Level 29 : DFS 응용
인접리스트
1)트리
2)그래프
어디갈때?
1)갔었는지 확인, 체크하고 간다
2)안갔으면 고고
DFS 복습!
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>>v(6);
string val = "ABTRCV";
void run(int now) {
cout << val[now] << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < v[now].size(); i++) {
int next = v[now][i];
run(next);
}
}
int main() {
v[0] = { 1,2 };
v[1] = { 3 };
v[2] = { 4,5 };
run(0);
return 0;
}
[출력]
A B R T C V
그래프
하는방법?
used 배열을 만들어서 간단하게 처리가능하당
트리 그래프 와의 차이점?
1)초기 셋팅, 방문했다고 처리하고 시작
2)
->가지치기복습하기!! 2023.8.27 일욜에
ex)
used 배열 지우는거랑 안지우는거 차이
오늘의 목표 이 두가지 차이 이해하기!
[문제]
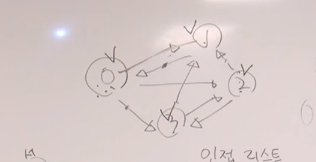
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int used[4];
vector<vector<int>>v(4);
void run(int now) {
cout << now << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < v[now].size(); i++) {
int next = v[now][i];
if (used[next] == 0) {
used[next] = 1;
run(next);
}
}
}
int main() {
v[0] = { 1,2,3 };
v[1] = { 0 };
v[2] = { 1,3 };
v[3] = { 1,2 };
used[0] = 1;
run(0);
return 0;
}
1)모든노드 한번씩만 탐색 - cycle
2)모든경로
그래프는 used배열 사용
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int used[3];
char path[10];
vector<vector<int>>v(3);
int cnt = 0;
void run(int now) {
if (used[2] == 1)cnt++;
for (int i = 0; i < v[now].size();i++) {
int next = v[now][i];
if (used[next] == 0) {
used[next] = 1;
run(next);
used[next] = 0;
}
}
}
int main() {
v[0] = { 1,2 };
v[1] = { 2 };
//now가 c일때 출력..
used[0] = 0;
run(0);
cout << cnt << "\n";
return 0;
}
[출력]
2
가중치 사용
1)모든경로- 함수종료후에 삭제 해주기 used[]=0;
2)
그래프에서 관계를 나타낼때 가중치값도 설정가능 하다.
[문제]
2번에 도착했을때, 모든 경로 sum 출력하기
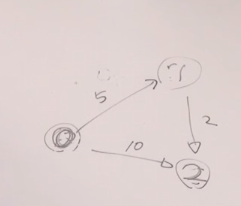
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int map[3][3] = {
0,5,10,
0,0,2,
0,0,0
};
int used[3];
void run(int now, int sum) {
if (used[2] == 1) {
cout << sum << " ";
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (map[now][i] == 0)continue;
if (used[i] == 1)continue;
used[i] = 1;
run(i, sum + map[now][i]);
used[i] = 0;
}
}
int main() {
used[0] = 1;
run(0, 0);
return 0;
}[출력]
7 10
[인접리스트 사용해서 최소비용 출력]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int n;
int weight;
};
vector<vector<Node>>v(3);
//최소비용출력
//Node 로 따로빼서 생각해보기
int mini = 21e8;
int used[3];
void run(int now, int sum) {
if (used[2] == 1) {
if (mini > sum) {
mini = sum;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < v[now].size(); i++) {
Node next = v[now][i];
if (used[next.n] == 1)continue;
used[next.n] = 1;
run(next.n, sum + next.weight);
used[next.n] = 0;
}
}
int main() {
v[0] = { {1,5},{2,10} };
v[1] = { {2,2} };
used[0] = 1;
run(0, 0);
cout << mini << "\n";
return 0;
}
[출력]
7
->Node next라고 따로 두고, 하기
최소비용찾기
중요
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int n;
int weight;
};
vector<vector<Node>>v(5);
int mini = 21e8; // 21 x 10^8
int used[5];
void run(int now, int sum) {
if (used[4] == 1) {
if (mini > sum) {
mini = sum;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < v[now].size(); i++) {
Node next = v[now][i];
if (used[next.n] == 1)continue;
used[next.n] = 1;
run(next.n, sum + next.weight);
used[next.n] = 0;
}
}
int main() {
v[0] = { {2,7},{3,2} };
v[1] = { {4,1} };
v[2] = { {1,4},{4,6} };
v[3] = { {2,1},{4,30} };
used[0] = 1;
run(0,0);
cout << mini <<"만원" << "\n";
return 0;
}
[출력]
8만원
[문제]
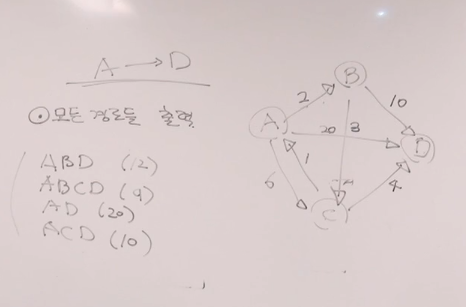
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
//a에서 d 모든 경로 출력하기
struct Node {
int n;
int weight;
};
vector<vector<Node>>v(4);
int used[4];
char path[10];
void run(int now, int sum) {
if (used[3] == 1) {
cout << sum << "\n";
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < v[now].size(); i++) {
Node next = v[now][i];
if (used[next.n] == 1)continue;
used[next.n] = 1;
run(next.n, sum + next.weight);
used[next.n] = 0;
}
}
int main() {
v[0] = { {1,2},{2,6},{3,20} };
v[1] = { {2,3},{3,10} };
v[2] = { {3,4},{0,1} };
used[0] = 1;
path[0] = 'A';
run(0, 0);
return 0;
}
출력이 왜이렇게 늦지?
