1. 리플렉션(Reflection)이란?
코드 그 자체를 데이터(메타 데이터)로서 다루는 기법. 즉, 객체의 형식(Type) 정보를 들여다보는 기능이다. 이 기능으로 런타임에 형식 정보(형식 이름, 프로퍼티 목록, 메소드 목록, 필드, 이벤트 목록)을 열어볼 수 있고, 형식의 이름만 있다면 동적으로 인스턴스를 만들 수도 있고, 그 인스턴스의 메서드를 호출할 수도 있다. 심지어 새로운 데이터 형식을 동적으로 만들 수도 있다.
💡 메타데이터?
데이터의 데이터. c#코드도 데이터지만 이 코드에 대한 정보도 존재한다. 이를 메타데이터라고 한다. 리플렉션이나 애트리뷰트를 통해 얻는 정보들도 c# 코드의 메타 데이터이다.
2. 형식의 정보 열어보기
2.1 (Object.GetType() 메서드와 Type 클래스)
Microsoft .NET은 System.Type 클래스 형식을 반환하는 메서드 Object.GetType()를 만들어놓음으로써 개발자들이 모든 형식을 들여다볼 수 있도록 설계했다.
Object는 모든 데이터 형식의 조상이기 때문에 모든 데이터 형식은 Object 형식이 갖는 메서드를 물려받을 수 있다.
그 중 GetType()메서드가 있어, 어떤 객체에서든 이 메서드를 호출하여 그 객체의 형식 정보를 얻을 수 있다.
💡GetType() 메서드는 Type 형식의 결과를 반환한다.
Type 형식은 .NET에서 사용하는 데이터 형식의 모든 정보를 담고 있다.
ㄴ 형식 이름, 소속된 어셈블리 이름, 프로퍼티 목록, 메서드 목록, 필드 목록, 이벤트 목록, 이 형식이 상속하는 인터페이스의 목록
📝 간단한 예시
- int 형식으로 선언된 a의 Type을 type 변수로 불러주고, 그 중에서 FieldInfo를 호출해주는 코드 만들기
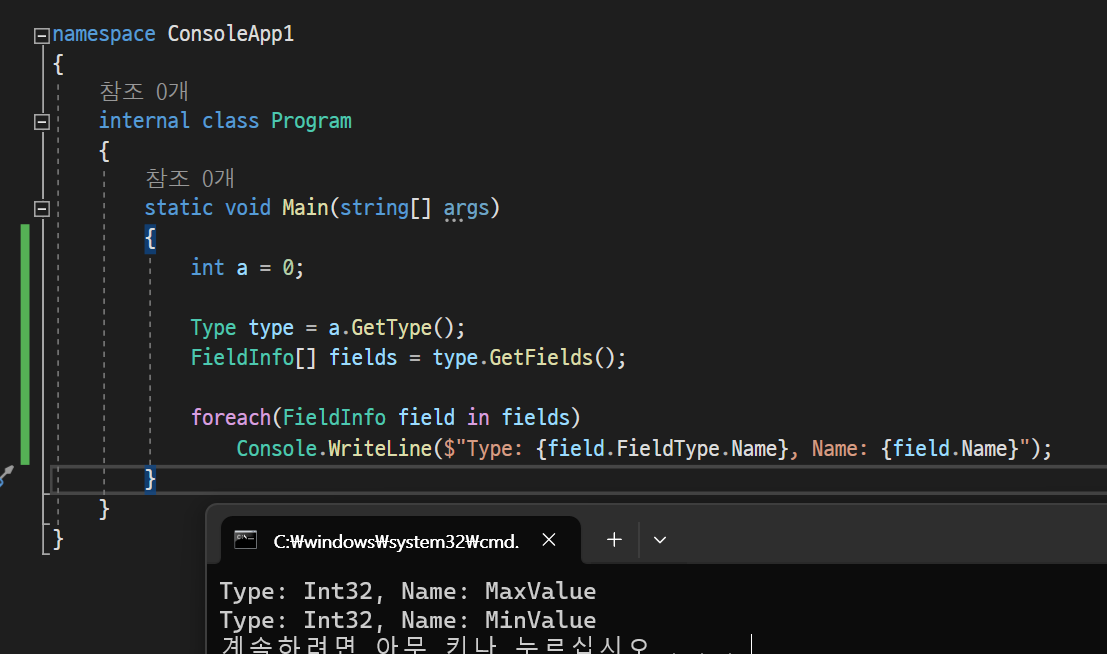 ㄴ
ㄴ FieldInfo: 필드의 특성을 검색하고 필드 메타데이터에 액세스할 수 있도록 해주는 System.Reflection의 클래스
2.2 System.Reflection.BindingFlags 열거형으로 검색 옵션 지정하기
GetFields()나 GetMethods() 같은 메서드는 검색 옵션을 지정할 수 있다.
