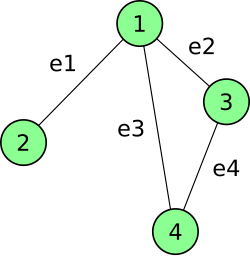
e1 e2 e3 e4 1 1 1 1 0 2 1 0 0 0 3 0 1 0 1 4 0 0 1 1
4. 그래프 탐색
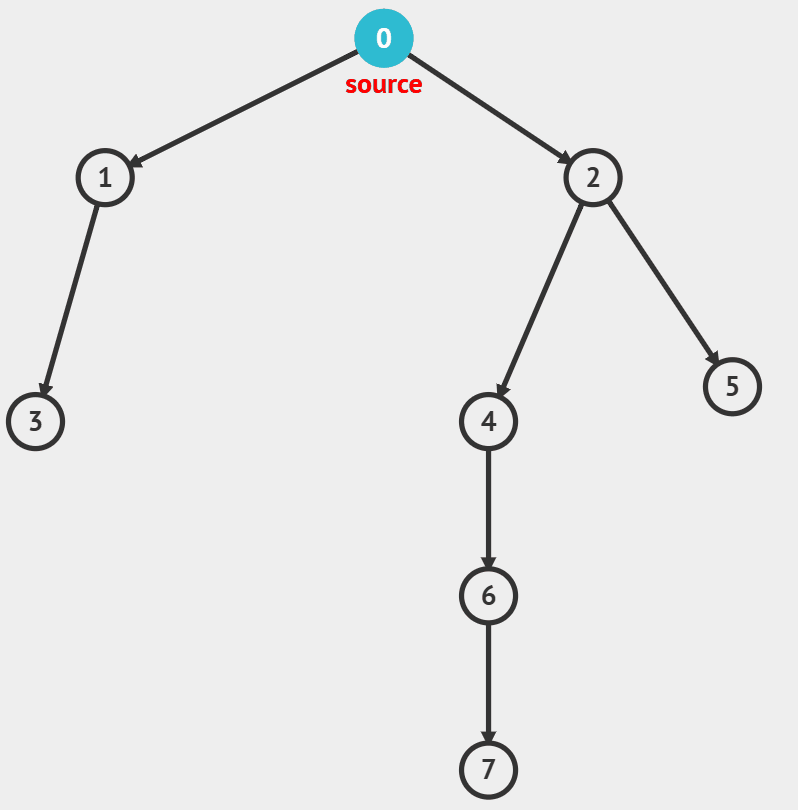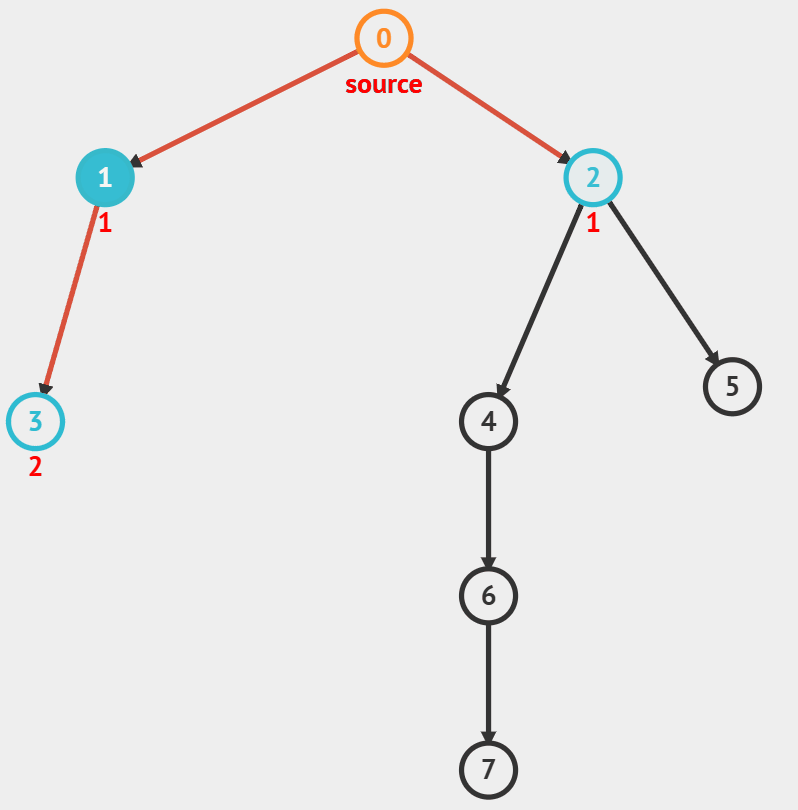