개요
- 정렬의 궁극적 목적은 데이터를 쉽고 빠르게 찾고자 하는것(탐색)
버블정렬
- 자료구조를 순회하면서 이웃한 요소끼리 데이터를 교환하며 정렬을 수행
- 버블정렬의 비교횟수 n(n-1)/2 즉 O(N^2)
Vitamin 5-1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void BubbleSort(int DataSet[], int length);
void BubbleSort(int DataSet[], int length)
{
int count = 1;
int loopCount = 1;
int checkLoopCount = 1;
int test = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length-1; i++)
{
test = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < length-1-i; j++) // 외부 loop마다 배열이 정렬되어 있는 상태인지 test
{
printf("\nCheckLoopCount : %d\n\n", checkLoopCount++);
if (DataSet[j] < DataSet[j+1])
{
test++;
}
}
if (test == length-1-i) // lenhtg - 1- i 인 이유 : 정렬이 확실하게 끝난 부분을 제외한 나머지 부분을 체크
{
printf("Break!!\n\n");
break;
}
for (int j = 0; j < length - 1-i; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < length; k++)
{
printf("%d ", DataSet[k]);
}
if (DataSet[j] > DataSet[j + 1])
{
/* printf("j+1 : %d\n", j + 1);
printf("j+1 %d\n\n", DataSet[j + 1]);*/
int temp = DataSet[j];
DataSet[j] = DataSet[j + 1];
DataSet[j + 1] = temp;
printf("SwapCount : %d\n\n", count++);
}
printf("\nLoopCount : %d\n\n", loopCount++);
printf("=====================\n\n");
}
}
}
int main(void) {
int leng = 0;
int arr[] = { 5,1,6,4,2,3 };
leng = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Leng : %d\n\n", leng);
BubbleSort(arr, leng);
for (int i = 0; i < leng; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
}- Output
Leng : 6
CheckLoopCount : 1
CheckLoopCount : 2
CheckLoopCount : 3
CheckLoopCount : 4
CheckLoopCount : 5
5 1 6 4 2 3 SwapCount : 1
LoopCount : 1
=====================
1 5 6 4 2 3
LoopCount : 2
=====================
1 5 6 4 2 3 SwapCount : 2
LoopCount : 3
=====================
1 5 4 6 2 3 SwapCount : 3
LoopCount : 4
=====================
1 5 4 2 6 3 SwapCount : 4
LoopCount : 5
=====================
CheckLoopCount : 6
CheckLoopCount : 7
CheckLoopCount : 8
CheckLoopCount : 9
1 5 4 2 3 6
LoopCount : 6
=====================
1 5 4 2 3 6 SwapCount : 5
LoopCount : 7
=====================
1 4 5 2 3 6 SwapCount : 6
LoopCount : 8
=====================
1 4 2 5 3 6 SwapCount : 7
LoopCount : 9
=====================
CheckLoopCount : 10
CheckLoopCount : 11
CheckLoopCount : 12
1 4 2 3 5 6
LoopCount : 10
=====================
1 4 2 3 5 6 SwapCount : 8
LoopCount : 11
=====================
1 2 4 3 5 6 SwapCount : 9
LoopCount : 12
=====================
CheckLoopCount : 13
CheckLoopCount : 14
Break!!
1 2 3 4 5 6
삽입정렬
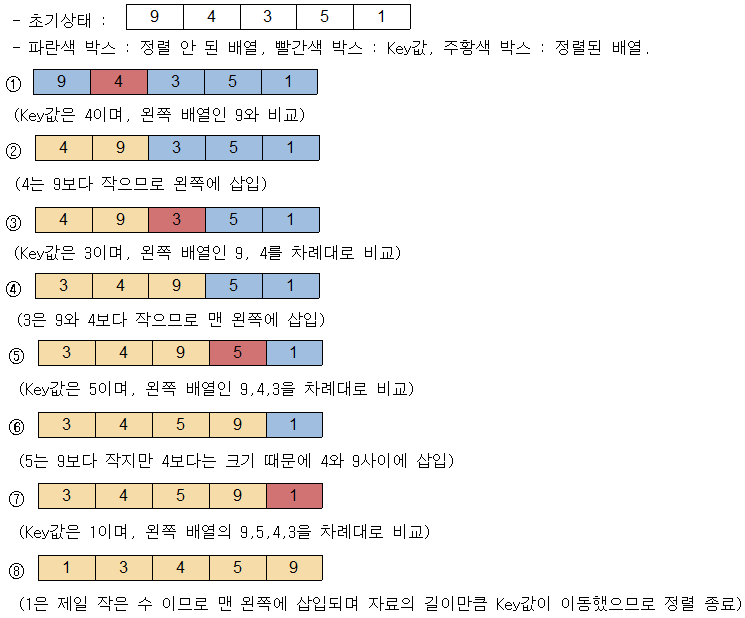
- 자료구조를 순차적으로 순회하면서 순서에 어긋나는 요소를 찾고 그 요소를 올바른 위치에 다시 삽입.
