https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
You are given the heads of two sorted linked lists
list1andlist2.
Merge the two lists into one sorted list. The list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Return the head of the merged linked list.
접근 방법 (iteration)
- 리턴값으로 사용할
merge연결 리스트를 만들고,list1,list2비교해 둘 중 작은val을 가지는 노드를merge에 넘겨주고 넘겨준 리스트의 포인터를 다음 노드로 옮기는 작업을 반복한다.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
# iterative
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
merge = head = ListNode()
while list1 and list2:
if list1.val <= list2.val:
list1, merge.next, merge = list1.next, list1, list1
else:
list2, merge.next, merge = list2.next, list2, list2
merge.next = list1 if list1 else list2
return head.next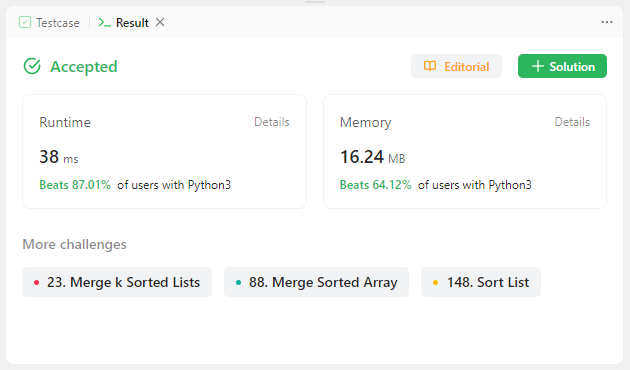
-
merge연결 리스트를 하나 선언하고,head포인터로 그 리스트의 맨 앞 부분을 가리키게 선언하였다. -
두 리스트로 반복문을 돌려 각 노드의 값을 비교하고, 작은 값을 갖는 노드를
merge.next에 연결한 후에merge와 해당 리스트의 포인터를 모두 뒤로 이동하는 방법을 사용했다. -
둘 중 한 리스트가 모두 병합되어 포인터가
None을 가리키면,if문을 사용하여 어느 리스트가 비었는지 체크한 후 남은 리스트를merge의 뒷부분에 연결시켜주었다.
접근 방법 (recursion)
- 교재를 참고해보니, 주어진 두 리스트가 정렬되어 있다는 점에서 착안하여 병합 정렬에서 마지막 두 리스트를 병합하는 방식으로 접근한 것을 확인하였다.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
# recursive
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not list2:
return list1
elif not list1 or list1.val > list2.val:
list1, list2 = list2, list1
list1.next = self.mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2)
return list1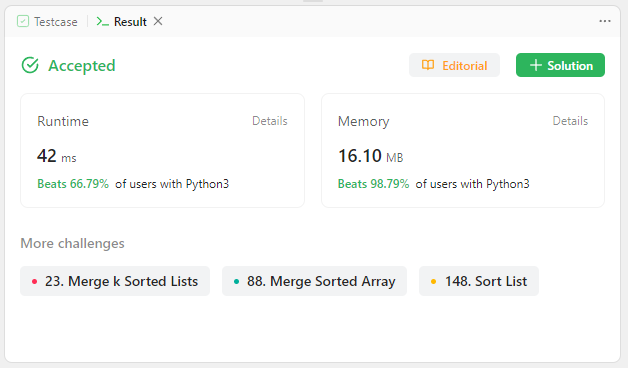
list1을 기준으로 삼고, 두 리스트가 가리키는 노드의 값을 비교하여list1이list2보다 클 경우 두 리스트를 스왑한 후,list1.next와list2를 매개변수로 하는 자기 자신을 호출하여 재귀적으로 해결하는 것을 볼 수 있었다.