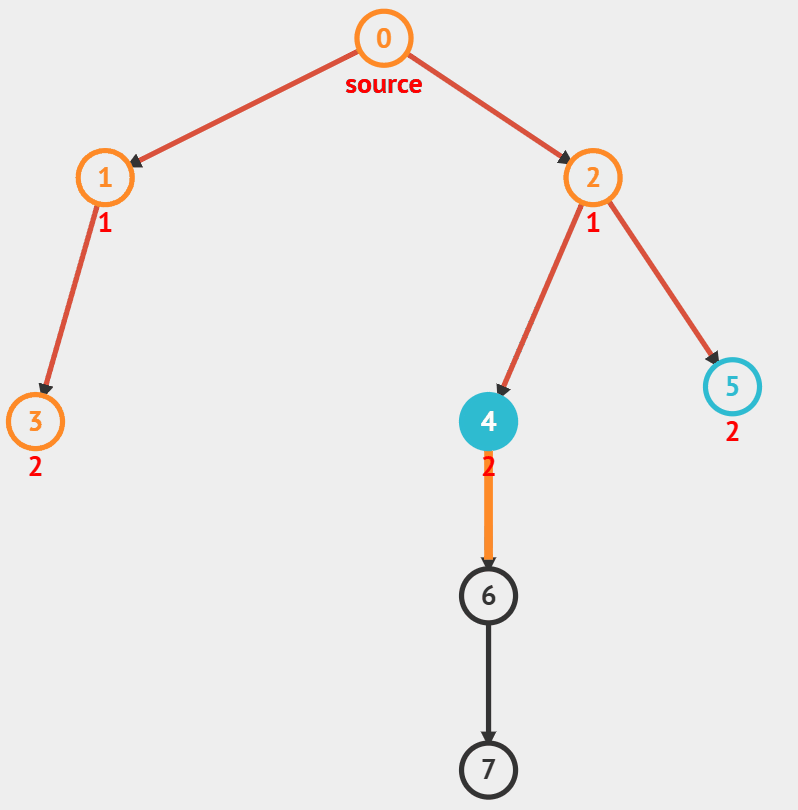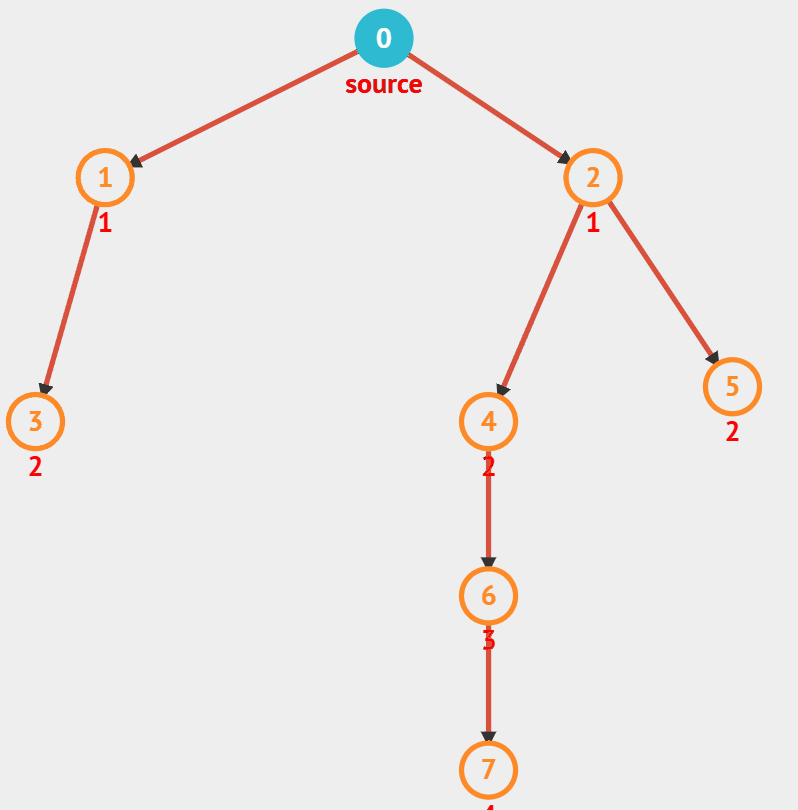
1) DFS
- 깊이 우선 탐색(Depth First Search), 말 그대로 갈 수 있는 최대 깊이까지 탐색하는 걸 우선으로 한다.