- public 항목만 조회
- 비(非) public 항목만 조회
- 둘 다 조회
- static 항목만 조회
- 인스턴스 항목만 조회
- 모든 조건을 포함하는 조건을 만들어서 조회
-> 이러한 검색 옵션은 System.Reflection.BindingFlags을 이용해서 구성된다.
⚠️ GetFields()나 GetMethods() 등의 메서드는 BindingFlags 매개변수를 받지 않는 버전으로도 오버로딩되어 있다! 이 경우 이 메서드들은 public 멤버만 반환한다.
📝 예시 (int의 주요 정보를 출력하는 예제)
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
static void PrintInterfaces(Type type)
{
Console.WriteLine("--------- Interfaces ---------");
Type[] interfaces = type.GetInterfaces();
foreach(Type i in interfaces)
Console.WriteLine($"Name: {i.Name}");
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void PrintFields(Type type)
{
Console.WriteLine("--------- Fields ---------");
FieldInfo[] fields = type.GetFields(
BindingFlags.NonPublic |
BindingFlags.Public |
BindingFlags.Static |
BindingFlags.Instance);
foreach (FieldInfo field in fields)
{
String accessLevel = "protected";
if (field.IsPublic)
accessLevel = "public";
else if (field.IsPrivate)
accessLevel = "private";
Console.WriteLine($"AccessLevel : {accessLevel}, Type: {field.FieldType.Name}, Name: {field.Name}");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void PrintMethods(Type type)
{
Console.WriteLine("--------- Methods ---------");
