▶ Python Overview
- 파이썬은 interpreted language(한줄씩)
- C와 같은 compiler language(한번에 돌아가는 언어)
- Object-Oriented
- dynamically typed language

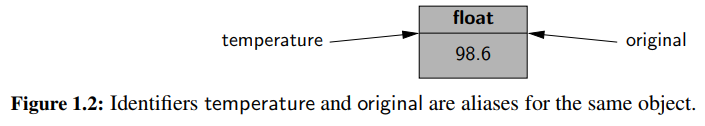
▶ Constructor(생성자)
`
w = Widget()
w = Widget(a,b,c)▶ Calling Methods
▶ Built-In Classes
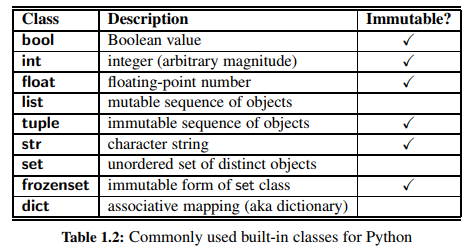
- Immutable class
: fixed value upon instantiation that can not subsequently be changed
e.x)floatclass is immutable
▶ class
Bool class
int class
# 캐스팅
int(3.14)
# -> answer: 3float class
float(2)
# floating point value 2.0
# -> answer: 2.0list class
list('hello')-> list of characters['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']
tuple class
- immutable version of sequence
The str class
print("""Welcome to GPA calculator. Please Enter the push button!""")The set class
The dict class
▶ Operators
Logical Operators
- short-circuit

Equality Operators

Comparison Operators
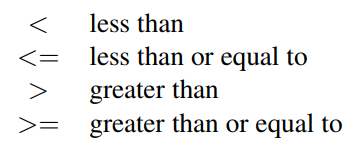
Arithmetic Operator

Bitwise Operator
- Python provides the following bitwise operators for integers

Sequence Operator

Sequence Comparisons

Operators for Sets

Operators for Dictionaries

▶ Conditionals

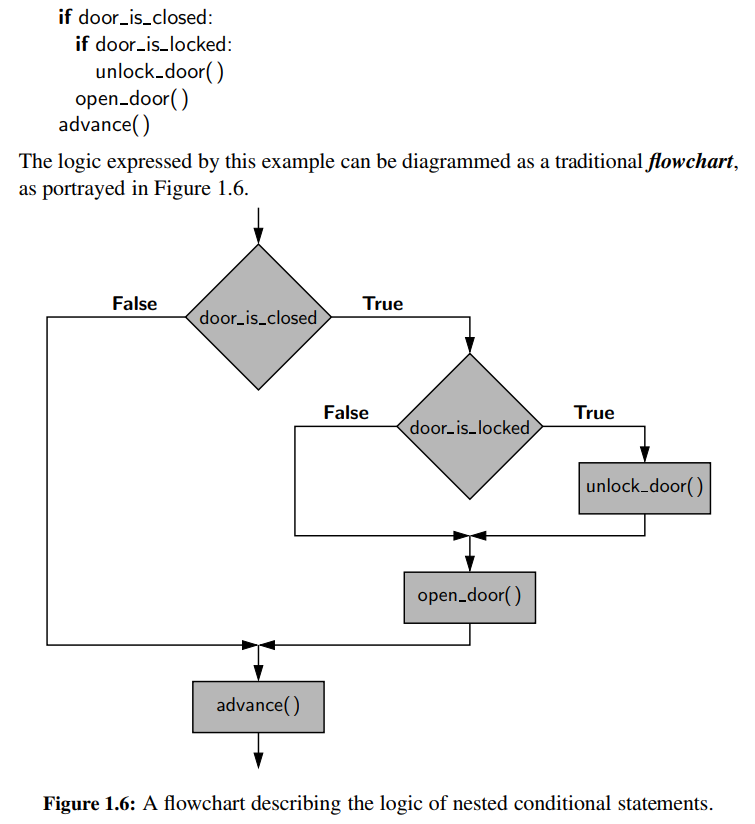
▶ Loops
While Loops
For Loops
Indexed For loop
Break and Continue Statements
▶ Functions
def count(data, targe):
n = 0
for item in data:
if item == target:
n += 1
return nInformation Passing
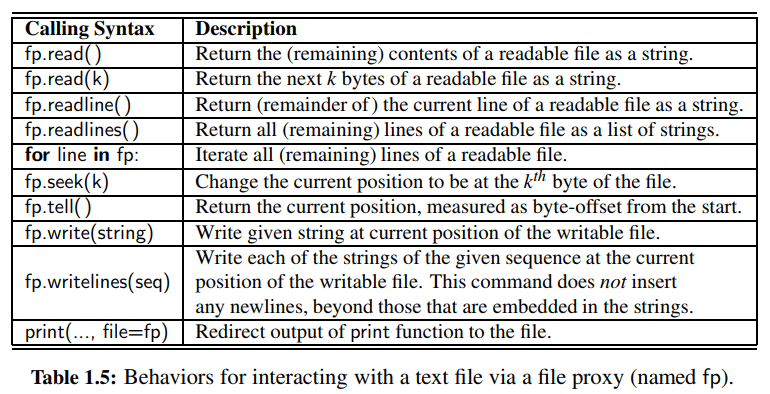
▶ Simple I/O