- 재귀 혹은 스택을 활용해서 구현한다.
- 모든 경로 방문, 특정 노드 사이의 경로 있는지 확인, 사이클이 있는지 확인
- stack이 빌 때까지 다음을 반복
- top을 가져온 후 pop
- top 정점의 방문여부를 확인
- 방문 하지 않은 경우
- 방문처리 후 top의 인접노드삽입 (삽입 순서는 조건에 따라서 ,오름차순으로 방문 원하면 큰거부터 넣어야)
- 방문 한 경우
- 아무것도 안함.
- 방문 하지 않은 경우
출처 : visualgo.net
- 재귀를 통한 DFS 구현
#include <iterator> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <unordered_map> using namespace std; unordered_map<int, vector<int>> adjList; vector<char> result; vector<bool> visited; void DFS(int start) { if (visited[start]) return; result.push_back(start + 'A'); visited[start] = true; for (auto& adjNode : adjList[start]) { DFS(adjNode); } } vector<char> solution(vector<pair<char, char>> graph, char start) { visited.resize(26,false); result = vector<char>(0); for (auto& [from, to] : graph) { adjList[from-'A'].push_back(to-'A'); } DFS(start-'A'); return result; } void init() { adjList.clear(); result.clear(); visited.clear(); } void print(vector<char> vec) { copy(vec.begin(), vec.end(), std::ostream_iterator<char>(cout, " ")); cout << endl; } int main() { //bool 반환할 때 true는 1, false는 0 입니다. print(solution({{'A', 'B'}, {'B', 'C'}, {'C', 'D'}, {'D', 'E'}}, 'A')); //출력값 : A B C D E init(); print(solution({{'A', 'B'}, {'A', 'C'}, {'B', 'D'}, {'B', 'E'}, {'C', 'F'}, {'E', 'F'}}, 'A')); //출력값 : A B D E F C return 0; }
2) BFS
- 너비 우선 탐색(Breadth First Search) 시작 노드에서 제일 가까운 노드들을 먼저 탐색한다.
- 큐를 활용해서 구현한다.
- 최단 경로
- queue가 빌 때까지 다음을 반복
- front를 가져온 후 pop
- front의 인접 노드들 중 방문하지 않은 노드가 있으면 방문 처리하고 삽입.(삽입 순서는 조건에 따라서)
출처 : visualgo.net
- BFS 구현