MethodInfo[] methods = type.GetMethods();
foreach (MethodInfo method in methods)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Type: {method.ReturnType.Name}, Name: {method.Name}, Parameter:");
ParameterInfo[] parameters = method.GetParameters();
for(int i = 0; i < parameters.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(parameters[i].ParameterType.Name);
if(i < parameters.Length -1)
Console.WriteLine(", ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void PrintProperties(Type type)
{
Console.WriteLine("--------- Properties ---------");
PropertyInfo[] properties = type.GetProperties();
foreach (PropertyInfo property in properties)
Console.WriteLine($"Type: {property.PropertyType.Name}, Type: {property.Name}");
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 0;
Type type = a.GetType();
PrintInterfaces(type);
PrintFields(type);
PrintProperties(type);
PrintMethods(type);
}
}
}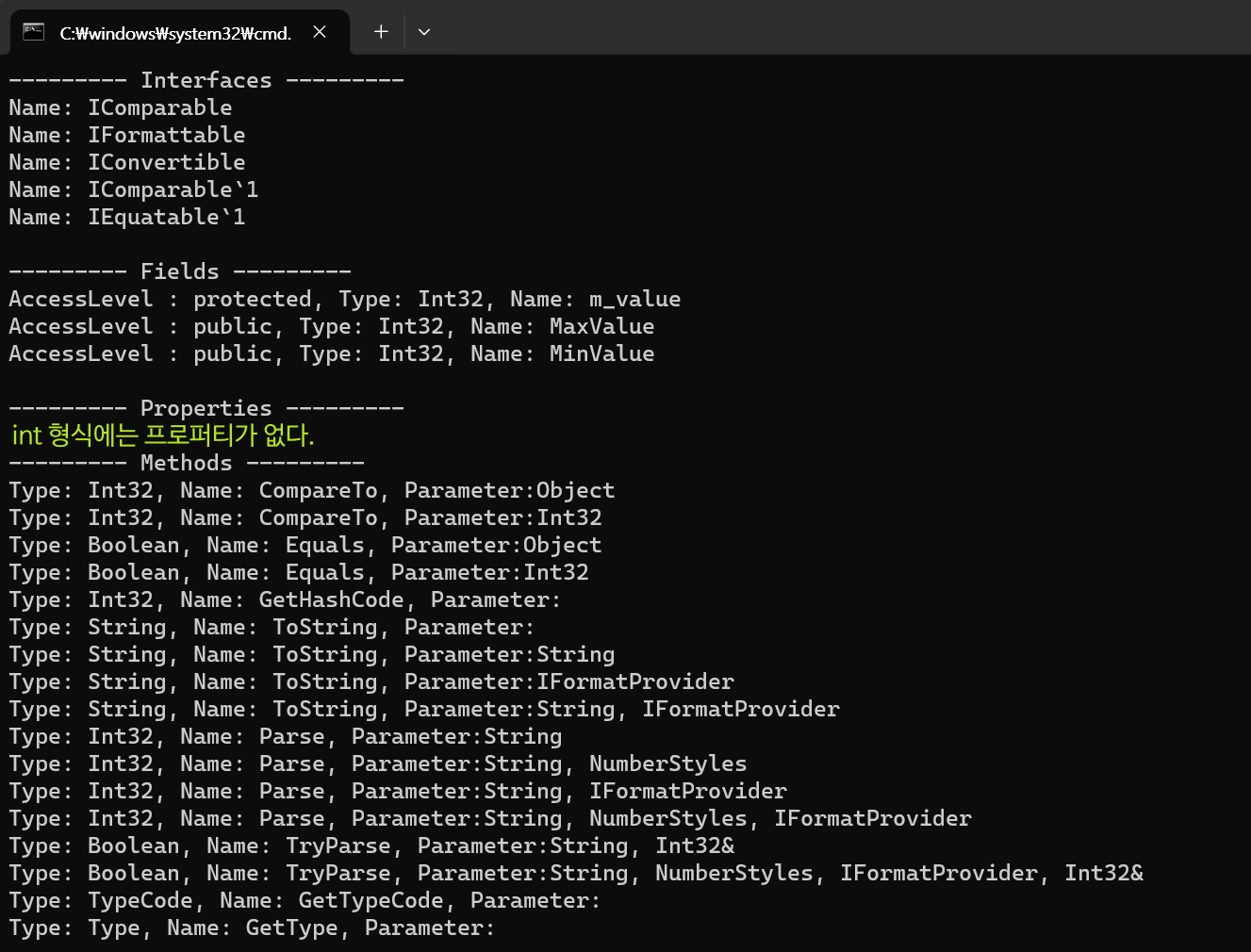 ⚠️ Object.GetType() 메서드를 사용하지 않고 형식 정보를 얻는 방법
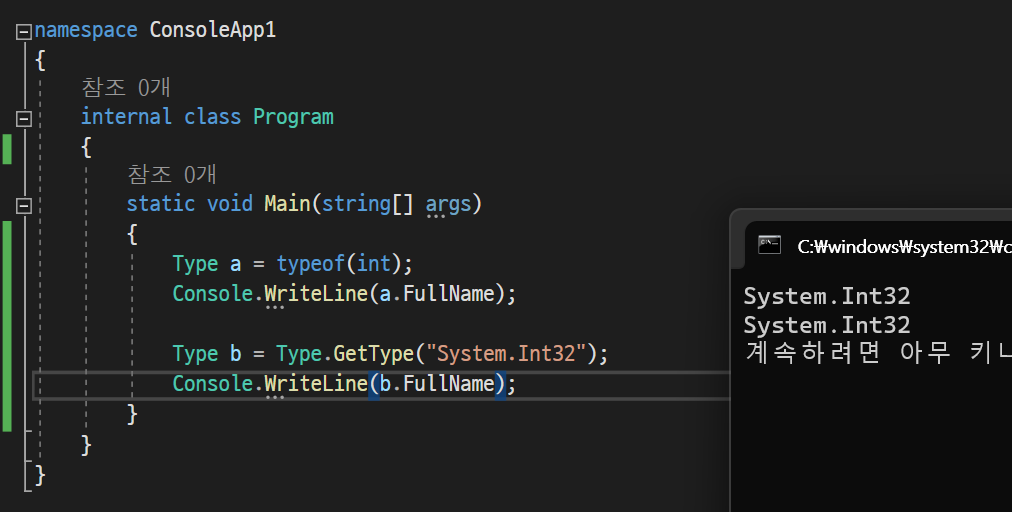
⚠️ Object.GetType() 메서드를 사용하지 않고 형식 정보를 얻는 방법
: Object.GetType() 메서드는 반드시 인스턴스가 있어야 호출할 수 있다. 즉, int 형식의 정보를 열어볼 때에도 int a = 0;과 같이 인스턴스를 만들고 초기화해야 한다. 이런 번거로운 과정 없이 형식 정보를 얻는 방법이 있다.
