QA MRC 모델 성능향상을 위해 각종 retrieval 모델을 구현해보며 알게된 점들을 정리하려고 한다.
1. 기본 개념
1.1 TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency)

- Term Frequency (TF): 특정 단어가 문서 내에서 얼마나 자주 나타나는지를 측정한다. 이 값이 높을수록 해당 단어가 문서에서 중요하다고 간주된다.
- Inverse Document Frequency (IDF): 특정 단어가 전체 문서 집합에서 얼마나 드물게 나타나는지를 측정한다. 드물게 나타나는 단어는 더 중요한 단어로 간주된다.
모든 문서에서 등장하는 단어는 중요도가 낮으며, 특정 문서에서만 자주 등장하는 단어는 중요도가 높다.
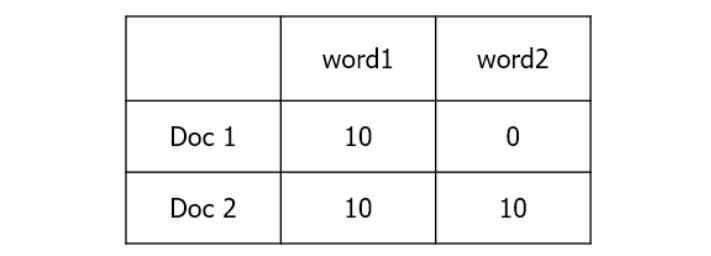
위의 예시에서 word1은 doc1, doc2에 모두 10회 등장하지만 doc1에서 상대적 중요도가 높다고 볼 수 있다.
IDF는 DF의 역수(1/DF)이다. DF는 전체 문서들 중에서 해당 문서를 제외한 나머지 문서에서 해당 단어가 몇 번 사용되었는지를 의미한다.

1.2 TF-IDF 계산해보기
아래 표를 보고 계산해보자.
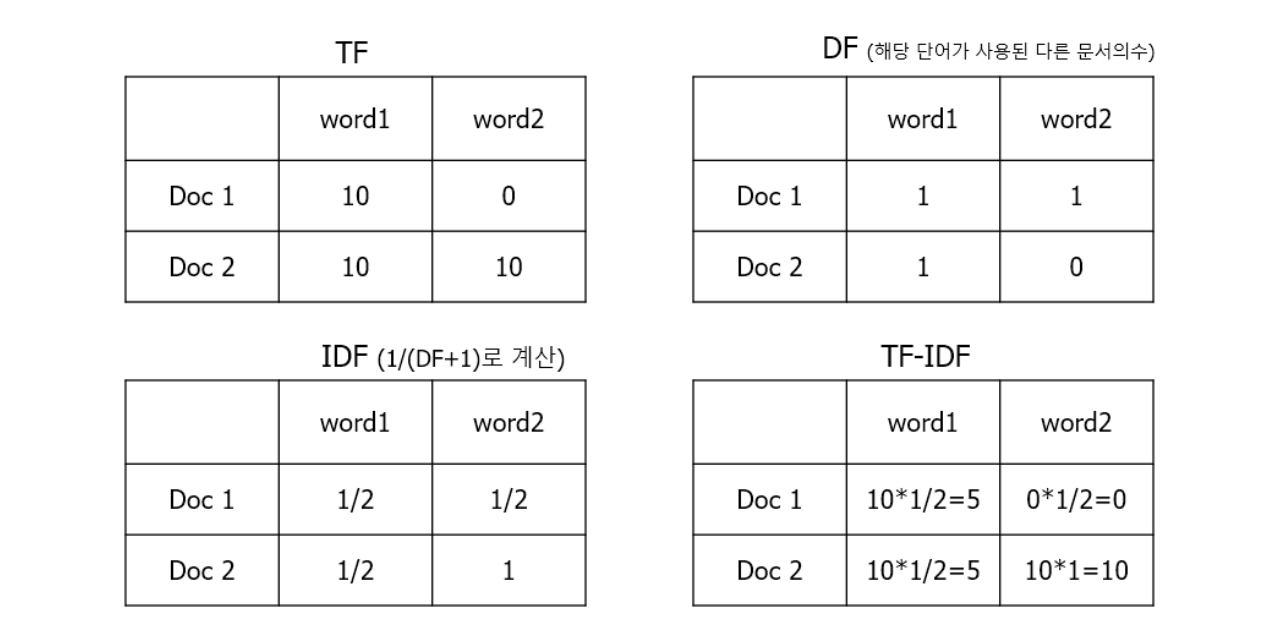
✔ DF 표
-
word1 의 경우 Doc1 입장에서 다른 문서(Doc2)에도 사용되었기 때문에 DF=1
-
word2의 경우 Doc1 입장에서 Doc2에 사용되었기 때문에 DF=1, Doc2 입장에서는 Doc1에 사용되지 않았기 때문에 0.
