1. Principles of network applications
creating a network app
- application layer를 제외한 layer들은 OS에 이미 내장된 기능들이다.
- transport, network, link, physical layer는 network-core device 이므로 구현할 필요 없다.
- 데이터를 생성 소비하는 대상이 아니라 배달해주는 역할
Client-server paradigm vs P2P
- Client-server paradigm
- server
- 항상 host의 역할
- 영구적인 IP
- scaling을 위해 data center에 존재
- client
- server와 통신
- 동적인 IP : 내가 쓰지 않을때는 다른 유저들이 써야하기 때문에
- 각 client끼리 직접 통신하지 않음
- ex) HTTP, IMAP, FTP
- server
- Peer-peer architecture
- 영구적인 server가 존재하지 않음
- 내가 client가 되기도 하고 server가 되기도 한다.
- self scalability
- 각 peer 끼리 간헐적으로 연결되며, IP 주소도 바뀐다.
Processes communicating
- process
- host 내에서 동작하는 프로그램
- host 내에서는 inter-process communication을 통해 process가 통신한다.
- host간의 통신은 message를 통해서 이루어진다.
- client process : communication 시작
- server process : contact wait
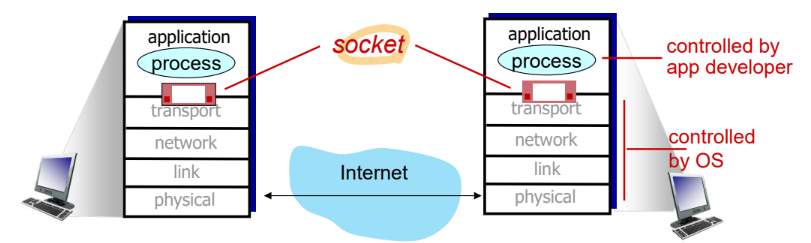
Sockets
- socket을 프로그래밍해서 어떤 방식으로 데이터를 socket에 전달하고 socket으로 온 data를 어떻게 가져올지를 만든다.
- socket이 core device와 통하는 문
- application에 있는 process가 data의 최종 도착지이자 data 생성지이다.
Addressing processes
- message를 받기 위해서 process는 identifier를 가지고 있어야 한다.
- Identifier
- IP address와 port number를 가진다.
- IP address는 host에 대한 정보
- port number는 process에 대한 정보
- HTTP : 80
- mail server : 25
Application-layer protocol defines
- types of messages
- message syntax, semantics
- rules,
- open protocols
What transport service does an app need?
- data integrity : 데이터가 깨져도 되는지 안되는지
- 깨져도 괜찮은 것의 예시는 audio streaming
- 깨진 데이터를 network source에서 data를 요구하면 실시간성이 떨어진다. 그냥 loss 하는 것이 효율적이다.
- timing : 실시간성(low delay)
- throughput : 중간에 끊기면 안된다.
- security
Internet transport protocols services (중요!)
- TCP service
- reliable transport : 손실 발생 안함
- flow control : 보내는 양을 알아서 조절
- congestion control : 혼잡 발생 안함
- connection-oriented : 연결 지향
- does not provide timing, minimum throughput guarantee, security
- UDP service
- unreliable data transfer : 중간에 문제 발생해도 복구나 재전송 x
- does not provide reliablility, flow control, congestion, timing, throughput, connection setup, security
2. Web and HTTP
HTTP overview
- HTTP HyperText Transfer Protocol
- web's application protocol
- client server model
- client가 server에게 request 요청하고 server가 해당 request에 해당하는 object를 reponse해준다.
- HTTP uses TCP
- client가 TCP connection 요청
- server의 응답
- HTTP message: browser(HTTP client)와 web server(HTTP server)간에 교환
- HTTP is "Stateless"
- server는 과거 client 요청에 대한 정보를 기억하지 않는다.
HTTP connections: two types
- No-persistent HTTP
- object 하나 보내고 연결 닫기
- persistent HTTP
- 하나의 tcp에서 object 여러 개 보내기
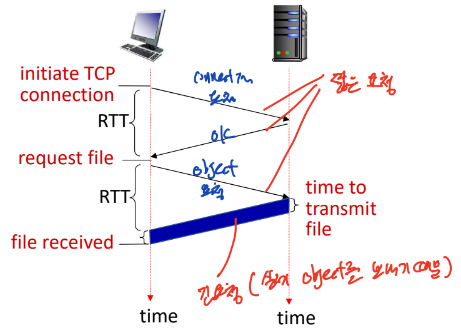
Non-persistent HTTP: response time
- RTT(Round Trip Time)
- 작은 packet이 client에서 server로 갔다가 돌아오는 시간
- Non-persistent HTTP response time = file 보내는 시간(긴 요청)
Persistent HTTP
Maintaining user/server state : cookies
- HTTP 는 stateless하다.
