DFS(깊이 우선 탐색)
DFS는 루트 노드나 임의의 노드에서 시작하여 최대한 깊숙히 들어가서 탐색한 후 다시 원점으로 돌아가 다른 루트로 탐색하는 알고리즘이다.
즉, 다음 노드로 넘어가기 전 해당 노드의 분기에 대해 완전 탐색을 하는 방식이다.
더이상 갈 길이 없을때까지 깊이 찾아가면서 탐색한다.
즉, 현재 정점과 인접 간선들을 하나씩 검사하다가, 아직 방문하지 않은 정점으로 향하는 간선이 있다면 그 간선을 무조건 방문한다. 이 과정에서 더이상 갈 곳이 없는 막힌 정점에 도달하면 마지막에 따라왔던 간선을 따라 뒤로 돌아가면서 탐색한다.
DFS는 Stack이나 재귀함수를 통해 구현하며, 모든 경로를 방문 해야 할 경우 사용하기에 적합하다.
하지만 Stack의 경우 배열을 2개 만드는 등 고려할 사항이 많아 재귀함수를 통해 구현 하는것이 좋다.
- 스택을 사용할 경우엔 오버플로우를 유의
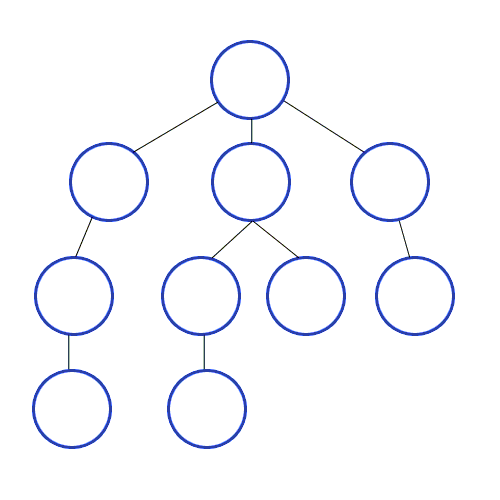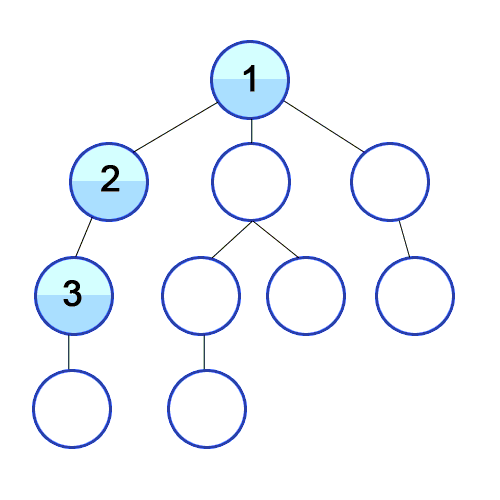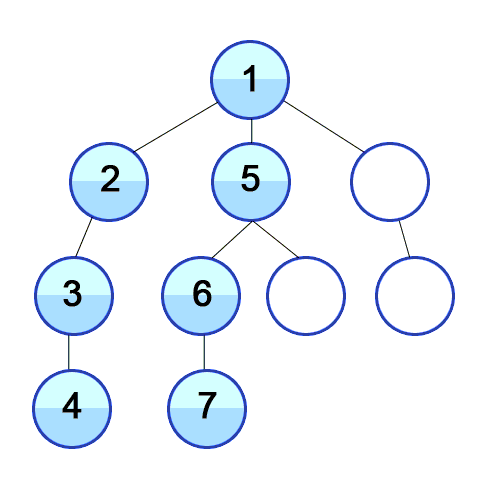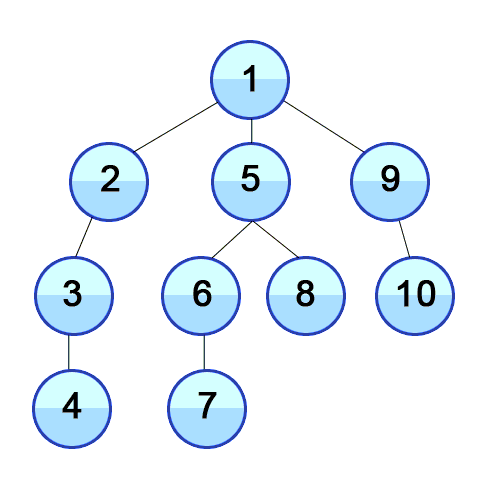
위 그림처럼 갈 길이 없을때까지 방문하다가 방문할 곳이 없으면 이전 위치로 돌아와 방문하지 않은 다른 길로 뻗어 나가면서 탐색해 나가는 방식이다.