IDF를 계산할 때에는 분모가 0이 되는 것을 방지하기 위해서 1을 더하고, 로그를 취한다.
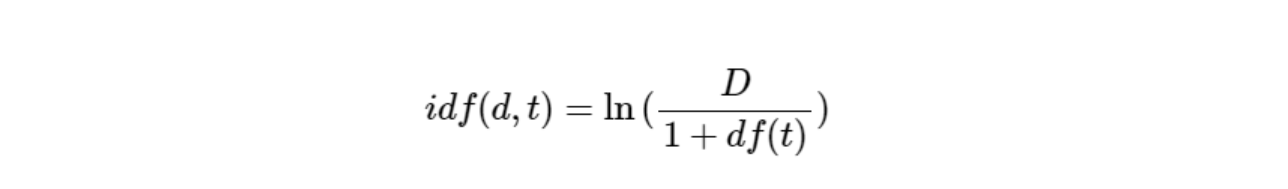
최종값은 tf x idf 로 계산된다.
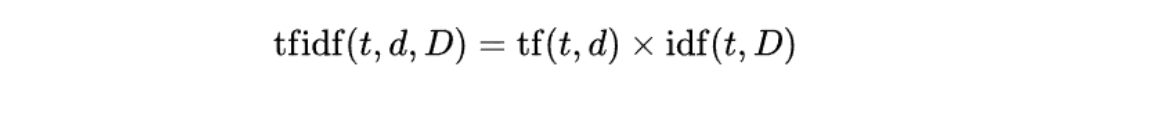
2. TF-IDF 코드
import json
import os
# 더미 데이터 생성
dummy_data = {
"1": {"text": "This is a sample document about AI."},
"2": {"text": "Machine learning is a subset of AI."},
"3": {"text": "Deep learning uses neural networks."},
"4": {"text": "Natural language processing is important in AI."},
"5": {"text": "Computer vision is another field of AI."}
}
# 데이터 저장
os.makedirs("data", exist_ok=True)
with open("data/wikipedia_documents.json", "w") as f:
json.dump(dummy_data, f)import json
import os
import pickle
import time
import random
from contextlib import contextmanager
from typing import List, NoReturn, Optional, Tuple, Union
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
seed = 2024
random.seed(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
@contextmanager
def timer(name):
t0 = time.time()
yield
print(f"[{name}] done in {time.time() - t0:.3f} s")
def tokenize_fn(text):
return text.split()
class TFIDFSparseRetrieval:
def __init__(
self,
tokenize_fn,
data_path: Optional[str] = "data/",
context_path: Optional[str] = "wikipedia_documents.json",
) -> NoReturn:
self.data_path = data_path
with open(os.path.join(data_path, context_path), "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
wiki = json.load(f)
self.contexts = list(dict.fromkeys([v["text"] for v in wiki.values()]))
print(f"Lengths of unique contexts : {len(self.contexts)}")
self.ids = list(range(len(self.contexts)))
#TF-IDF 벡터라이저 초기화
# tokenizer: 텍스트를 토큰화하는 함수
# ngram_range: (1, 2)는 단일 단어와 두 단어의 조합을 모두 고려
# max_features: 사용할 최대 특성(단어) 수를 50,000개로 제한
self.tfidfv = TfidfVectorizer(
tokenizer=tokenize_fn, ngram_range=(1, 2), max_features=50000,
)
self.p_embedding = None
self.indexer = None
def get_sparse_embedding(self) -> NoReturn:
pickle_name = f"sparse_embedding.bin"
tfidfv_name = f"tfidv.bin"
emd_path = os.path.join(self.data_path, pickle_name)
tfidfv_path = os.path.join(self.data_path, tfidfv_name)
# 이전에 저장된 TF-IDF 임베딩과 벡터라이저가 있으면 로드
if os.path.isfile(emd_path) and os.path.isfile(tfidfv_path):
with open(emd_path, "rb") as file:
self.p_embedding = pickle.load(file)
with open(tfidfv_path, "rb") as file:
self.tfidfv = pickle.load(file)
print("Embedding pickle load.")