- cookie를 사용해서 이전의 요청을 기억할 수 있다.
- authorization : 인증절차
- shopping carts
- recomendations : 추천
- user session state
Web caches (proxy servers)
- Goal: client의 request를 origin 서버까지 가지 않고 주기
- 장점
- response time 줄이기
- traffic 줄이기 : origin server 과부화 방지
- 과정
- 중간에 proxy 서버를 두고 client의 요청이 들어오면 먼저 proxy server가 cache hit 하는지 확인
- cache hit이 발생하면 바로 response
- 발생 안하면 origin server로 request 하기
- Cache는 ISP에 설치
- 이유는 proxy server는 사용자와 가까이 존재해야 하기 때문이다.
3. E-mail, SMTP, IMAP
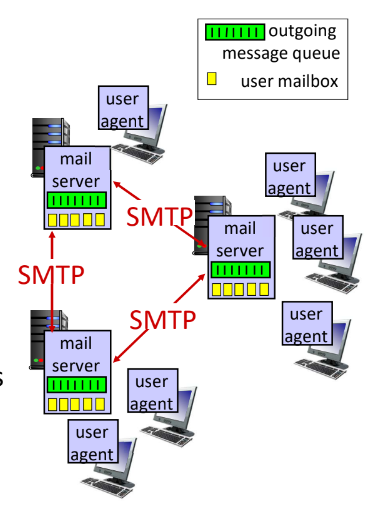
- 3가지 구성요소
- user agents
- mail servers
- 들어오는 message는 user mail box에 저장
- 나가는 message는 outgoing message queue에 저장
- simple mail transfer protocol : SMTP
- the RFC(5321)
- TCP 쓴다 -> 안정적이니까 (port 25)
- 동작 단계
- handshaking(greeting)
- transfer of messages
- closure
- Mail access protocols
- SMTP : sender에서 receiver 의 server까지의 protocol
- push 프로토콜!
- IMAP, HTTP : receiver server에서 receiver로 가는 protocol
- pull 프로토콜! (mail server에서 agent로 갈때 SMTP를 쓸 수 없는 이유)
- IMAP (Internet Mail Access Protocol-RFC 3501)
- HTTP : web based interface on top of STMP, IMAP
- SMTP : sender에서 receiver 의 server까지의 protocol
4. The Domain Name System DNS
DNS : Domain Name System
- 웹 서버 주소를 IP 주소로 바꿔주는 역할
- IP 주소는 컴퓨터가 이해하는 주소이고 웹 서버 주소는 사람이 이해하는 주소
- 많은 양의 데이터 가지고 있어서 해결책 필요!
- distributed database : 분산 시스템 -> central은 고장나면 한방에 다 가버림
- application-layer protocol : 계층 시스템
DNS: services, structure
- DNS services
- host aliasing
- host 이름이 어려운 경우 별칭을 가질 수 있다.
- load distribution
- 웹 서버가 여러 IP를 쓰는 경우
- 요청이 여러번 들어올 때 다른 IP로 분산시켜서 과부화 방지하기
- host aliasing
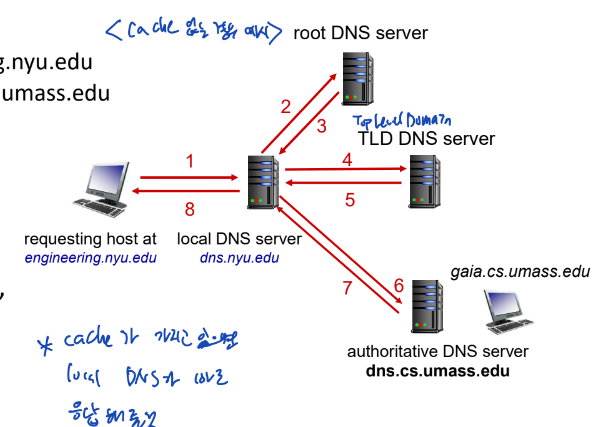
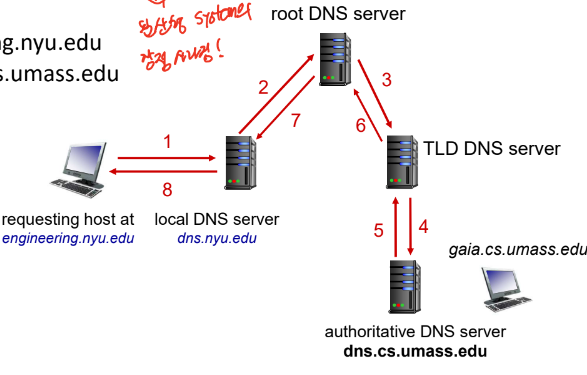
DNS: a distributed, hierarchical database
- Root->Top Level Domain->Authoritative
Local DNS name servers
- 위에서 말한 계층 구조에 속하지 않는다.
