오늘은 순위를 나타내는 법을 Rank 함수를 통해 알아보겠다.
순위화 ( Rank 함수 사용하지 않을 경우)
- 각 학생의 평점을 보여주는 student_grades(ID, GPA) 라는 뷰를 가정하고, 각 학생의 평점을 기준으로 GPA 대신 순위를 보여주는 질의를 작성하라.
select ID,
( 1 + ( select count (*) from student_grades B where B.GPA > A.GPA) ) as s_rank
// count 함수를 이용해 순위를 나타냄 : 나보다 높은 학생 수 + 1 = 등수
// e.g 만약, 내가 1등일 경우, B.GPA > A.GPA 를 만족하는 B.GPA 가 존재하지 않음. 즉, 0+1 해서 1등
from studnet_grades A
order by s_rank;순위화 ( Rank 함수 사용)
- rank 함수 를 order by 명세 를 사용하여 순위화를 수행하시오.
select ID, rank() over (order by GPA desc) as s_rank
from student_grades위의 코드에서는 GPA를 내림차순으로 정렬하며 RANK 함수를 사용하였다.
그러나 정렬된 순서가 아니다.
정렬된 순서대로 결과물을 얻기 위해선 Order by 절을 사용해야한다.
select ID, rank() over (order by GPA desc) as s_rank
from student_grades
order by s_rank윈도우(window)
- rank() 가 적용되는 특정 행의 집합을 의미
- rank()를 윈도우 함수라고 부름
- 윈도우 함수는 group by 절과 함께 사용하는 집계 함수와는 다르게 입력 받은 행의 집합을 '집약'하지 않음.
- 윈도우 함수는 JOIN, WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING 다음 그리고 Order by 절 이전에 실행.
partition by 를 이용한 분할된 릴레이션에서의 순위화
- 뷰 student_grades 처럼 정의되지만 학과명을 포함하는 dept_grades(ID, dept_name, GPA) 라는 뷰를 가정.
- 학과별 학생의 평점 순위를 구하시오
select ID, dept_name,
rank() over (partition by dept_name order by GPA desc) as dept_rank
// dept_name으로 릴레이션을 분할
// 그 후 분할 된 릴레이션 안에서 GPA 내림차순으로 정렬
from dept_grades
order by dept_name, dept_rank;기타 순위화 함수
- percent_rank : 백분위 순위
- cume_dist: cumulative distribution 의 약자로, 누적 분포
- row_number 행 번호
- null first : 널 값이 순서상 '처음' 오도록
- null last: 널 값이 순서상 '마지막'에 오도록
ntile(n) 순위화 함수
- 정렬된 튜플들을 입력 받아, 같은 수의 튜플을 가지는 n개의 버킷으로 나눈다.
- 백분위수 기반으 히스토그램을 구축하는데 유용
- 평점에 기반을 두어 각 학생을 네 개의 분할로 나누는 질의를 구하라
select ID,
ntile(4) over (order by GPA desc) as quartile
from student_grades;Rank 함수 중간 요약
- Partition by 절은 결과 집합의 행을 rank()함수가 적용될 각각이 파티션으로 나누다
- 그 후, order by 절은 각각의 파티션에 분배된 행을 정렬시킨다.
윈도우 함수 sum
- 윈도우 함수는 튜플의 범위에 대한 집계 함수를 계산하는데 유용하다.
- e.g) 동향 분석, 범위에 대한 집계
select date, sum(value) over
// 여기서 sum 은 group by 가 아니라 윈도우에 대하여 적용되는 윈도우 함수
(order by date betwwen rows 1 preceding and 1 following)
// 현재 행 기준 앞 1행, 뒤 1행 포함 범위 지정
from sales기타 윈도우 정의 예
-
between rows unbounded preceding and current
첫번째 행부터 현재 행 까지 -
rows unbounded preceding
첫번째 행부터 현재 행 까지 -
range between 10 preceding and current row
현재 행 값 -10 에서 현재 값 사이의 값 있는 모든 행. -
range 를 사용하면 row를 사용할 때와 달리, sort 속성의 값이 같은 모든 행을 대상으로 하는 것을 의미
-
e.g)
("a", 1000) , ("b", 700), ("b", 700), ("c", 300) 의 튜플이 있을 때,
range between 1 preceding and 1 following row 를 사용하면
("a", 1000) , ("b", 700), ("c", 300)
row betwwen 1 preceding and 1 following row 사용하면
("a", 1000) , ("b", 700), ("b", 700)
데이터 분석 및 OLAP
-
OLAP: 온라인 분석 처리
Online Analytical Processing
: 대용량의 데이터를 거의 실시간으로 응답(지연을 무시할 수 있을 정도로 작음) -
OLTP: 온라인 트랜젝션 처리
Online Transaction Processing
: select, insert, update, delete 등 데이터의 입력, 저장, 반환에 초점을 둠.