else:
# 문서 컬렉션(self.contexts)에 대해 TF-IDF 변환 수행
print("Build passage embedding")
self.p_embedding = self.tfidfv.fit_transform(self.contexts)
print(self.p_embedding.shape)
# TF-IDF 임베딩과 벡터라이저를 파일로 저장
with open(emd_path, "wb") as file:
pickle.dump(self.p_embedding, file)
with open(tfidfv_path, "wb") as file:
pickle.dump(self.tfidfv, file)
print("Embedding pickle saved.")
def retrieve(
self,
query_or_dataset: Union[str, List], # 검색할 쿼리 또는 쿼리 리스트
topk: Optional[int] = 1 # 반환할 상위 문서의 개수
) -> Union[Tuple[List, List], pd.DataFrame]:
assert self.p_embedding is not None, "get_sparse_embedding() 메소드를 먼저 수행해줘야합니다."
if isinstance(query_or_dataset, str):
doc_scores, doc_indices = self.get_relevant_doc(query_or_dataset, k=topk)
print("[Search query]\n", query_or_dataset, "\n")
# 상위 k개의 문서에 대한 정보 출력
for i in range(topk):
print(f"Top-{i+1} passage with score {doc_scores[i]:4f}")
print(self.contexts[doc_indices[i]])
return (doc_scores, [self.contexts[doc_indices[i]] for i in range(topk)])
elif isinstance(query_or_dataset, list):
total = []
with timer("query exhaustive search"):
doc_scores, doc_indices = self.get_relevant_doc_bulk(
query_or_dataset, k=topk
)
for idx, example in enumerate(
tqdm(query_or_dataset, desc="Sparse retrieval: ")
):
tmp = {
"question": example,
"id": idx,
"context": " ".join(
[self.contexts[pid] for pid in doc_indices[idx]]
),
}
total.append(tmp)
return pd.DataFrame(total)
def get_relevant_doc(self, query: str, k: Optional[int] = 1) -> Tuple[List, List]:
# 쿼리를 TF-IDF 벡터로 변환
with timer("transform"):
query_vec = self.tfidfv.transform([query])
assert (
np.sum(query_vec) != 0
), "오류가 발생했습니다. 이 오류는 보통 query에 vectorizer의 vocab에 없는 단어만 존재하는 경우 발생합니다."
with timer("query ex search"):
result = query_vec * self.p_embedding.T
if not isinstance(result, np.ndarray):
result = result.toarray()
# 각 쿼리에 대해 유사도 점수로 문서 정렬
sorted_result = np.argsort(result.squeeze())[::-1]
doc_score = result.squeeze()[sorted_result].tolist()[:k]
doc_indices = sorted_result.tolist()[:k]
return doc_score, doc_indices
def get_relevant_doc_bulk(
self, queries: List, k: Optional[int] = 1
) -> Tuple[List, List]:
query_vec = self.tfidfv.transform(queries)
assert (
np.sum(query_vec) != 0
), "오류가 발생했습니다. 이 오류는 보통 query에 vectorizer의 vocab에 없는 단어만 존재하는 경우 발생합니다."