- local cache를 이용해서 Top Level(root) 까지 가는 것 방지
- proxy랑 비슷함
DNS name resolution
- iterated query
- local DNS가 cache hit 발생하면 응답해주기
- recursive query
- iterative가 더 좋은 방식임 -> recursive의 경우는 root가 가장 큰 오버헤드를 받기 때문에 분산형 시스템의 장점이 사라진다.
5. P2P applications
- 생략
6. Video streaming and content distribution networks
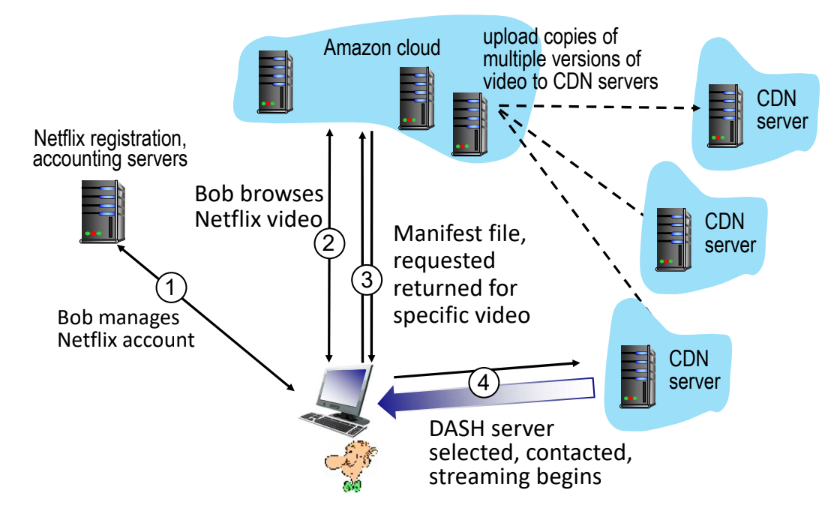
Video Streaming and CDNs
- stream video traffic : 일반 사람들이 많이 쓴다.
- challenge
- scale (확장성) : 매우 큰 사용자 수
- heterogeneity (이질성) : 디바이스마다 성능이 다르다
- solution
- distributed
- application-level infrastructure
Multimedia: video
- video는 순차적인 이미지의 모음이다
- 영상 내 및 영상 간 중복을 사용하여 영상 부호화에 사용되는 비트 수를 줄이기..
- spatial : 이미지의 한 픽셀 주변 픽셀의 data는 유사하다.
- temporal : frame i와 frame i+1의 data는 유사하다
- CBR (constant bit rate)
- encoding rate 일정
- 축구 경기 처럼 frame간 차이가 큰 영상에는 쓰기 어렵다.
- VBR (variable bit rate)
- encoding rate 변화
- 이 경우에 bandwidth는 대체로 평균값과 최댓값의 사이값으로 설정
Streaming stored video
- 구조
- video server -> Internet -> Client
- 위 구조를 사용하면 Internet은 server와 client간의 독점적인 link가 아니다!
- 서버와 클라이언트 간 대역폭이 시간이 지남에 따라 달라지며, 네트워크 congestion 수준이 변한다.
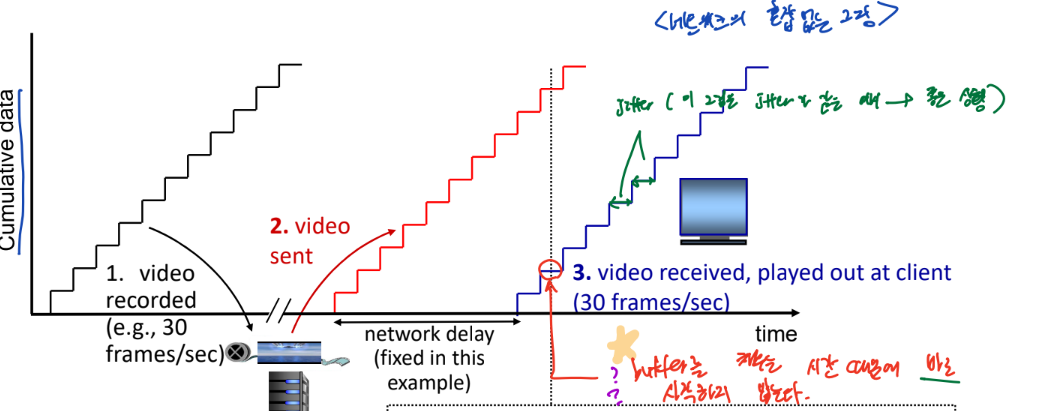
- 이상적인 상황의 그림
- Jitter의 간격이 같다
- jitter : packet delay variations
- Jitter의 간격이 같다
참고사항
- Queue라는 구조가 존재하는 이유
- 서버의 서비스 능력과 입출력 능력 간의 차이가 있기 때문
- 서버의 능력보다 입출력이 항상 크면 queue가 필요 없다!