//아래 코드는 테스트 코드 입니다. #include <iterator> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <unordered_map> #include <unordered_set> #include <queue> using namespace std; unordered_map<int, vector<int>> adjList; vector<int> result; unordered_set<int> visited; void BFS(int start) { queue<int> q; q.push(start); visited.insert(start); result.push_back(start); while(!q.empty()) { int front = q.front(); q.pop(); for (auto& adj : adjList[front]) { if (visited.find(adj) == visited.end()) { visited.insert(adj); result.push_back(adj); q.push(adj); } } } } vector<int> solution(vector<pair<int,int>> graph, int start) { for (auto& [from, to] : graph) { adjList[from].push_back(to); } BFS(start); return result; } void init() { adjList.clear(); result.clear(); visited.clear(); } void print(vector<int> vec) { copy(vec.begin(), vec.end(), std::ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); cout << endl; } int main() { print(solution({{1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {3, 6}, {3, 7}, {4, 8}, {5, 8}, {6, 9}, {7, 9}}, 1)); //출력값 : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 init(); print(solution({{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {5, 0}}, 1)); //출력값 : 1 2 3 4 5 0 return 0; }
DFS와 BFS의 visited 처리 순서에 주의
- DFS는 다음에 방문할 노드를 삽입
- BFS는 지금 방문할 노드를 삽입
5. 최단 경로
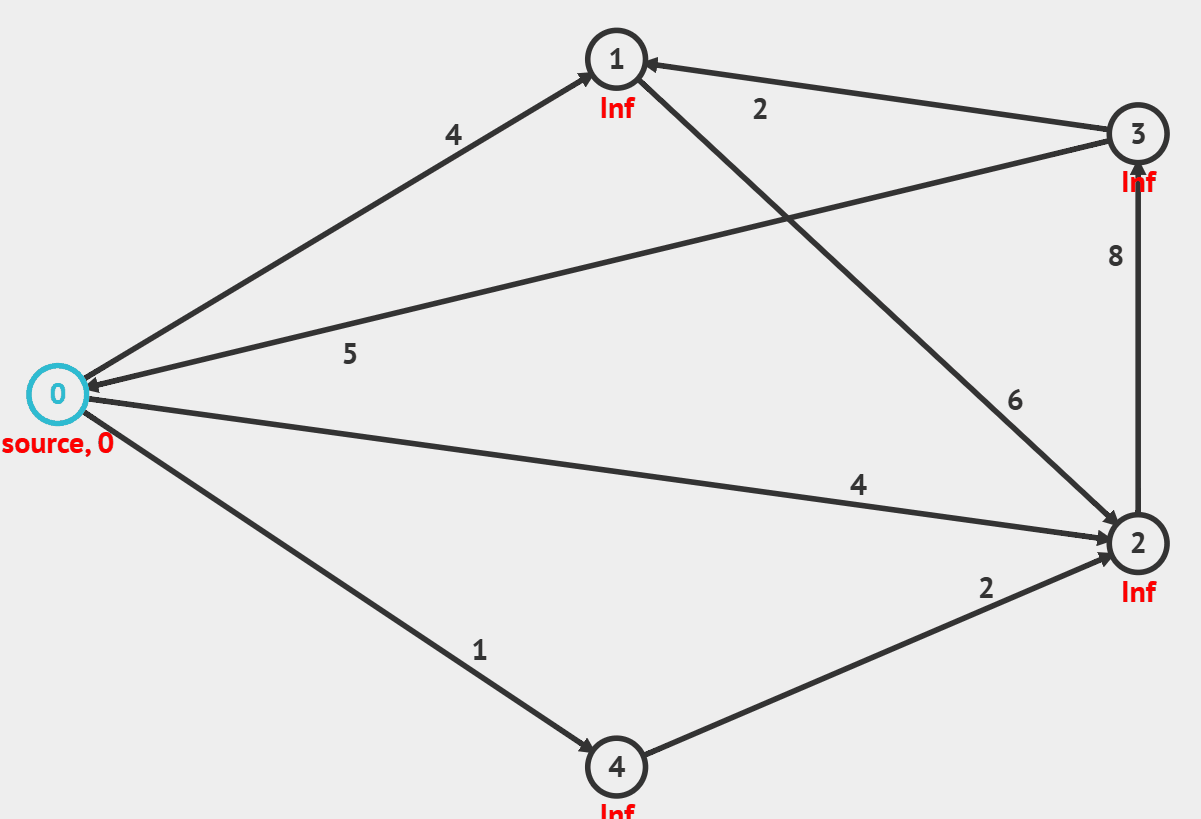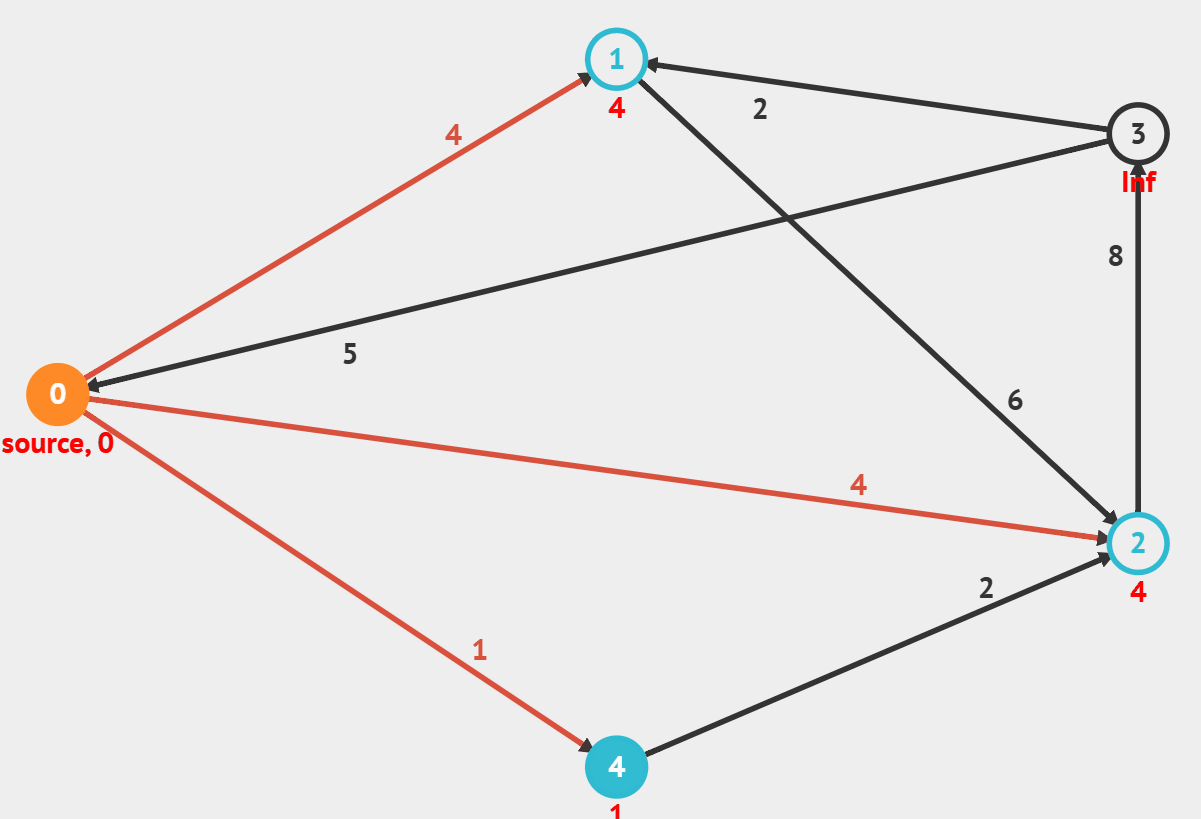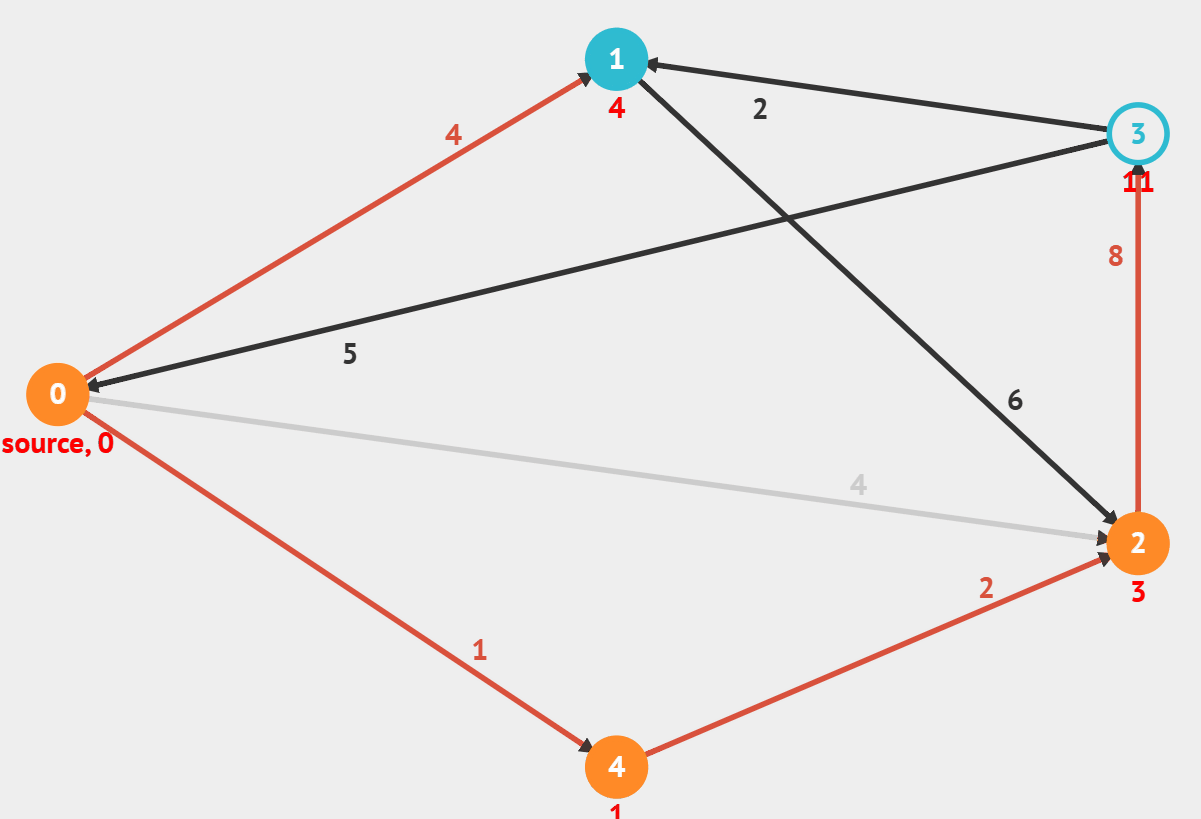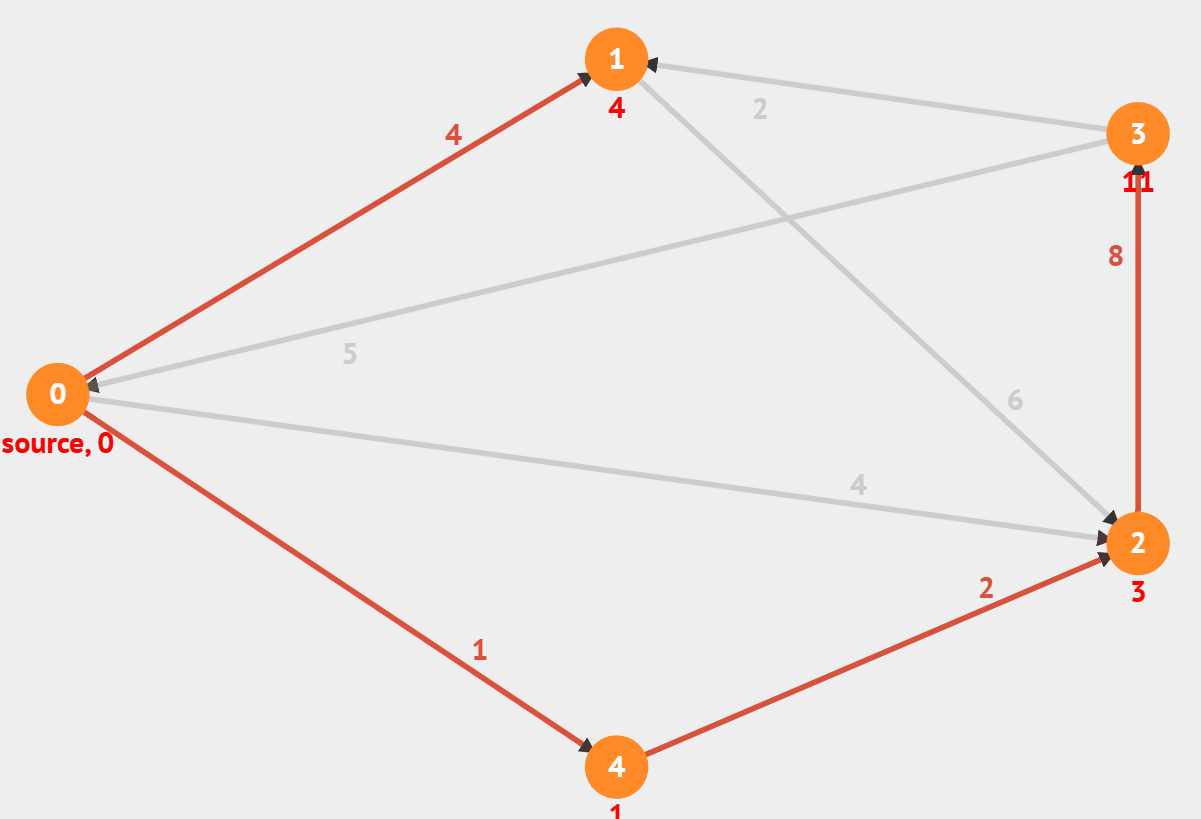
1) 다익스트라 (Dijkstra)
- 시작 노드에서 다른 모든 노드에 도달하는 최단 경로를 구하는 알고리즘
- 음의 가중치가 있는 경우 사용 불가
- 시작 노드 설정 ( 최소 비용 = 0, 직전 노드는 자기 자신)
- 나머지 노드들의 최소비용은 INF, 직전 노드 또한 INF
- 그래프에서 방문할 수 있는 노드중 현재까지의 최소 비용이 가장 작은 노드 선택.