아래 예시를 통해서 조금 더 자세히 알아보면 DFS는 다음과 같은 순서로 진행된다.
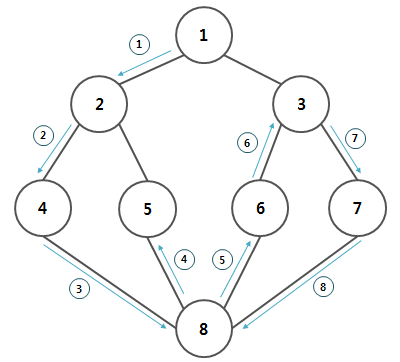
1번 정점: 2번, 3번 정점을 모두 방문하지 않은 상태
2번 정점 방문2번 정점: 1번, 4번, 5번 정점과 연결된 상태이고 1번 정점은 방문한 상태
4번 정점 방문4번 정점: 2번, 8번 정점과 연결된 상태이고 2번 정점은 방문한 상태
8번 정점 방문8번 정점: 4번, 5번, 6번, 7번 정점과 연결된 상태이고 4번 정점은 방문한 상태
5번 정점 방문5번 정점: 2번, 8번 정점과 연결된 상태이고 연결된 정점은 모두 방문한 상태
이전에 방문한 정점으로 돌아감 (8번 정점)8번 정점: 4번, 5번, 6번, 7번 정점과 연결된 상태이고 4번, 5번 정점은 방문한 상태
6번 정점 방문6번 정점: 3번, 8번 정점과 연결된 상태이고 8번 정점은 방문한 상태
3번 정점 방문3번 정점: 1번, 6번, 7번 정점과 연결된 상태이고 1번, 6번 정점은 방문한 상태
7번 정점 방문7번 정점: 3번, 8번 정점과 연결된 상태이고 연결된 정점은 모두 방문한 상태
더 이상 방문할 정점이 없으므로 탐색 종료
DFS의 장, 단점
장점
-
단지 현 경로상의 노드들만을 기억하면 되므로 저장공간의 수요가 비교적 적다.
-
목표 노드가 깊은 단계에 있을 경우 해를 빨리 구할 수 있다.
-
너비 우선 탐색(BFS)보다 구현이 간단하다.
단점
-
해가 없는 경로에 깊이 빠질 가능성이 있다.
따라서 실제의 경우 미리 지정한 임의의 깊이까지만 탐색하고 목표노드를 발견하지 못하면 다음의 경로를 따라 탐색하는 방법을 사용해야 한다. -
얻어진 해가 최단 경로가 된다는 보장이 없다.
이는 목표에 이르는 경로가 다수인 문제에 대해 깊이우선 탐색은 해에 다다르면 탐색을 끝내버리므로, 이때 얻어진 해는 최적이 아닐 수 있다. -
너비 우선 탐색(BFS)보다 단순 검색 속도가 느리다.
DFS의 시간 복잡도
DFS는 그래프의 모든 간선을 조회한다.
즉, 그래프 내에 적은 숫자의 간선만을 가지는 희소 그래프(Sparse Graph) 의 경우 인접 행렬보다 인접 리스트를 사용하는 것이 유리하다.