- 범위는 처음에 2에서 1칸씩 늘어남.
- 범위의 맨뒤 요소를 그 앞요소와 비교한다. 이때 맨뒤 요소를 제외한 나머지 요소는 전 과정에서 이미 정렬이 끝난상태이다.
- 비교결과 맨뒤 요소가 잘못된 위치에 있는경우 범위내 올바른 위치에 그 요소를 삽입한다. 이 결과 범위는 정렬이 완료된 상태이다.
- 올바른 위치는 한칸씩 앞쪽으로(index:0쪽으로)가면서 작은 요소가 나올때까지 비교
- 범위를 하나 늘려 이 과정을 반복한다.
- 삽입정렬은 버블정렬과 비교했을때 자료구조가 정렬되어있다면 각 반복마다 비교연산은 1번만 수행 (N-1)*1!
QuickSort
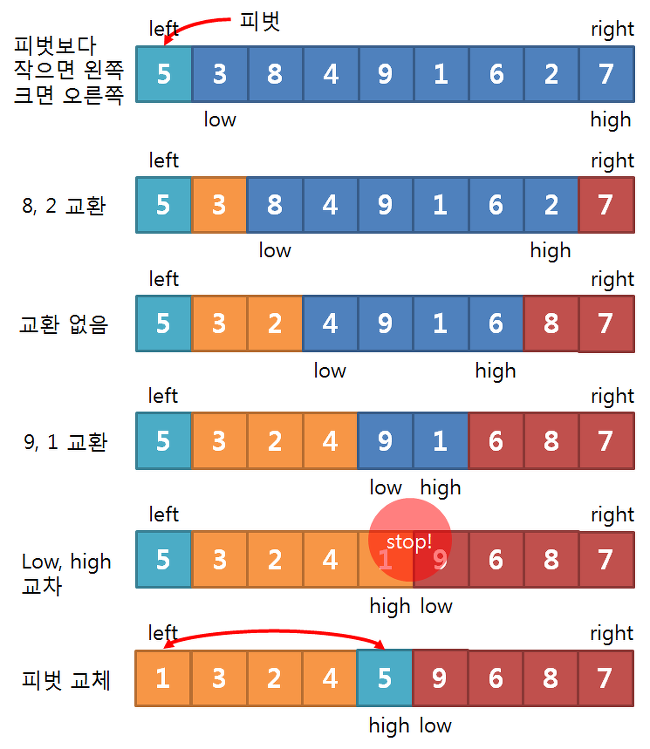
(출처 ㅣ https://akdl911215.tistory.com/386)
- 분할 정복(Divide and Conquer)에 바탕을둔 알고리즘
- 기준요소(Pivot)설정과 분할의 반복
- 피벗을 가장 왼쪽으로 했을 경우 Partition의 반환값은 right여야함
-> 둘이 교차하는 경우 ..
QuickSort 성능
BestCase
- 재귀 호출의 깊이 : log2 N
- 분할을 위한 비교 회수 : 한 깊이 마다 N ( 모든 원소를 pivot과 비교 )
WorstCase
- 매 재귀호출마다 자료구조의 분할이 1:n-1로 이루어지는 경우
- 깊이 : n-1
- 총 비교횟수 (n*(n-1))/2
averageCase
- 1.39n*log2(N) : 최선의 경우에 비해 39%정도 느림
qsort()
함수 포인터
- 변수와 상수처럼 함수도 메모리상에 존재한다.
- 함수에 대한 포인터를 가지고 있다면 해당 포인터가 가리키는 메모리에 위치한 함수를 실행가능.
Vitamin 5-2
int ComparePointDescend(const void* num_1, const void* num_2) {
int* _num_1 = (int*)num_1;
int* _num_2 = (int*)num_2;
if (*_num_1 < *_num_2)
return 1;
if (*_num_1 == *_num_2)
return 0;
if (*_num_1 > *_num_2)
return -1;
}Output
Before...
5 1 4 2 6 3
After...
6 5 4 3 2 1qsort() 응용문제
- 번외)
* 큰 구조체에서 StackOverFlow 문제
https://gonyzany.tistory.com/493- [프로젝트] 메뉴[서 "속성" 속성을 선택합니다.
2. [링커] -> "시스템"에서 "스택 예약 크기" 입력합니다.