files
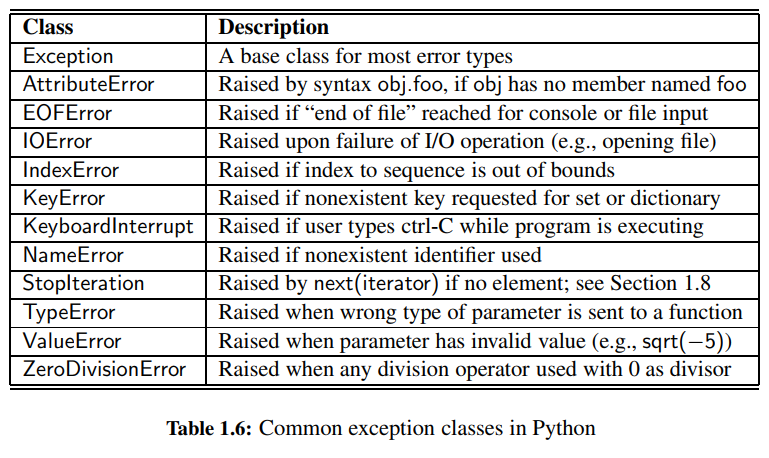
▶ Exception Handling
Common Exceptions
Raising an Exception
raise ValueError('x cannot be nemgative')Catching an Exception
- 예외 처리를 함으로써 성능 향상을 꾀할 수 있음.
try-catch문을 이용하여 예외 처리 가능
try:
ratio = x/y
except ZeroDivisionError:
...do something else...▶ Iterators and Generators
Iterators
- each call to the built-in function,
next(i), produces a subsequent element from the underlying series, with a StopIteration exception raised to indicate that there are no further elements. - An iterable is an object, obj, that produces an iterator via the syntax
iter(obj)
Generators
- generator for the factors of n
def factors(n):
for k in range(1, n+1):
if n % k == 0:
yield k▶ Additional Python Conveniences
Conditional Expressions
Comprehension Syntax
[expression for value in iterable if condition]is same as
result = []
for value in iterable:
if condition:
result.append(expression)Packing and Unpacking
Packing
data = 2, 4, 6, 8- data being assigned to the
tuple (2,4,6,8) - automatic packing of tuple
Unpacking
a,b,c,d = range(7, 11)- assigning
a = 7, b = 8, c = 9, d = 10
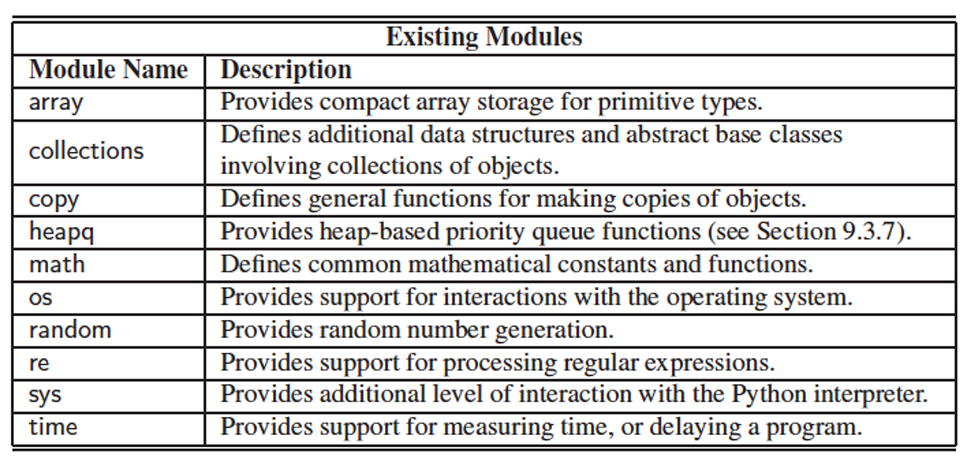
▶ Modules
import math