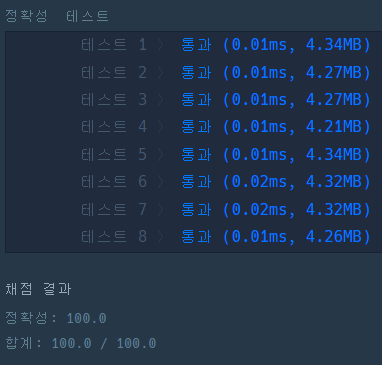
대표적인 최소신장트리 문제이다. 밑의 코드는 프림 알고리즘이다.
프림알고리즘은 다음과 같은 단계로 이루어진다.
1. 전체 N개의 노드를 잇는 최소신장트리는 T개와 N-T개의 노드로 이루어진 최소신장트리의 합집합이다.
2. 위 개념을 이용해서 특정 노드부터 시작하여 최소신장트리를 확장해나간다.
3. 0부터 시작하여 인접한 엣지 중 가중치가 가장 작은 것을 찾는다. 이 과정을 N-1개의 엣지가 선택될 때까지 반복한다. (혹은 N개의 노드가 이어질 때까지)
4. 이 과정에서 이미 포함된 노드들 끼리 사이클이 생길 수 있기 때문에 싸이클 체크를 해준다. (프림은 최소신장트리가 확장되어나가는 방식이기 때문에 현재 최소신장트리에 포함되지 않은 새로운 노드가 추가되는 방식이다. 따라서 set을 이용해서 간단하게 노드 중복체크를 해줄 수 있다.)
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef struct __node_info {
int cost;
int from;
int to;
} node_info;
struct comp {
bool operator() (const node_info &a, const node_info &b) {
return a.cost > b.cost;
}
};
int solution(int n, vector<vector<int>> costs) {
int answer = 0;
priority_queue<node_info, vector<node_info>, comp> q;
vector<vector<int>> graph(n, vector<int>(n, 0));
set<int> s;
for(auto it : costs) {
graph[it[0]][it[1]] = it[2];
graph[it[1]][it[0]] = it[2];
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
if(graph[0][i])
q.push( { graph[0][i], 0, i } );
s.insert(0);
while(s.size() != n) {
node_info node = q.top(); q.pop();
if(s.find(node.to) != s.end())
continue;
s.insert(node.to);
answer += node.cost;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
if(graph[node.to][i])
q.push({graph[node.to][i], node.to, i});
}
return answer;
}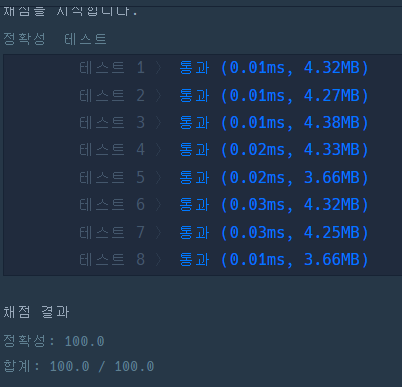
다음은 크루스칼 알고리즘이다.
크루스칼은 전체 엣지 중 가중치가 작은 엣지들을 우선적으로 선택하고, 만약 싸이클이 없다면 최소신장트리에 포함시킨다.
특히, getParent를 통해서 공통 분모를 가지고있는지 여부를 체크하고, 만약 공통 분모를 가진다면 이는 싸이클로 판단한다.
코드는 다음과 같다.
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef struct __node_info {
int cost;
int from;
int to;
} node_info;
struct comp {
bool operator() (const node_info &a, const node_info &b) {
return a.cost > b.cost;
}
};
vector<int> p;
int getParent(int node)
{
if(node == p[node])
return node;
// 가장 최신이며 가장 윗 부모를 가질 수 있도록 중간 노드들을 최신 정보로 갱신
return p[node] = getParent(p[node]);
}
int solution(int n, vector<vector<int>> costs) {
int answer = 0;
p.resize(n, 0);
// i의 부모는 i
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
p[i] = i;
priority_queue<node_info, vector<node_info>, comp> q;
for(auto it : costs)
q.push({it[2], it[0], it[1]});
int edges = 0;
while(1) {
if(q.empty())
break;
node_info node = q.top(); q.pop();
int from_parent = getParent(node.from);
int to_parent = getParent(node.to);
// 만약 두 노드의 부모가 같다면 싸이클
if(from_parent == to_parent)
continue;
/* 그것이 아니라면 부모 사이의 관계를 정해줌
본 문제에선 from이 항상 to보다 작은 듯.
따로 작성하진 않았지만 from이 to보다 작도록 추가 코드를 작성해주는 것이 안전함
*/
p[to_parent] = from_parent;
answer += node.cost;
// n - 1개의 엣지가 만들어졌으면 break가능. 최적화용 코드
edges++;
if(edges == n - 1)
break;
}
return answer;
}