week05. RB Tree
균형 이진 탐색 트리 중 하나인 RB Tree 구현
RB Tree가 등장하게 된 배경.
- 기존 이진 탐색 트리는 각 노드가 모두 자식 노드가 2개인 경우 노드 하나를 찾는 데 시간 복잡도 O(log n) 을 보장한다.
- 그러나 각 노드가 왼쪽 노드에만 자식이 있어서 트리가 트리가 아닌 선형 구조가 되어버리면 시간 복잡도 O(log n)을 보장할 수 없음.
- 이를 보장하기 위해 노드 삽입, 삭제 한 쪽으로 노드가 치우쳐지지 않도록 연산을 추가해 왼쪽 오른쪽의 밸런스를 맞춘 트리.
삽입 삭제 연산이 조금 복잡해지고 rotate 연산도 추가로 진행하게 되는데, 이 연산들을 통해서 만약 시간 복잡도가 올라간다면 기존의 이진 탐색트리가 더 효율적이지 않나? 라고 생각할 수 있다. 실제로 밸런스를 맞추기 위해 삽입 1번을 위해 여러 번 rotate를 진행하는 경우도 있다. 그러나 이런 작업을 통해 밸런스를 맞추는 것이 시간 복잡도 개선에 더 도움이 된다.
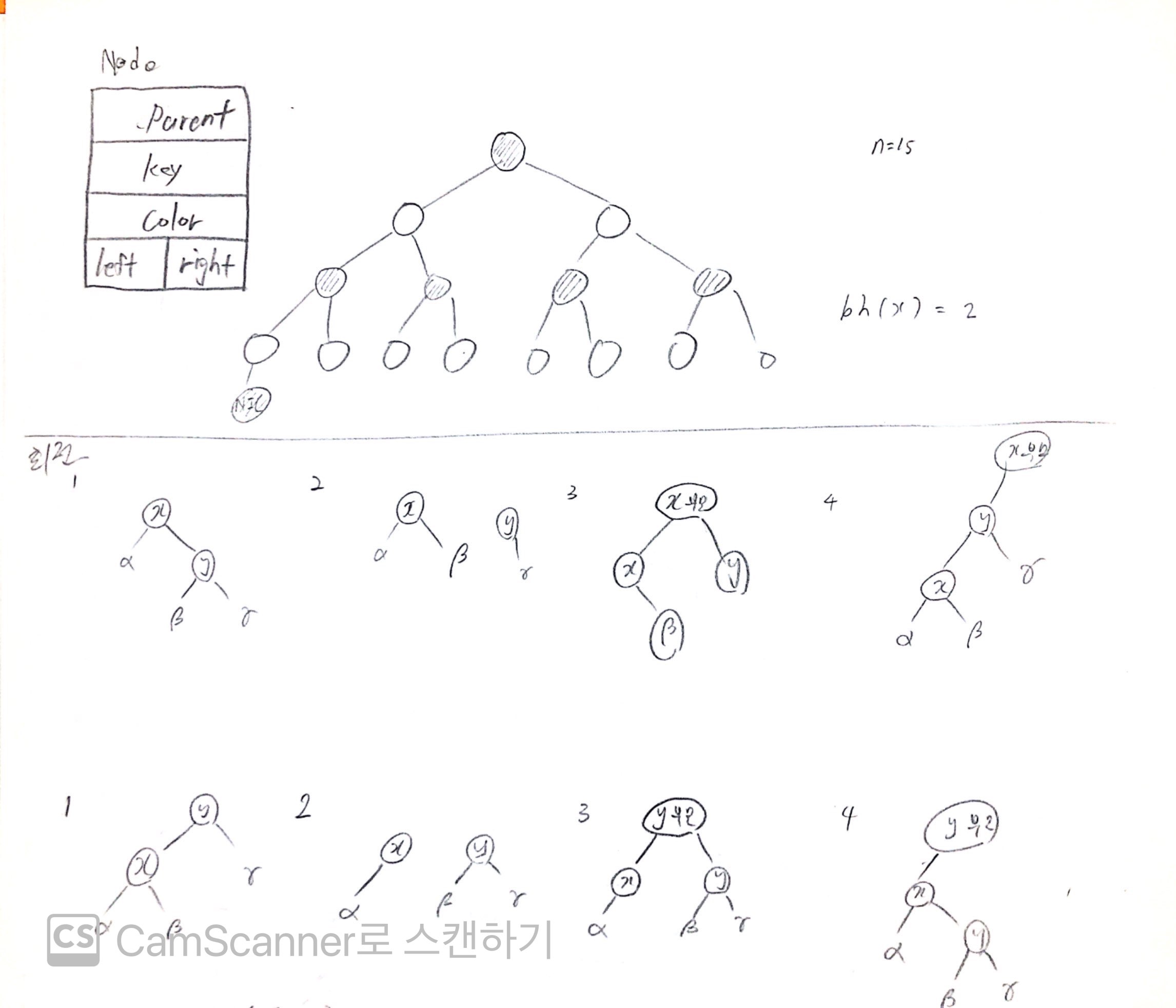
회전 부분에서 윗 그림이 left_rotate, 아랫 그림이 right_rotate.
