출처
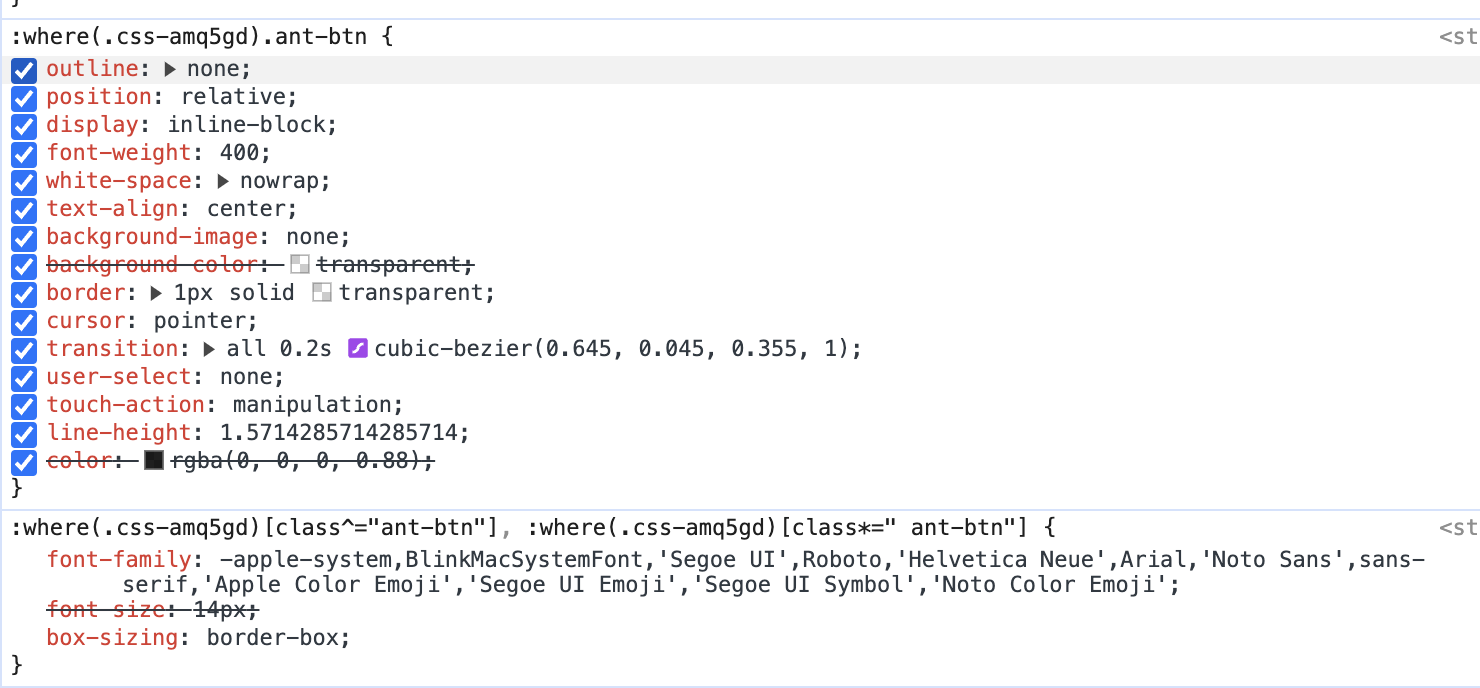
디자인 라이브러리인, antd의 버튼 컴포넌트를 보다 찾아봤습니다.
:where(), :is
h1 > b, h2 > b, h3 > b, h4 > b, h5 > b, h6 > b {
color: hotpink;
}
:is(h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6) > b {
color: hotpink;
}
/* 선택자 처음 */
:where(h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6) > b {
color: hotpink;
}
/* 선택자 중간 */
article :is(header,footer) > p {
color: gray;
}
/* 선택자 끝 */
.dark-theme :where(button,a) {
color: rebeccapurple;
}
/* 여러 가지 사용 */
:is(.dark-theme, .dim-theme) :where(button,a) {
color: rebeccapurple;
}
/* 결합 */
:is(h1,h2):where(.hero,.subtitle) {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
/* 중첩 */
.hero:is(h1,h2,:is(.header,.boldest)) {
font-weight: 900;
}- 선택자를 그룹화 할 수 있습니다.
- 선택자가 반복될 경우 유용 합니다.
차이점
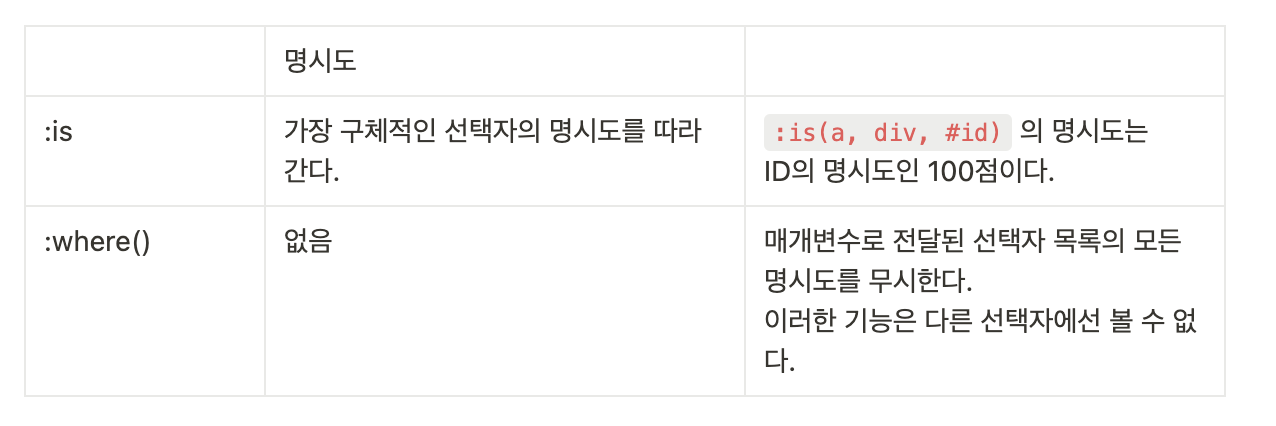
- 명시도란, CSS 선언에 적용되는 가중치로, 일치하는 선택자 내의 선택자 유형의 수에 의해 결정 됩니다
- :is() 의 경우 가장 구체적인 선택자의 명시도를 따라가기에 예상과 달리 동작할 수 있습니다.
article > :is(header, #nav) {
background: white;
}
/* 아래가 더 낫다 */
article > header,
article > #nav {
background: white;
}