컴퓨터가 느린거였음 ㅋㅋㅋㅋ
[출력]
9
12
10
20
Q.왜 now 가 3이면 출력인거지? used[3]==1일때 출력하면 안되나?
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int n;
int weight;
};
vector<vector<Node>>v(4);
int used[4];
char path[10];
void run(int now, int sum, int lev) {
if (used[3] == 1) {
cout << sum << " " << "\n";
cout << path << " ";
}
for (int i = 0; i < v[now].size(); i++) {
Node next = v[now][i];
if (used[next.n] == 1)continue;
used[next.n] = 1;
path[lev + 1] = 'A' + next.n;
run(next.n, sum + next.weight, lev + 1);
path[lev + 1] = 0;
used[next.n] = 0;
}
}
int main() {
v[0] = { {1,2},{2,6},{3,20} };
v[1] = { {2,3},{3,10} };
v[2] = { {3,4},{0,1} };
used[0] = 1;
path[0] = 'A';
run(0, 0, 0);
return 0;
}
[출력]
9
ABCD 12
ABD 10
ACD 20
AD
이르케 출력되는 이유가 모지?
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int n;
int weight;
};
vector<vector<Node>>v(4);
int used[4];
char path[10];
void run(int now, int sum, int lev) {
if (now==3) {
cout << path;
cout << " ";
cout << sum << "\n";
}
for (int i = 0; i < v[now].size(); i++) {
Node next = v[now][i];
if (used[next.n] == 1)continue;
used[next.n] = 1;
path[lev + 1] = 'A' + next.n;
run(next.n, sum + next.weight, lev + 1);
path[lev + 1] = 0;
used[next.n] = 0;
}
}
int main() {
v[0] = { {1,2},{2,6},{3,20} };
v[1] = { {2,3},{3,10} };
v[2] = { {3,4},{0,1} };
used[0] = 1;
path[0] = 'A';
run(0, 0, 0);
return 0;
}
에잇 내가 맞게했었는데, 괜히 path배열이랑 sum 이랑 두개자리때문에 ㅋㅋㅋ
1)그래프를 초기화하고
2)탐색하기
BFS
BFS 준비하기
1)레벨이란 개념을 몇번 이동했는지라고 생각하라
(1)한번가서 갈수있는곳
(2)두번가서 갈수있는곳
[문제]
BFS 출력순서
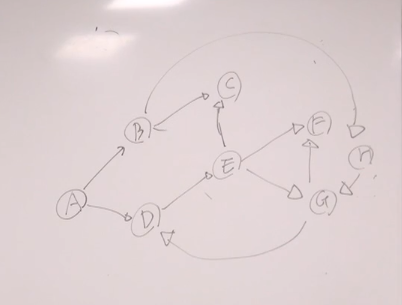
[출력]
[문제]
특정 여행지로 가는데, 최소 환승수를 구해라
정숭수 ㅋㅋ
DFS,BFS 둘중에 더빠른게 문제 마다 다르다.
BFS 사용, queue
자료구조
1)스택
2)큐
자료구조란 저장 방법
큐란 줄세우기다!
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
char ch;
int n;
};
int main() {
queue<Node>q;
q.push({ '4',6 });
q.push({ '3',5 });
q.push({ 'a',15 });
q.push({ 'b',17 });
while (!q.empty()) {
cout << q.front().ch << " " << q.front().n << "\n";
q.pop();
}
return 0;
}
1)while문: q가 비지 않는동안
2)
큐는 대기줄이다.
벡터랑 다른점
1)벡터는 push_back() 큐는 q.push()
2)데이터 읽기 벡터는 top() 큐는 front()
배운거
1)모든경로탐색하는거
2)모든경로
3)최소비용