: 저장된 데이터(데이터 웨어하우스)를 잘 분석할 수 있도록 하는 것에 초점 -
다차원 데이터(multidimensional data)
- 측정 속성(measure attribute)
어떤 가치를 정량적으로 측정하고 집계하기 위한 속성
e.g) 판매된 품목 수와 품목 가격
- 차원 속성(dimension attribute)
측정 속성과 측정 속성의 요약을 그룹화하고 표현하기 위한 차원 속성
e.g) 품목 식별자, 품목이 판매된 날짜, 품목 판매 위치, 품목 구매 고객
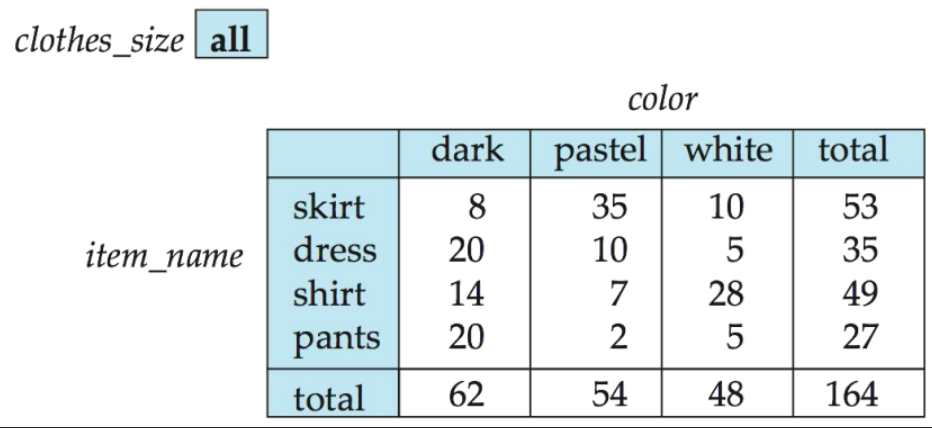
크로스탭(cross-tab) 또는 피벗 테이블(pivot table)
- 차원 속성 중 하나(item_name)에 대한 값이 행 머리글을 형성
- 다른 차원 속성(color)의 값은 열 머리글을 형성
- 다른 차원 속성(clothes_size)는 맨 위에 나열
- 개별 셀의 값은 셀을 지정하는 측정 속성(quantity)의 집계값
롤업 연산
- 나열된 속성의 각 전위(prefix) 속성에 대해 그룹 생성
select item_name, color, sum(quantity) as quantity
from sales
group by rollup (item_name, color)// 이 경우 group by rollup 절은 3개의 그룹 형성
{
( item_name, color ),
( item_name, ),
( )
}// 위 질의의 결과는 union 연산을 사용하는 다음 질의와 같음
( select item_name, color, sum(quantity) as quantity
from sales
group by item_name, color )
union
( select item_name, null as color , sum(quantity) as quantity
from sales
group by item_name )
union
( select null as item_name, null as color, sum(quantity) as quantity
from sales
)큐브 연산
- 나열된 속성의 모든 부분집합으로 구성된 많은 수의 그룹을 생성
select item_name, color, clothes_size, sum(quantity)
from sales
group by cube(item_name, color, clothes_size)위 코드는 다음 8개의 그룹을 생성
{
(item_name, color, clothes_size),
(item_name, color),
(item_naem, clothes_size),
(item_name),
(color, clothes_size),
(color),
(clothes_size),
()
}
// 롤업에서 처럼 각 그룹에 없는 속성에 대해서는 null 값을 포함하여 결과를 생성하고,
// 각 그룹에 대해 생성된 결과들의 합집합을 구하면 같은 질의문 만들 수 있음확장 집계
select item_name, color, clothes_size, sum(quantity)
from sales
group by rollup(item_name), rollup(color, clothes_size)// 6개 그룹 생성
// 1번과 2번은 같은 의미
1.
{
(item_name),
(),
x
(color, clothes_size),
(color, ),
()
}
// *--------------------------------* //
2.
{
(item_name, color, clothes_size),
(item_name, color),
(item_name),
(color, clothes_size),
(color)
()
}- 특정 그룹핑(grouping) 리스트만 명세 가능
group by grouping sets ((color, clothes_size), (clothes_size, item_name))
// 2그룹만 얻는다.- 일반적인 null 과 롤업/큐브에 의해 생성되는 null 을 구분하기 위해 grouping() 함수를 사용할 수 있다.
- 값이 all 을 나타내는 null 이면 1을 반환하고 다른 모든 경우에는 0을 반환한다.
select item_name, color, clothes_size, sum(quantity),
grouping(item_name) as item_name_flag
grouping(color) as color_flag
grouping(clothes_size) as size_flag
from sales
group by cube(item_name, color, clothes_size)