- 해당 노드를 거쳐서 인접 노드에 가는 것과 기존의 경로 중 작은 값으로 갱신 (직전 노드도 갱신)
출처 : visualgo.net
#include <iterator> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <unordered_map> #include <queue> #include <climits> using namespace std; unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int, int>>> graph; vector<vector<int>> dijkstraVec; void Dijkstra(int start, int numNodes) { dijkstraVec.clear(); //[0] 시작점에서 i까지의 거리 //[1] i의 직전 노드 dijkstraVec.resize(numNodes, vector<int>(2, INT_MAX)); //최소비용 dijkstraVec[start][0] = 0; //직전 노드 dijkstraVec[start][1] = 0; vector<bool> visited(numNodes,false); auto cmp = [](const pair<int,int>& a, const pair<int,int>& b){ return a.first > b.first; }; // dist, 노드번호 priority_queue<pair<int,int>, vector<pair<int,int>>, decltype(cmp)> unVisited(cmp); unVisited.push({0, start}); // 거리 정보가 갱신된 노드만 q에 넣음 // 연결 그래프라면 모든 노드를 탐방 while(!unVisited.empty()) { auto& [dist, u] = unVisited.top(); unVisited.pop(); if (visited[u]) continue; visited[u] = true; for (auto& [v, weight] : graph[u]) { if (visited[v]) continue; if (dijkstraVec[v][0] > dist + weight) { dijkstraVec[v][0] = dist + weight; dijkstraVec[v][1] = u; unVisited.push({dijkstraVec[v][0], v}); } } } } vector<int> solution(int start, int numNodes, vector<tuple<int, int, int>> edges) { vector<int> answer; graph.clear(); for (auto& [from, to, weight] : edges) { graph[from].push_back({to, weight}); } Dijkstra(start, numNodes); for (auto& v : dijkstraVec) { answer.push_back(v[0]); } return answer; } void print(vector<int> vec) { copy(vec.begin(), vec.end(), std::ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); cout << endl; } int main() { print(solution(0, 3, {{0, 1, 9},{0, 2, 3},{1, 0, 5},{2, 1, 1}})); //출력값 : 0 4 3 print(solution(0, 4, {{0, 1, 1}, {1, 2, 5}, {2, 3, 1}})); //출력값 : 0 1 6 7 return 0; }
2) 벨만 포드 (Bellman - Ford)
- 시작 노드에서 다른 모든 노드에 도달하는 최단 경로를 구하는 알고리즘
- 다익스트라와 달리 매 단계마다 모든 간선의 최소비용 갱신
- 음의 사이클이 있는 경우 사용 불가.
- 시작 노드 설정 ( 최소 비용 = 0, 직전 노드는 자기 자신)
- 나머지 노드들의 최소비용은 INF, 직전 노드 또한 INF
- 다음을 노드개수 -1 만큼 반복
- 시작 노드 u에서 임의의 노드k를 거쳐서 다른 노드 v로 가는 경로 u->k->v 가 u->v보다 값이 작으면 정보 갱신
- 마지막으로 위의 과정을 한번 더 시행
- 만약 최소 값이 갱신되면 음의 사이클이 존재.