#include "rbtree.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
// 기존에 있던 함수 이외에 새로 만든 함수들
node_t *find_key(node_t *root, node_t *nil, const key_t key);
void free_rbtree(node_t *root, node_t *nil);
void left_rotate(rbtree *t, node_t *x);
void right_rotate(rbtree *t, node_t *x);
void rbtree_insert_fixup(rbtree *t, node_t *z);
void rbtree_delete_fixup(rbtree *t, node_t *x);
void rb_transplant(rbtree *t, node_t *u, node_t *v);
void make_array(node_t *root, node_t *nil, key_t *arr, const size_t n);
rbtree *new_rbtree(void) {
rbtree *p = (rbtree *)calloc(1, sizeof(rbtree));
// TODO: initialize struct if needed
p->nil = (node_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(node_t));
p->root = p->nil;
p->nil->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
return p;
}
// 전위순회로 돌면서 메모리 반환
void delete_rbtree(rbtree *t) {
// TODO: reclaim the tree nodes's memory
free_rbtree(t->root, t->nil);
free(t->nil);
free(t);
}
void free_rbtree(node_t *root, node_t *nil) {
if (root == nil)
return;
free_rbtree(root->left, nil);
// printf("%d\n", root->key);
free_rbtree(root->right, nil);
free(root);
}
void left_rotate(rbtree *t, node_t *x) {
node_t *y = x->right;
x->right = y->left;
if (y->left != t->nil)
y->left->parent = x;
y->parent = x->parent;
if (x->parent == t->nil)
t->root = y;
else if (x == x->parent->left)
x->parent->left = y;
else
x->parent->right = y;
y->left = x;
x->parent = y;
}
void right_rotate(rbtree *t, node_t *x) {
node_t *y = x->left;
x->left = y->right;
if (y->right != t->nil)
y->right->parent = x;
y->parent = x->parent;
if (x->parent == t->nil)
t->root = y;
else if (x == x->parent->right)
x->parent->right = y;
else
x->parent->left = y;
y->right = x;
x->parent = y;
}
node_t *rbtree_insert(rbtree *t, const key_t key) {
// TODO: implement insert
// part1. 새 노드의 컬러를 RED로 해서 삽입
node_t *z = calloc(1, sizeof(node_t));
node_t *y = t->nil; // 삽입할 노드 위치의 부모 노드. nil은 트리가 빈 트리일 경우를 대비한 초기값
node_t *x = t->root; // y를 찾기 위한 포인터
z->key = key;
// 삽입할 위치의 부모를 찾기 위한 반복문
while (x != t->nil) {
y = x;
if (key < x->key)
x = x->left;
else
x = x->right;
}
z->parent = y;
// 빈 트리인 경우
if (y == t->nil)
t->root = z; // 루트를 z로 설정
// 키 삽입할 위치 찾기
else if (key < y->key)
y->left = z;
else
y->right = z;
z->left = t->nil;
z->right = t->nil;
z->color = RBTREE_RED;
rbtree_insert_fixup(t, z);
return t->root;
}
void rbtree_insert_fixup(rbtree *t, node_t *z) {
node_t *y; // 삽입한 z의 삼촌 노드
// 색상 전환을 해도 빨간 노드가 붙어있을 수 있으므로 반복
while (z->parent->color == RBTREE_RED) {
if (z->parent == z->parent->parent->left) // 부모노드가 왼쪽 자식인 경우
{
y = z->parent->parent->right; // 오른쪽 자식을 삼촌 노드로 지정
if (y->color == RBTREE_RED) // z, z의 부모, 삼촌이 모두 빨강인 경우
{
z->parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK; // 부모 노드를 검정으로
y->color = RBTREE_BLACK; // 삼촌 노드도 검정
z->parent->parent->color = RBTREE_RED; // 할아버지노드 빨강
z = z->parent->parent; // z의 위치를 할아버지로 변경. 할아버지랑 부모노드랑 같은 빨강일 수도 있으므로.