# 쿼리 벡터와 문서 임베딩 간의 내적 계산
result = query_vec * self.p_embedding.T
if not isinstance(result, np.ndarray):
result = result.toarray()
doc_scores = []
doc_indices = []
for i in range(result.shape[0]):
sorted_result = np.argsort(result[i, :])[::-1]
doc_scores.append(result[i, :][sorted_result].tolist()[:k])
doc_indices.append(sorted_result.tolist()[:k])
return doc_scores, doc_indices
# 실행 예시
retriever = TFIDFSparseRetrieval(tokenize_fn)
retriever.get_sparse_embedding()
# 단일 쿼리 테스트
single_result = retriever.retrieve("What is AI?", topk=2)
print("\nSingle query result:")
print(single_result)
# 다중 쿼리 테스트
multi_result = retriever.retrieve(["What is machine learning?", "Explain deep learning"], topk=2)
print("\nMulti query result:")
print(multi_result)결과
Lengths of unique contexts : 5
Build passage embedding
(5, 50)
Embedding pickle saved.
[transform] done in 0.001 s
[query ex search] done in 0.001 s
[Search query]
What is AI?
Top-1 passage with score 0.179151
Machine learning is a subset of AI.
Top-2 passage with score 0.170358
Computer vision is another field of AI.
Single query result:
([0.17915084430495923, 0.17035763308351742], ['Machine learning is a subset of AI.', 'Computer vision is another field of AI.'])
[query exhaustive search] done in 0.002 s
/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/sklearn/feature_extraction/text.py:521: UserWarning: The parameter 'token_pattern' will not be used since 'tokenizer' is not None'
warnings.warn(
Sparse retrieval: 100%
2/2 [00:00<00:00, 31.56it/s]
Multi query result:
question id \
0 What is machine learning? 0
1 Explain deep learning 1
context
0 Machine learning is a subset of AI. Computer v...
1 Deep learning uses neural networks. Machine le... TfidfVectorizer
- 문서 집합을 TF-IDF 행렬로 변환한다.
- 문서를 벡터화하고 각 단어의 중요도를 계산한다.
- fit() 메서드로 어휘를 학습하고, transform() 메서드로 문서를 벡터화한다.
get_sparse_embedding()
- 전체 문서 집합에 대해 TF-IDF 임베딩을 생성하고 저장한다.
- TfidfVectorizer를 사용하여 문서를 벡터화한다.
- 생성된 임베딩을 나중에 검색에 사용할 수 있도록 저장한다.
retrieve()
- 실제 검색 기능을 수행하는 메인 메서드이다.
- 단일 쿼리 또는 여러 쿼리에 대해 관련 문서를 검색한다.
- get_relevant_doc() 또는 get_relevant_doc_bulk()를 호출하여 검색을 수행한다.
get_relevant_doc()
- 단일 쿼리에 대해 관련 문서를 검색한다.
- 쿼리를 TF-IDF 벡터로 변환하고 문서 임베딩과의 유사도를 계산한다.
get_relevant_doc_bulk()
- 여러 쿼리에 대해 한 번에 관련 문서를 검색한다.
- 모든 쿼리를 TF-IDF 벡터로 변환하고 문서 임베딩과의 유사도를 계산한다.
TF-IDF는 문서 내 단어의 상대적 중요도를 측정하는 기법이다.
TF(Term Frequency): 특정 단어가 한 문서에서 등장하는 빈도를 의미한다.
DF(Document Frequency): 특정 단어가 여러 문서 중 몇 개의 문서에 등장했는지를 나타낸다.
IDF(Inverse Document Frequency): DF의 역수를 취한 값으로, 특정 단어가 전체 문서에서 얼마나 희소한지를 나타낸다.
TF만 사용할 경우 "그리고", "있다" 같은 단어가 자주 등장하는 문서에서 중요하다고 판단될 수 있다. 반대로, IDF는 특정 문서에서만 등장하는 단어의 가치를 높게 평가하여 불필요한 단어의 영향을 줄인다.
결국, TF-IDF를 사용하면 문서에서 중요한 키워드를 추출하거나, 검색 엔진에서 문서의 연관도를 계산하는 데 유용하게 활용할 수 있다.