- [프로젝트] 메뉴[서 "속성" 속성을 선택합니다.
int ComaprePoint(const void* ele_1, const void* ele_2) {
Point* p_1 = (Point*)ele_1;
Point* p_2 = (Point*)ele_2;
if (p_1->point > p_2->point)
return -1;
if (p_1->point == p_2->point)
return 0;
if (p_1->point < p_2->point)
return 1;
}연습문제
void BubbleSort(int DataSet[], int length)
{
int count = 1;
int loopCount = 1;
int checkLoopCount = 1;
int test = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < length - 1; j++) // 이미 정렬되어있는 배열인지 테스트
{
//printf("\nCheckLoopCount : %d\n\n", checkLoopCount++);
if (DataSet[j] < DataSet[j + 1])
{
test++;
}
}
if (test == length - 1)
{
printf("DataSet Already Sorted!!!\n\n");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < length-1; i++)
{
test = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < length-1-i; j++) // 외부 loop마다 배열이 정렬되어 있는 상태인지 test
{
printf("\nCheckLoopCount : %d\n\n", checkLoopCount++);
if (DataSet[j] < DataSet[j+1])
{
test++;
}
}
if (test == length-1-i) // lenhtg - 1- i 인 이유 : 정렬이 확실하게 끝난 부분을 제외한 나머지 부분을 체크
{
printf("Break!!\n\n");
break;
}
for (int j = 0; j < length - 1-i; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < length; k++)
{
printf("%d ", DataSet[k]);
}
if (DataSet[j] > DataSet[j + 1])
{
/* printf("j+1 : %d\n", j + 1);
printf("j+1 %d\n\n", DataSet[j + 1]);*/
int temp = DataSet[j];
DataSet[j] = DataSet[j + 1];
DataSet[j + 1] = temp;
printf("SwapCount : %d\n\n", count++);
}
printf("\nLoopCount : %d\n\n", loopCount++);
printf("=====================\n\n");
}
}
}void InsertionSort(Node** head)
{
int length = DLL_GetNodeCount(*head);
printf("debug:: length %d\n", length);
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < length; k++)
{
Node* Current = DLL_GetNodeAt(*head, k);
printf("Debug::List[%d] : %d\n", k, Current->data);
}
Node* targetNode = DLL_GetNodeAt(*head, i); // 범위내 가장 앞 노드
printf("debug::targetNodeData : %d\n", targetNode->data);
for (int j = i-1; j >= 0; j--)
{
printf("debug:: j:%d j값 %d\n", j ,DLL_GetNodeAt(*head, j)->data);
if (DLL_GetNodeAt(*head,j)->data >= targetNode->data)
{
continue;
}
else
{
int key = targetNode->data;
DLL_InsertAfter(DLL_GetNodeAt(*head, j), DLL_CreateNode(key));
DLL_RemoveNode(head, targetNode);
DLL_DestroyNode(targetNode);
}
}
}
}int Partition(int DataSet[], int Left, int Right)
{
int First = Left;
if (Right-Left >= 3)
{
for (int i = Left; i < Left+2; i++) // pivot 구하기 첫 3요소중 중앙값을 가장 앞으로 보내기
{
for (int j = Left; j < Left + 2 - i; j++)
{
if (DataSet[i] > DataSet[i + 1])
{
Swap(&DataSet[i], &DataSet[i + 1]);
}
}
}
Swap(&DataSet[Left], &DataSet[Left+1]);
}
int pivot = DataSet[First];
printf("pivot = %d\n\n", pivot);
Left++;
while (Left < Right)
{
while (Left < Right && DataSet[Left] <= pivot) // left cursur는 pivot보다 큰 값을 찾아 나간다.
{
Left++;
}
while (Right >= Left && DataSet[Right] >= pivot) // right는 pivot보다 작은 값을 찾아나간다.
{
Right--; // right가 pivot보다 작은 값을 찾지 못한경우 right =
}
if (Left < Right) // 두 curser가 만나지 않았다면 swap
{
Swap(&DataSet[Left], &DataSet[Right]);
}
else // 만난경우 종료
{
break;
}
}
printf("L : %d, R : %d \n\n",Left,Right);
Swap(&DataSet[First], &DataSet[Right]); // 결과적으로 pivot 왼쪽에는 pivot보다 작은 값이, 오른쪽에는 큰값이 모인다.
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
printf("%d ", DataSet[i]);
}
printf("\n\n");
return Right;
}void QucikSort(int DataSet[], int Left, int Right)
{
//if (Left < Right) { // Trivial 해진 경우 -> 추가적인 분할이 불가능 해 진 경우
// int index = Partition(DataSet, Left, Right);
// QucikSort(DataSet, Left, index - 1);
// QucikSort(DataSet, index + 1, Right);
//}
LinkedListStack* Stack;
LLS_CreateStack(&Stack);
int tempLeft = Left;
int tempRight = Right;
LLS_Push(Stack, LLS_CreateNode(Right));
LLS_Push(Stack, LLS_CreateNode(Left));
while (!LLS_IsEmpty(Stack))
{
tempLeft = LLS_Pop(Stack)->data;
tempRight = LLS_Pop(Stack)->data;
printf("%d %d\n\n", tempLeft, tempRight);
if (tempLeft < tempRight) {
int index = Partition(DataSet, tempLeft, tempRight);
LLS_Push(Stack, LLS_CreateNode(tempRight));
LLS_Push(Stack, LLS_CreateNode(index+1));
LLS_Push(Stack, LLS_CreateNode(index-1));
LLS_Push(Stack, LLS_CreateNode(tempLeft));
}
}
}