| 인접 행렬 구현 | 인접 리스트 구현 |
|---|---|
| O(N^2) | O(N+E) |
- N은 정점의 수, E는 간선의 수
DFS 인접 리스트 구현
import java.util.ArrayList;
// 그래프(인접리스트) 클래스
class DfsGraph {
private int nV; // 정점의 개수
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> dfsGraph; // 그래프
private boolean[] visitArr; // 정점 방문 여부 확인 배열
// 그래프 초기화 생성자
public DfsGraph(int nV) {
this.nV = nV; // 정점 개수 초기화
this.dfsGraph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); // 그래프 생성
// 그래프 초기화
// put(int x, int y) 에서 입력되는 정점의 값은 0 이상의 정수이나
// ArrayList의 index는 0 부터 시작이므로
// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 방지를 위해
// 정점을 담는 인접리스트의 size는 1을 더하여 초기화해줌
// 즉, 입력받은 정점의 개수에 +1을 해줌
// ex) initSize = 3
// graph[0]
// graph[1] -> 2 -> 3
// graph[2] -> 1 -> 3 -> 4
// graph[3] -> 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5
for(int i=0; i<this.nV+1; i++) {
this.dfsGraph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
// 정점 방문 여부 확인 배열 초기화
// 그래프와 마찬가지로 정점의 개수에 +1하여 초기화
this.visitArr = new boolean[this.nV+1];
}
// 그래프 return
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> getGraph() {
return this.dfsGraph;
}
// 그래프의 특정 노드 return
public ArrayList<Integer> getNode(int i) {
return this.dfsGraph.get(i);
}
// 그래프 추가 (양방향)
public void put(int x, int y) {
this.dfsGraph.get(x).add(y);
this.dfsGraph.get(y).add(x);
}
// 그래프 추가 (단방향)
public void putSingle(int x, int y) {
this.dfsGraph.get(x).add(y);
}
// 그래프 출력 (인접리스트)
public void printGraphToAdjList() {
for(int i=1; i<this.dfsGraph.size(); i++) {
System.out.print("정점 " + i + "의 인접리스트");
for(int j=0; j<this.dfsGraph.get(i).size(); j++) {
System.out.print(" -> " + this.dfsGraph.get(i).get(j));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// 정점 방문 여부 확인 배열 초기화
public void clearVisitArr() {
for(int i=0; i<this.visitArr.length; i++) {
this.visitArr[i] = false;
}
}
// 그래프 탐색 (재귀호출)
public void dfs(int vIdx) {
// dfs()에 파라미터로 넘어온 vIdx는 방문한 것이므로
// 방문배열의 해당 index값을 true로 바꿔주고 값을 출력함.
this.visitArr[vIdx] = true;
System.out.print(vIdx + " ");
// 인접리스트로 구현된 그래프에서
// 해당 index에 맞는 리스트를 가져와서 반복
for(int i : this.dfsGraph.get(vIdx)) {
// 해당 정점(i)이 정점 방문 여부 확인 배열에서
// 방문하지 않은 상태(false)인 경우
if(this.visitArr[i] == false) {
dfs(i); // dfs() 재귀호출
}
}
}
}
public class DfsByArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int nV = 8; // 정점의 개수
int nE = 10; // 간선의 개수
// 입력받은 정점의 개수로 그래프 초기화
DfsGraph dfsGraph = new DfsGraph(nV);
// ex) 정점 8, 간선 10
dfsGraph.put(1, 2);
dfsGraph.put(1, 3);
dfsGraph.put(2, 4);
dfsGraph.put(2, 5);
dfsGraph.put(3, 6);
dfsGraph.put(3, 7);
dfsGraph.put(4, 8);
dfsGraph.put(5, 8);
dfsGraph.put(6, 8);
dfsGraph.put(7, 8);
// 입력한 정점과 간선으로 구성된 인접리스트 출력
dfsGraph.printGraphToAdjList();
// 정점 순서대로 그래프 탐색
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 1부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.dfs(1);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 2부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(2);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 3부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(3);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 4부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(4);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 5부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(5);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 6부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(6);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 7부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(7);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 8부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(8);
}
}
- 실행결과
정점 1의 인접리스트 -> 2 -> 3
정점 2의 인접리스트 -> 1 -> 4 -> 5
정점 3의 인접리스트 -> 1 -> 6 -> 7
정점 4의 인접리스트 -> 2 -> 8
정점 5의 인접리스트 -> 2 -> 8
정점 6의 인접리스트 -> 3 -> 8
정점 7의 인접리스트 -> 3 -> 8
정점 8의 인접리스트 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7
정점 1부터 탐색 : 1 2 4 8 5 6 3 7