}
else{ // 삼촌 노드가 검정색인 경우
if (z == z->parent->right) { // z가 오른쪽 자식인 경우
z = z->parent; // left_rotate를 위한 사전 작업
left_rotate(t, z);
}
z->parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK; // right_rotate를 위한 사전 작업 1
z->parent->parent->color = RBTREE_RED; // right_rotate를 위한 사전 작업 2
right_rotate(t, z->parent->parent);
}
}
else { // 부모 노드가 오른쪽 자식인 경우
y = z->parent->parent->left; // 할아버지의 왼쪽 노드를 삼촌으로
if (y->color == RBTREE_RED) // z, z의 부모, 삼촌이 모두 빨강인 경우
{
z->parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
y->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
z->parent->parent->color = RBTREE_RED;
z = z->parent->parent;
}
else{
if (z == z->parent->left) {
z = z->parent;
right_rotate(t, z);
}
z->parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
z->parent->parent->color = RBTREE_RED;
left_rotate(t, z->parent->parent);
}
}
}
t->root->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
}
node_t *rbtree_find(const rbtree *t, const key_t key) {
// TODO: implement find
return find_key(t->root, t->nil, key);
}
node_t *find_key(node_t *root, node_t *nil, const key_t key) {
if (root == nil)
return NULL; // nil은 트리 안에서만 사용하기 위해서 만듬. 밖에서 값이 없다는 것을 표현해주고 싶으면 nil이 아니라 NULL을 반환해주는 것이 맞다.
if (root->key == key)
return root;
else if (root->key > key)
return find_key(root->left, nil, key);
else
return find_key(root->right, nil, key);
}
node_t *rbtree_min(const rbtree *t) {
// TODO: implement find
node_t *tmp = t->root;
while (tmp->left != t->nil)
tmp = tmp->left;
return tmp;
}
node_t *rbtree_max(const rbtree *t) {
// TODO: implement find
node_t *tmp = t->root;
while (tmp->right != t->nil)
tmp = tmp->right;
return tmp;
// return t->root;
}
int rbtree_erase(rbtree *t, node_t *z) {
// TODO: implement erase
node_t *y = z; // z의 빈자리를 대체할 수를 가진 노드
node_t *x; // 살려야 될 z의 자식 노드 (많아봐야 1개. 있을 수도 없을 수도 있다)
color_t y_ori_color = y->color;
// 오른쪽 자식밖에 없는 경우 and 자식이 둘 다 없는 경우
if (z->left == t->nil) {
x = z->right;
rb_transplant(t, z, z->right);
}
// 왼쪽 자식밖에 없는 경우
else if (z->right == t->nil) {
x = z->left;
rb_transplant(t, z, z->left);
}
// 자식이 둘 있는 경우
else{
// z의 오른쪽 자식 중 최솟값 찾는 루틴
y = z->right;
while (y->left != t->nil){
y = y->left;
}
y_ori_color = y->color;
x = y->right;
if (y->parent == z)
x->parent = y;
else{
rb_transplant(t, y, y->right);
y->right = z->right;
y->right->parent = y;
}
rb_transplant(t, z, y);
y->left = z->left;
y->left->parent = y;
y->color = z->color;
}
free(z);
if (y_ori_color == RBTREE_BLACK)
rbtree_delete_fixup(t, x);
return 0;
}
void rbtree_delete_fixup(rbtree *t, node_t *x) {
node_t *w;
while (x != t->root && x->color == RBTREE_BLACK) {
if (x == x->parent->left){
w = x->parent->right;
if (w->color == RBTREE_RED){
w->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
x->parent->color = RBTREE_RED;
left_rotate(t, x->parent);
w = x->parent->right;
}
if (w->left->color == RBTREE_BLACK && w->right->color == RBTREE_BLACK) {
w->color = RBTREE_RED;
x = x->parent;
}
else {
if (w->right->color == RBTREE_BLACK) {
w->left->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
w->color = RBTREE_RED;
right_rotate(t, w);
w = x->parent->right;
}
w->color = x->parent->color;
x->parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
w->right->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
left_rotate(t, x->parent);
x = t->root;
}
}
// right와 left를 바꾼 경우와 같다
else {
w = x->parent->left;
if (w->color == RBTREE_RED){
w->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
x->parent->color = RBTREE_RED;
right_rotate(t, x->parent);
w = x->parent->left;
}
if (w->right->color == RBTREE_BLACK && w->left->color == RBTREE_BLACK) {
w->color = RBTREE_RED;
x = x->parent;
}
else {
if (w->left->color == RBTREE_BLACK) {
w->right->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
w->color = RBTREE_RED;
left_rotate(t, w);
w = x->parent->left;
}
w->color = x->parent->color;
x->parent->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
w->left->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
right_rotate(t, x->parent);
x = t->root;
}
}
}
x->color = RBTREE_BLACK;
}
void rb_transplant(rbtree *t, node_t *u, node_t *v) {
if (u->parent == t->nil)
t->root = v;
else if (u == u->parent->left)
u->parent->left = v;
else
u->parent->right = v;
v->parent = u->parent;
}
int idx = 0;
int rbtree_to_array(const rbtree *t, key_t *arr, const size_t n) {
// TODO: implement to_array
// 중위순회하면 정렬된 배열을 얻을 수 있다
make_array(t->root, t->nil, arr, n);
idx = 0;
return 0;
}
void make_array(node_t *root, node_t *nil, key_t *arr, const size_t n) {
if (root == nil)
return;
if (idx == n)
return;
make_array(root->left, nil, arr, n);
arr[idx] = root->key;
idx++;
make_array(root->right, nil, arr, n);
}