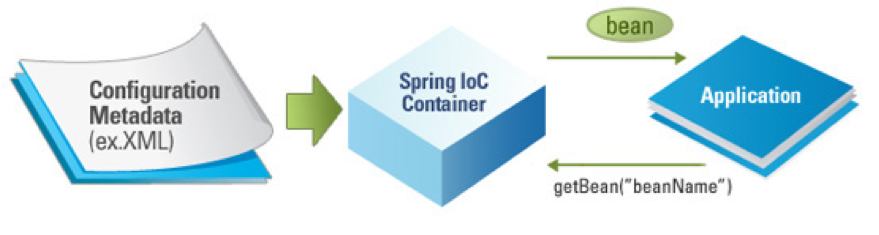
Spring에서는 Spring Container, IoC Container라는 개념을 사용한다.
Container는 인스턴스의 생명주기를 관리하며, 생성된 인스턴스들에게 추가적인 기능을 제공하도록 하는 것이다.
즉 Container는 개발자가 작성한 코드의 처리과정을 위임받은 독립적인 존재라고 생각하면 된다.
Container는 적절한 설정만 되어있다면 누구의 도움 없이도 작성한 코드를 스스로 참조한 뒤 알아서 객체의 생성과 소멸을 컨트롤해준다.
Spring Container는 Spring Framework의 핵심부에 위치하며, 종속 객체 주입을 이용하여 Application을 구성하는 Component들을 관리한다.
이때 Spring Container에서 생성되는 객체를 Bean이라고 한다.
Bean
Bean은 Spring IoC Container가 관리하는 자바 객체, Spring Bean Container에 존재하는 객체를 말한다.
Spring IoC(Inversion of Control) Contatiner에 의해 인스턴스화, 관리, 생성된다.
Bean Container는 의존성 주입을 통해 Bean 객체를 사용할 수 있도록 해준다.
Spring에서 Bean은 보통 Singleton으로 존재한다.
Singleton : 어떤 Class가 최초 한번만 메모리를 할당하고(Static) 그 메모리에 객체를 만들어 사용하는 디자인 패턴
Spring에서 POJO(Plain Old Java Object)를 Beans라고 부른다.
POJO : 본래 자바의 장점을 살리는 특정 '기술'에 종속되어 동작하는 것이 아닌 '오래된' 방식의 '순수한' 자바객체
Beans는 Application의 핵심을 이루는 객체이며, 대부분 Container에 공급하는 설정 메타 데이터(XML 파일)에 의해 생성된다.
Container는 이 메타 데이터를 통해 Bean의 생성, Bean Life Cycle, Bean Dependency(종속성) 등을 알 수 있다.
new 연산자로 생성하는 객체는 Bean이 아니고, ApplicationContext.getBean()으로 얻어질 수 있는 객체는 Bean이다.
즉, Spring에서의 Bean은 ApplicationContext가 알고있는 객체, 즉 ApplicationContext가 만들어서 그 안에 담고있는 객체를 의미한다.
Bean 생성 방식
Component Scanning
Spring IoC Container가 IoC Container를 만들고 그 안에 Bean을 등록할때 사용하는 Interface들을 Life Cycle Callback이라고 부른다.
Life Cycle Callback 중에는 @Component이 붙어있는 모든 Class의 Instance를 생성해 Bean으로 등록하는 작업을 수행하는 Annotation Processor가 등록 돼있다.
Instance : 일반적으로 실행 중인 임의의 프로세스, 해당 클래스의 구조로 컴퓨터 저장공간에서 할당되어 현재 생성된 Object를 의미.
이때, @ComonentScan Annotation이 붙어있는 Class가 이에 해당한다.
즉, @ComponentScan, @Component Anotation을 사용해서 Bean을 등록하는 방법이다.
@ComponentScan은 어느 지점부터 Component를 찾으라고 알려주는 역할을 하고,
@Component는 실제로 찾아서 Bean으로 등록할 Class를 의미한다.
@ComponentScan은 @Component이 부여된 Class를 찾아 자동으로 Bean으로 등록해주는 역할을 한다.