- 최소경로 보장 x
출처 : visualgo.net
#include <iterator> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <unordered_map> #include <unordered_set> #include <climits> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; unordered_set<int> allvertices; unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int,int>>> graph; // <minVAl,u> unordered_map<int, pair<int,int>> distAndUList; bool BellmanFord(int source) { for(auto& vertex : allvertices) { distAndUList[vertex] = make_pair(INT_MAX, INT_MAX); } distAndUList[source] = {0,0}; for (int i=0; i<allvertices.size()-1; i++) { // k = 거쳐갈 노드 for (auto& k : allvertices) { if (distAndUList[k].first == INT_MAX) continue; //u->k->v 와 비교해서 값 갱신 for (auto& [v, weight] : graph[k]) { if (distAndUList[v].first > distAndUList[k].first + weight) { distAndUList[v].first = distAndUList[k].first + weight; distAndUList[v].second = k; } } } } // k = 거쳐갈 노드 for (auto& k : allvertices) { //u->k->v 와 비교해서 값 갱신 for (auto& [v, weight] : graph[k]) { if (distAndUList[k].first == INT_MAX) continue; //u->k->v 와 비교해서 값 갱신 if (distAndUList[v].first > distAndUList[k].first + weight) { return false; } } } return true; } vector<int> solution(int num_vertices, vector<tuple<int, int, int>> edges, int source) { vector<int> answer; // 간선을 정보를 통해서 그래프의 구조 파악 for(auto& [from, to, weight] : edges) { allvertices.insert(from); allvertices.insert(to); graph[from].push_back({to, weight}); } bool belowZeroCycle = !BellmanFord(source); vector<pair<int, int>> sortedDist; for (auto& [v, data] : distAndUList) { sortedDist.push_back({v, data.first}); // v: 정점 번호, data.first: 거리 } sort(sortedDist.begin(), sortedDist.end()); // v 기준 정렬 if (!belowZeroCycle) { for (auto& [u , dist] : sortedDist) { answer.push_back(dist); } } else { answer.push_back(-1); } return answer; } void print(vector<int> vec) { copy(vec.begin(), vec.end(), std::ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); cout << endl; } int main() { print(solution(5, {{0, 1, 4}, {0, 2, 3}, {0, 4, -6}, {1, 3, 5}, {2, 1, 2}, {3, 0, 7}, {3, 2, 4},{4, 2, 2}}, 0)); //출력값 : 0 -2 -4 3 -6 print(solution(4, {{0, 1, 5}, {0, 2, -1}, {1, 2, 2}, {2, 3,-2}, {3, 0, 2}, {3, 1, 6}}, 0)); //출력값 : -1 return 0; }
3) 플로이드 워셜 (Floyd-Warshall)
- 위의 2가지 방법은 시작 노드를 설정하고 최단 거리를 찾는다.
- 플로이드 워셜은 모든 노드간의 최소 경로를 구해준다.
//아래 코드는 테스트 코드 입니다. #include <iterator> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <unordered_map> #include <unordered_set> #include <climits> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; unordered_set<int> allvertices; unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int,int>>> graph; vector<vector<int>> distanceMatrix; int n = 0; void FW() { distanceMatrix.resize(n, vector<int>(n,INT_MAX)); for (int i=0; i<n; i++) { distanceMatrix[i][i] = 0; } for(auto& [from, data] : graph) { for (auto& [to, weight] : data) { distanceMatrix[from][to] = weight; } } for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j=0; j < n; j++) { if (distanceMatrix[i][k] != INT_MAX && distanceMatrix[k][j] != INT_MAX) { distanceMatrix[i][j] = min(distanceMatrix[i][j], distanceMatrix[i][k] + distanceMatrix[k][j]); } } } } } vector<int> solution(vector<tuple<int, int, int>> edges) { graph.clear(); allvertices.clear(); distanceMatrix.clear(); n = 0; vector<int> answer; // 간선을 정보를 통해서 그래프의 구조 파악 for(auto& [from, to, weight] : edges) { if(allvertices.insert(from).second) n++; if(allvertices.insert(to).second) n++; graph[from].push_back({to, weight}); } FW(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 음수 사이클 존재 if (distanceMatrix[i][i] < 0) { answer.push_back(-1); return answer; } } vector<int> temp(allvertices.begin(), allvertices.end()); sort(temp.begin(), temp.end()); // 값을 확인하기 위한 출력코드 int source = 0; for (int v : temp) { answer.push_back(distanceMatrix[source][v] == INT_MAX ? -1 : distanceMatrix[source][v]); } return answer; } void print(vector<int> vec) { copy(vec.begin(), vec.end(), std::ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " ")); cout << endl; } int main() { print(solution({{0, 1, 4}, {0, 2, 3}, {0, 4, -6}, {1, 3, 5}, {2, 1, 2}, {3, 0, 7}, {3, 2, 4},{4, 2, 2}})); //출력값 : 0 -2 -4 3 -6 print(solution({{0, 1, 5}, {0, 2, -1}, {1, 2, 2}, {2, 3,-2}, {3, 0, 2}, {3, 1, 6}})); //출력값 : -1 return 0; }