typeof연산자와Type.GetType()메서드 활용
- typeof 연산자: 형식의 식별자 자체를 인수로 받는다
- Type.GetType(): 네임스페이스를 포함한 형식의 전체 이름을 인수로 받는다
3. 리플렉션을 이용해서 객체 생성하기
3.1 동적으로 특정 형식의 인스턴스 생성하기_System.Activator.CreateInstance()
코드 안에서 런타임에 특정 형식의 인스턴스를 만들 수 있게 되면 프로그램이 조금 더 동적으로 동작할 수 있도록 구성할 수 있다.
object a = Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(int));ㄴ 인스턴스를 만들려는 형식의 Type 객체를 매개변수에 넘기면, Activator.CreateInstance() 메서드는 입력받은 형식의 인스턴스를 생성하여 반환한다.
- 일반화를 지원하는 버전의 CreateInstace() 메서드 ex.
List<int>의 인스턴스
List<int> list = Activator.CreateInstance<List<int>>();3.2 동적으로 데이터 값 할당하기(프로퍼티)_PropertyInfo.SetValue()
Type.GetProperties()의 반환형식인 PropertyInfo 클래스의 객체는 SetValue()와 GetValue()라는 메서드를 갖는다.
SetValue() : 프로퍼티에 값을 할당
GetValue() : 프로퍼티로부터 값을 읽기
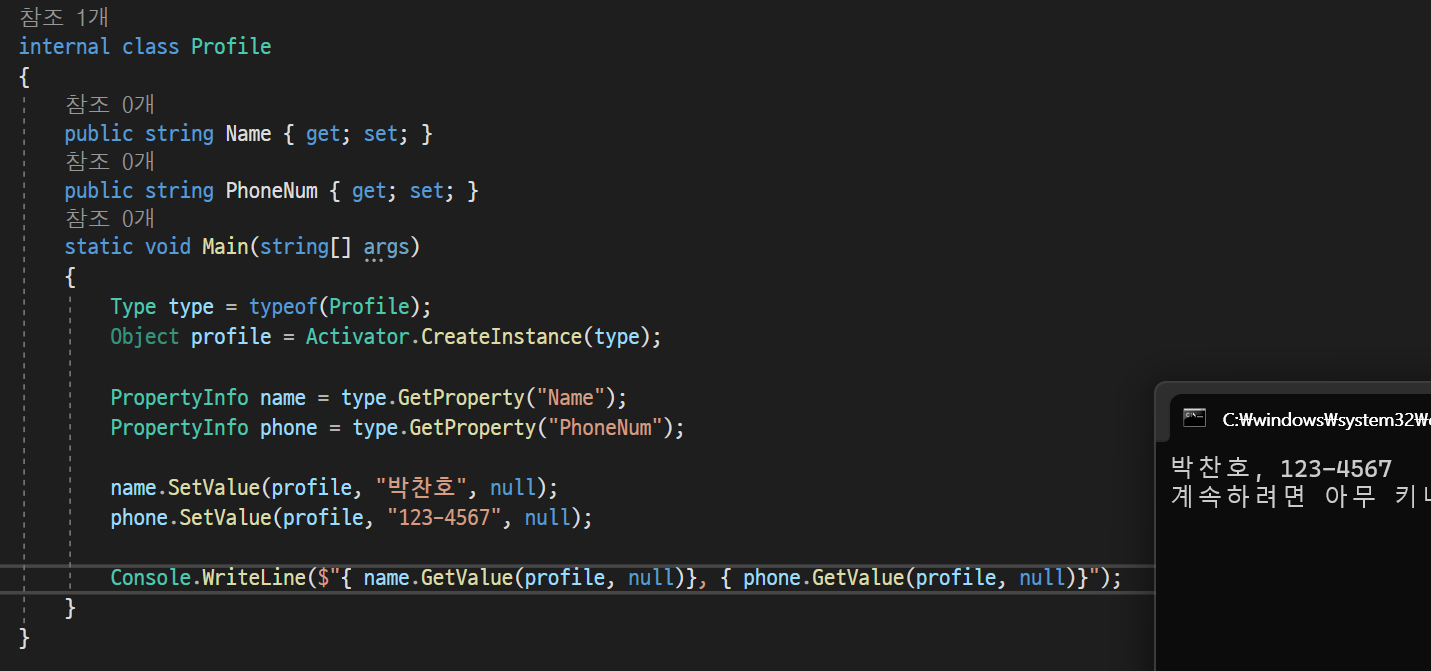
- Type.GetProperties(): 그 형식의 모든 프로퍼티를 PropertyInfo 형식의 배열로 반환
- Type.GetProgerty(): 특정 이름의 프로퍼티를 찾아 그 프로퍼티의 정보를 담은 하나의 PropertyInfo 객체만 반환
- 마지막 인수에 null을 쓴 이유:
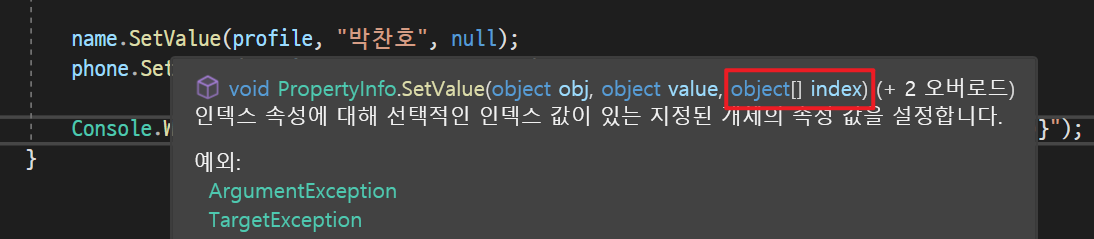 PropertyInfo클래스는 프로퍼티뿐만 아니라 인덱서의 정보도 담을 수 있다. 즉, 인덱서의 인덱스를 위해 사용되는데 프로퍼티는 인덱서가 필요 없으므로 이 예제에서 null로 할당한 것.
PropertyInfo클래스는 프로퍼티뿐만 아니라 인덱서의 정보도 담을 수 있다. 즉, 인덱서의 인덱스를 위해 사용되는데 프로퍼티는 인덱서가 필요 없으므로 이 예제에서 null로 할당한 것.
3.3 동적으로 메서드 호출하기_MethodInfo.Invoke()
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Profile
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string PhoneNum { get; set; }
public void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Name: {Name}, Phone: {PhoneNum}");
}
}
internal class program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type type = typeof(Profile);
Profile profile = (Profile)Activator.CreateInstance(type);
profile.Name = "박찬호";
profile.PhoneNum = "123-4567";
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Print");
//Invoke(클래스 객체 변수명, 호출할 메서드의 인수)
//현재 호출하는 메서드인 profile.Print()의 인수가 없으므로 null할당
method.Invoke(profile, null);
}
}
}4. 새로운 형식 만들기_System.Reflection.Emit 네임스페이스
동적으로 새로운 형식을 만드는 작업은 System.Reflection.Emit 네임스페이스에 있는 클래스들을 통해 이뤄진다.
