Executors란
Thread나 Runnable처럼 low 레벨의 api를 직접 다루는 것이 아니라 (interrupt, join, sleep 등을 사용해서 쓰레드를 만들고 관리하는 것) 이러한 작업들을 고수준의 api에게 위임하기 위해 만들어졌다. Executors가 쓰레드를 만들고 관리하기 때문에 Runnable만 제공해주면 된다.
Executor 인터페이스
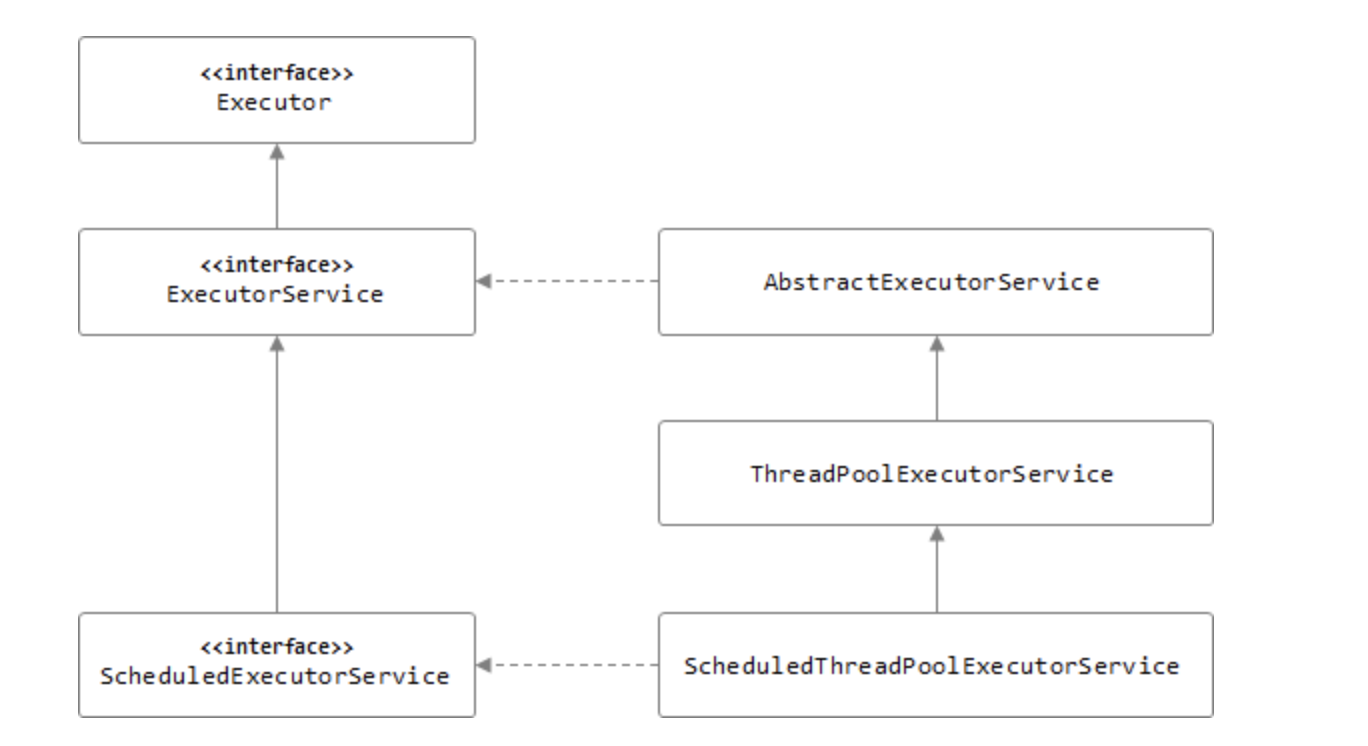
Executors 사용 예시
public class ExecutorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ExecutorService 인터페이스 사용
/* ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
executorService.submit(getRunnable("Hello "));
executorService.submit(getRunnable("Hong "));
executorService.submit(getRunnable("The "));
executorService.submit(getRunnable("Java "));
executorService.submit(getRunnable("Thread "));*/
// 다음 작업이 들어올 때까지 계속 대기하기 때문에 프로세스가 죽지 않아서 명시적으로 shutdown()을 해줘야한다.
// ScheduledExecutorService 인터페이스 사용
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
// scheduledExecutorService.schedule(getRunnable("Hello"), 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(getRunnable("Hello"), 1,2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 1초 기다렸다가 2초마다 출력
// scheduledExecutorService.shutdown(); // 현재 진행 중인 작업을 완료하고 종료하겠다.
// executorService.shutdownNow(); // 지금 돌고 있는 것 상관없이 지금 즉시 종료하겠다.
}
private static Runnable getRunnable(String message) {
return () -> System.out.println(message + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}Callable 인터페이스
Runnable 인터페이스 같지만, 리턴값을 가질 수 있다. (Runnable은 반환 타입이 void)
Future 인터페이스
비동기적인 작업의 현재 상태를 조회하거나 결과를 가져올 수 있게 제공해주는 인터페이스이다.
결과는 계산이 완료될 때 get()으로 가져올 수 있는데 get() 이전까지는 기다리지 않고 코드를 실행하다가 get() 하고나서 멈추고 결과값이 계산될 때까지 기다리다가 완료 후 결과를 검색한다. 이러한 방식을 블로킹 콜이라고 한다.
- invokeAll : 실행 각 작업의 완료를 모두 기다린 후 결과를 한 번에 전달하는 메서드이다. 각 작업을 모두 기다려야 하기 때문에 하나라도 완료가 늦어질 경우 전체 속도가 느려질 수 있는 단점이 있다.