@ComponentScan이 붙어있는 Class가 있는 package에서부터 모든 하위 package의 모든 Class를 찾아 다니며,
@Component나 @Component를 사용하는 다른 Annotation을 사용하는 Class를 찾는다.
[EX] Stereotype Annotation(@Controller, @Service, @Repository 등)
Stereotype Annotation들은 내부적으로 @Component Annotation을 사용한다.
Configuration
Configuration을 이용한 Bean 등록 방법은, XML에 설정하는 방법과 Java Class에 설정하는 방법이 있다.
Bean 설정파일은 XML과 자바 설정파일로 작성할 수 있는데 일반적으로는 XML에 설정하지만, 최근 추세는 자바 설정파일을 좀 더 많이 사용한다.
@Configuration 사용, @Bean 정의
먼저 Java class에서 @Configuration Annotation을 사용해서 직접 @Bean을 등록해주는 방법이다.
일반적으로 xxxxConfiguration와 같이 명명한다.
@Bean Annotation을 사용해 직접 Bean을 정의하면 자동으로 Bean으로 등록된다.
이렇게 Bean을 직접 정의해서 등록하면 @Component Annotation을 붙이지 않아도 된다.
@Configuration
public class ExampleConfiguration {
@Bean
public ExampleController exampleController() {
return new ExampleController;
}
}exampleController()에서 리턴되는 객체(ExampleController)가 IoC Container 안에 Bean으로 등록된다.
@Configuration Annotation을 보면 이 Annotation도 내부적으로 @Component를 사용하기 때문에 @ComponentScan의 검색 대상이 되고,
그에 따라 Bean을 정의한 @Configuration이 읽힐때 그 안에 정의한 Bean들이 IoC Container에 등록되는 것이다.
XML 파일에 설정
XML 파일에 직접 Bean을 등록하여 Application의 Bean을 설정하는 방법이다.
XML 방식으로 Bean을 정의하는데 필요한 속성들은 아래와 같다.
- class(필수) : 정규화된 자바 class 이름
- id : bean의 고유 식별자
- scope : 객체의 범위 (sigleton, prototype 등)
- constructor-arg : 생성 시 생성자에 전달할 인수
- property : 생성 시 bean setter에 전달할 인수
- init-method, destroy-method
기본적인 양식은 아래와 같다.
<!-- A simple bean definition -->
<bean id="..." class="..."></bean>
<!-- A bean definition with scope-->
<bean id="..." class="..." scope="singleton"></bean>
<!-- A bean definition with property -->
<bean id="..." class="...">
<property name="message" value="Hello World!"/>
</bean>
<!-- A bean definition with initialization method -->
<bean id="..." class="..." init-method="..."></bean>실제 사용되는 예시는 아래와 같다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd">
<bean id="dog" class="com.spring.Dog">
<property name="myName" value="poodle"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="cat" class="com.spring.Cat">
<property name="myName" value="bella"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="petOwner" class="com.spring.PetOwner" scope="singleton">
<constructor-arg name="animal" ref="dog"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>Bean Scope
Spring은 기본적으로 모든 Bean을 Singleton으로 생성하여 관리한다.
Singleton Bean은 Spring Container에서 한 번 생성 후, Container가 사라질 때 Bean도 제거.
생성된 하나의 Instance는 Single Beans Cache에 저장되고, 해당 Bean에 대한 요청과 참조가 있으면 캐시된 객체를 반환.
하나만 생성되기 때문에 동일한 것을 참조, 기본적으로 모든 Bean은 Scope가 명시적으로 지정되지 않으면 Singleton.
구체적으로는 Application 구동 시 JVM 안에서 스프링이 Bean마다 하나의 객체를 생성하는 것을 의미한다.
그래서 Spring을 통해서 Bean을 주입 받으면 언제나 주입받은 Bean은 동일한 객체라는 가정하에서 개발 한다.

request, session, global session의 Scope는 일반 Spring Application이 아닌, Spring MVC Web Application에서만 사용
🙆♂️ 참고사이트 🙇♂️
IoC(Inversion of Control), DI(Dependency Injection), Spring Container, Bean 정리[꾸준하게]
싱글톤과 스프링[Toward the Developer]
[Spring] Spring Bean의 개념과 Bean Scope 종류[heejeong Kwon]