Emit(이밋)은 프로그램이 실행 중에 만들어낸 새 형식을 CLR의 메모리에 '내보낸다'는 의미로 생각하면 된다. Emit 네임스페이스에서 제공하는 클래스들은 코드 요소를 만들어낸다는 의미에서 ~Builder꼴의 이름을 갖는다.
- 사용요령
- AssemblyBuilder를 이용해서 어셈블리를 만든다.
- ModuleBuilder를 이용해서 생성한 어셈블리 안에 모듈을 만들어 넣는다.
- 생성한 모듈 안에 TypeBuilder로 클래스(형식)을 만들어 넣는다.
- 생성한 클래스 안에 메서드(MethodBuilder)나 프로퍼티(PropertyBuilder)를 만들어 넣는다.
- 생성한 것이 메서드라면 ILGenerator를 이용해서 메서드 안에 CPU가 실행할 IL명령들을 넣는다. -> 메서드가 실행할 코드
CalculatorAssembly 생성
AssemblyBuilder newAssembly =
AssemblyBuilder.DefineDynamicAssembly
(new AssemblyName("CalculatorAssembly"), AssemblyBuilderAccess.Run);AssemblyBuilder는 스스로 생성하는 생성자가 없기 때문에 다른 팩토리 클래스(객체의 생성을 담당하는 클래스를 일컫는 말)의 도움을 받아야한다.
ㄴ 이 예제에서는 DefineDynamicAssembly() 메서드를 호출하면 AssemblyBuilder의 인스턴스를 만듦
Calculator 모듈 생성
ModuleBuilder newModule = newAssembly.DefineDynamicModule("Calculator");Sum1To100 클래스 생성
TypeBuilder newType = newModule.DefineType("Sum1To100");Calculate() 메서드 생성
MethodBuilder newMethod = newType.DefineMethod(
"Calculate",
MethodAttributes.Public,
typeof(int), //반환 형식
new Type[0]); //매개 변수예제 전체 코드
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//어셈블리 생성
AssemblyBuilder newAssembly = AssemblyBuilder.DefineDynamicAssembly(new AssemblyName("CalculatorAssembly"), AssemblyBuilderAccess.Run);
//모듈 생성
ModuleBuilder newModule = newAssembly.DefineDynamicModule("Calculator");
//클래스 생성
TypeBuilder newType = newModule.DefineType("Sum1To100");
//메서드 새성
MethodBuilder newMethod = newType.DefineMethod(
"Calculate",
MethodAttributes.Public,
typeof(int), //반환 형식
new Type[0]); //매개 변수
//IL 명령 삽입
ILGenerator generator = newMethod.GetILGenerator();
generator.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4, 1); //32비트 정수(1)를 계산 스택에 넣는다.
for (int i =2; i<=100; i++)
{
//32비트 정수[i]를 계산 스택에 넣는다
generator.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4, i);
//계산 후 계산 스택에 담겨 있는 두 개의 값을 꺼내 더한 후,
//그 결과를 다시 계산 스택에 넣는다.
generator.Emit(OpCodes.Add);
}
//계산 스택에 담겨 있는 값을 반환
generator.Emit(OpCodes.Ret);
//Sum1To100 클래스를 CLR에 제출 - 새로운 형식 만들기 끝!
newType.CreateType();
//이 형식의 인스턴스를 동적으로 생성해서 이용하기
object sum1To100 = Activator.CreateInstance(newType);
MethodInfo Calculate = sum1To100.GetType().GetMethod("Calculate");
Console.WriteLine(Calculate.Invoke(sum1To100, null));
}
}
}ㄴ 출력값: 5050
📄참고자료
<이것이 c#이다> 3판 - 박상현 지음 (한빛미디어)
[MSDN]라이브러리_System.Reflection