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
Callable<String> hello = () -> {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
return "Hello";
};
Callable<String> java = () -> {
Thread.sleep(3000L);
return "Java";
};
Callable<String> hong = () -> {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
return "Hong";
};
List<Future<String>> futures = executorService.invokeAll(Arrays.asList(hello, java, hong));
for(Future<String> future : futures) {
System.out.println(future.get());
}- invokeAny : invokeAll의 단점을 보완하기 위한 것으로 모두 기다릴 필요 없이 먼저 처리된 것을 먼저 전달하기 위해 사용되는 메서드이다.
String invokeAny = executorService.invokeAny(Arrays.asList(hello, java, hong));
System.out.println(invokeAny);CompletableFuture란
자바에서 비동기 프로그래밍을 지원하는 인터페이스이다. Future에서 하기 어려웠던 작업들을 수월하게 할 수 있다.
- Future에서 하기 어려웠던 작업들
1) Future를 외부에서 완료시킬 수 없다. 취소하거나 get()에 타임아웃을 설정할 수 없다.
2) 블로킹 코드(get())를 사용하지 않고서는 작업이 끝났을 때 콜백을 실행할 수 없다.
-> Future를 통해 결과값을 만들고 무언가를 하는 작업은 get() 이후에 와야한다.
3) 여러 Future를 조합할 수 없다. 예) 이벤트 정보를 가져온 다음에 이벤트에 참여한 회원 목록 가져오기
4) 예외처리용 API를 제공하지 않는다.
1) 비동기로 작업 실행하기
- 리턴값이 없는 작업: runAsync() 사용
- 리턴값이 있는 작업: supplyAsync() 사용
2) 콜백 제공하기
- thenApply(Function): 리턴값을 받아서 다른 값으로 바꾸는 콜백
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("Hello " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
}).thenApply((s) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return s.toUpperCase();
});
System.out.println(future.get());- thenAccept(Consumer): 리턴값을 받아서 리턴하지 않고, 그냥 작업을 처리하는 콜백
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("Hello " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
}).thenAccept((s) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());
});
future.get();- thenRun(Runnable): 리턴값을 받지 않고 다른 작업을 처리하는 콜백
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("Hello " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
}).thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
future.get();- CompletableFuture는 별다른 Executor를 사용하지 않아도 내부적으로 포크 조인풀에 있는 commonPool을 쓰게되는데 원한다면 직접 쓰레드풀을 만들어서 제공할 수 있다. runAsync() 나 supplyAsync() 메서드를 호출할 때 2번째 인자로 줄 수 있다. 콜백을 실행할 풀을 다른 곳에서 실행하고 싶을 때는 thenRunAsync(), thenAcceptAsync(), thenRunAsync() 등을 제공하고 있어서 2번째 인자로 넣어줄 수 있다.
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("Hello " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
}, executorService).thenRunAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}, executorService);
future.get();
executorService.shutdown();3) 조합하기
- thenCompose(): 두 작업이 서로 이어서 실행하도록 조합한다. 두 작업이 서로 연관관계가 있을 때 사용한다.
CompletableFuture<String> hello = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("Hello " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future = hello.thenCompose(CompletableFutureTest::getWorld);
System.out.println(future.get());
private static CompletableFuture<String> getWorld(String message) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("World : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return message + " World";
});
}- thenCombine(): 두 작업을 독립적으로 실행하고 둘 다 종료했을 때 콜백을 실행한다. 두 작업이 연관관계가 없어 따로 실행하고 모두 완료된 결과를 바탕으로 추가 작업을 하고 싶을 때 사용한다.
CompletableFuture<String> hello = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("Hello " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
});
CompletableFuture<String> world = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("World : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "World";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future = hello.thenCombine(world, (h, w) -> h + " " + w); // BiFunction
System.out.println(future.get());- allOf(): 여러 작업을 모두 실행하고 모든 작업 결과에 콜백을 실행한다.
CompletableFuture<String> hello = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("Hello " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
});
CompletableFuture<String> world = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("World : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "World";
});
List<CompletableFuture<String>> futures = Arrays.asList(hello, world);
CompletableFuture[] futuresArray = futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[futures.size()]);
CompletableFuture<List<String>> results = CompletableFuture.allOf(futuresArray)
.thenApply(v -> futures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
results.get().forEach(System.out::println); - anyOf(): 여러 작업 중에 가장 빨리 끝난 하나의 결과에 콜백을 실행한다.
CompletableFuture<String> hello = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("Hello " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
});
CompletableFuture<String> world = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("World : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "World";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.anyOf(hello, world).thenAccept(System.out::println);
future.get();4) 예외처리하기
- exceptionally(Function)
boolean throwError = true;
CompletableFuture<String> hello = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if(throwError) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
System.out.println("Hello " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
}).exceptionally(ex -> {
System.out.println(ex);
return "Error!";
});
System.out.println(hello.get());- handle(BiFunction): 첫번째 파라미터는 정상적인 경우의 결과값, 두번째 파라미터는 예외 발생 시 에러를 넣어줘서 정상적으로 종료되었을 때랑 에러가 발생했을 때랑 두 경우 모두 사용할 수 있다.
boolean throwError = true;
CompletableFuture<String> hello = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if(throwError) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
System.out.println("Hello " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "Hello";
}).handle((result, ex) -> {
if(ex != null) {
System.out.println(ex);
return "ERROR!";
}
return result;
});
System.out.println(hello.get());*참고 자료
백기선 - 더 자바, Java 8