정점 2부터 탐색 : 2 1 3 6 8 4 5 7
정점 3부터 탐색 : 3 1 2 4 8 5 6 7
정점 4부터 탐색 : 4 2 1 3 6 8 5 7
정점 5부터 탐색 : 5 2 1 3 6 8 4 7
정점 6부터 탐색 : 6 3 1 2 4 8 5 7
정점 7부터 탐색 : 7 3 1 2 4 8 5 6
정점 8부터 탐색 : 8 4 2 1 3 6 7 5
DFS 인접 행렬 구현
//인접행렬을 이용한 DFS 구현
// 그래프(인접행렬) 클래스
class DfsGraph {
private int nV; // 정점의 개수
private int[][] dfsGraph; // 그래프
private boolean[] visitArr; // 정점 방문 여부 확인용도
// 그래프 초기화
public DfsGraph(int nV) {
this.nV = nV;
// 그래프 초기화
// put(int x, int y) 에서 입력되는 정점의 값은 0 이상의 정수지만
// 배열의 index는 0 부터 시작이므로
// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 방지를 위해 서
// 정점을 담는 인접행렬의 행과 열 size에 1을 더하여 초기화
this.dfsGraph = new int[this.nV+1][this.nV+1];
// 정점 방문 여부 확인 배열 초기화
// 그래프와 마찬가지로 정점의 개수에 +1하여 초기화
this.visitArr = new boolean[this.nV+1];
}
// 그래프 return
public int[][] getGraph() {
return this.dfsGraph;
}
// 그래프 추가 (양방향)
public void put(int x, int y) {
// 정점 x와 y가 연결되어있음을 의미
this.dfsGraph[x][y] = this.dfsGraph[y][x] = 1;
}
// 그래프 추가 (단방향)
public void putSingle(int x, int y) {
this.dfsGraph[x][y] = 1;
}
// 그래프 출력 (인접행렬)
public void printGraphToAdjArr() {
for(int i=0; i<this.dfsGraph.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<this.dfsGraph[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(" " + this.dfsGraph[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// 정점 방문 여부 확인 배열 초기화
public void clearVisitArr() {
for(int i=0; i<this.visitArr.length; i++) {
this.visitArr[i] = false;
}
}
// 그래프 탐색 (재귀호출)
public void dfs(int vIdx) {
// dfs()에 들어온 vIdx는 방문한 것이므로
// 방문배열의 해당 index값을 true로 바꿔주고 값을 출력함.
this.visitArr[vIdx] = true;
System.out.print(vIdx + " ");
// 인접 행렬로 구현된 그래프에서
// 정점의 개수(nV) 만큼 탐색
for(int i=1; i<=this.nV; i++) {
// dfsGraph[][]의 해당 정점이 연결되어있는 것으로 표시되어 있으나 (연결은 1로 표시)
// 방문 배열에서 방문하지 않은 상태(false)인 경우
// 방문해야하는 상황
if(dfsGraph[vIdx][i] == 1 && visitArr[i] == false) {
dfs(i); // dfs() 재귀호출로 방문을 의미
}
}
}
}
public class DfsByArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int nV = 8; // 정점의 개수
int nE = 10; // 간선의 개수
// 입력받은 정점의 개수로 그래프 초기화
DfsGraph dfsGraph = new DfsGraph(nV);
// ex) 정점 8, 간선 10
dfsGraph.put(1, 2);
dfsGraph.put(1, 3);
dfsGraph.put(2, 4);
dfsGraph.put(2, 5);
dfsGraph.put(3, 6);
dfsGraph.put(3, 7);
dfsGraph.put(4, 8);
dfsGraph.put(5, 8);
dfsGraph.put(6, 8);
dfsGraph.put(7, 8);
// 입력한 정점과 간선으로 구성된 인접행렬 출력 보기용도
dfsGraph.printGraphToAdjArr();
// 정점 순서대로 그래프 탐색
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 1부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.dfs(1);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 2부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(2);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 3부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(3);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 4부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(4);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 5부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(5);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 6부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(6);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 7부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(7);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("정점 8부터 탐색 : ");
dfsGraph.clearVisitArr();
dfsGraph.dfs(8);
}
}
- 실행 결과
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
정점 1부터 탐색 : 1 2 4 8 5 6 3 7
정점 2부터 탐색 : 2 1 3 6 8 4 5 7
정점 3부터 탐색 : 3 1 2 4 8 5 6 7
정점 4부터 탐색 : 4 2 1 3 6 8 5 7
정점 6부터 탐색 : 6 3 1 2 4 8 5 7
정점 7부터 탐색 : 7 3 1 2 4 8 5 6
정점 8부터 탐색 : 8 4 2 1 3 6 7 5
🙆♂️ 참고사이트 🙇♂️
(탐색알고리즘) 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS : Depth First Search)[KTKO 개발 블로그와 여행 일기]
Java DFS(Depth First Search) 구현하기[FREESTROKES DEVLOG]
알고리즘 Graph - DFS(깊이 우선 탐색)[Manducku`s Code]
[알고리즘] 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS)이란[heejeong Kwon]
DFS & BFS[gyoogle/tech-interview-for-developer]