- 기본적으로 입출력 < 처리할 데이터 이다
- buffer 를 채우는 시간?
- 이상적인 상황의 그림에서 계단식인 이유는 buffer의 용량이 1이라고 했을 때 이 1을 다 채워야 동작하기 때문
- 이 시간동안 동영상에 빙글빙글 도는 로딩화면이 나오는 것
- 해결책 : playout buffer
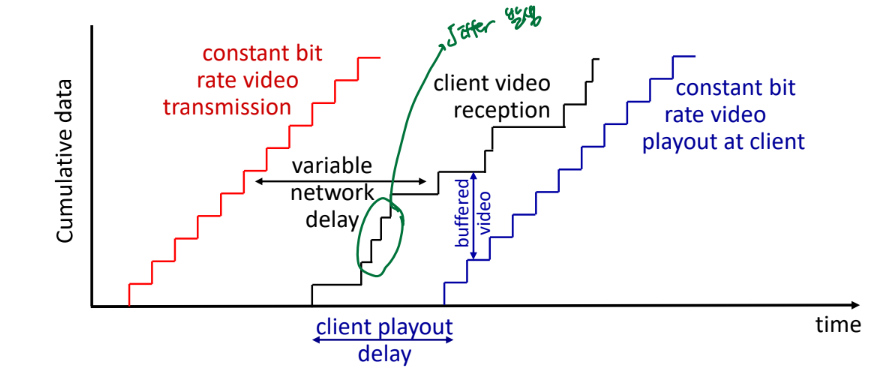
playout buffering
- client side buffer and playout delay
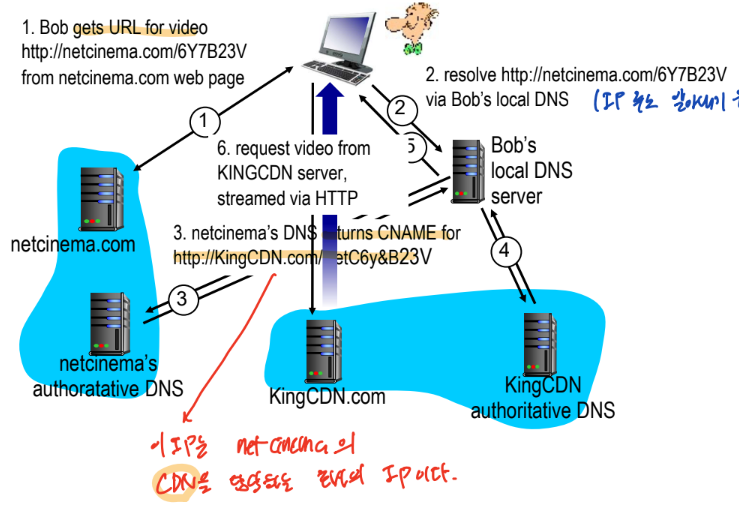
Streaming multimedia : DASH
- DASH(Dynamic, Adaptive Streaming over HTTP
- server
- 다양한 사이즈로 encoding
- manifest file : encoding 된 정볼르 저장
- client
- client가 어떤 encoding으로 받아들이지를 정한다!
- manifest file을 확인해서 상황에 받는 것을 가져온다
- Intelligence at client : client가 아래 세가지를 어떤 것으로 할지 결정하는것
- When
- What encoding rate
- Where
- intelligence가 server에 있다면 과부화 발생할것임
- Streaming video = encoding + DASH + playout buffering
- server
Content distribution networks(CDNs)
- 각 스트리밍 서비스가 자신만의 server를 가지고 제공하는 것
- challenge : 엄청나게 많은 유저들에게 로딩 없이 보내는 것이 목표
- option 1 : single large server
- 한방에 고장, congestion 문제, scalability 낮음
- option 2 : CDN
- store/serve multiple copies
- 종류
- enter deep : access network 안에 server 설치
- bring home : ISP에 server 설치
- option 1 : single large server
- 동작 방식