
0. git 배경지식
git은 공부할 것들이 많지만, 기본적으로 알아두면 좋을 사항은 다음과 같다.
4 states of git
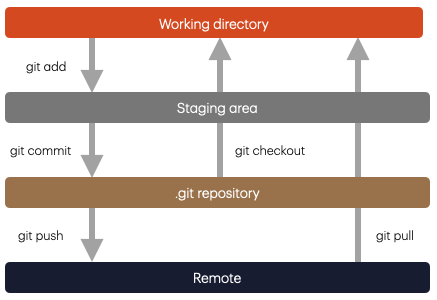
4 basic commands
- pull
- add
- commit
- push
1. git 설치
# on Linux (Debian/Ubuntu)
sudo apt install git
# conda 환경에서 다운로드 할 경우
conda install git2. github에서 repository 생성
이 때 생성한 repository의 web URL을 복사해야 한다.
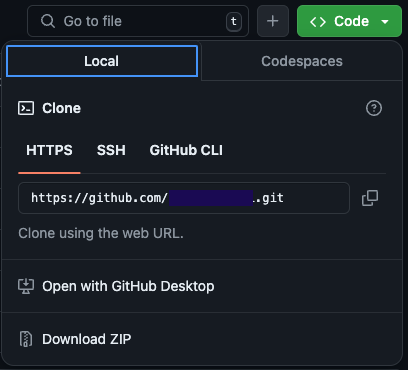
3. 로컬 repository 설정
리눅스 로컬 디렉토리에서 git 저장소를 만들어 주고, 이를 github의 repository와 연동해 주는 작업
# 연결하고자 하는 프로젝트 파일들을 저장할 디렉토리로 이동
cd /path/to/your/project
# git repo 초기화 작업
git init
# github repo와 연동
git remote add origin https://github.com/repository-name.git
git remote -v특히 git remote -v이 부분은 꼭 해 주어야 한다!
결과는 다음과 같다.
origin https://github.com/repository-name.git (fetch) # 데이터를 가져올 URL
origin https://github.com/repository-name.git (push) # 데이터를 보낼 URL
git remote와git clone의 차이점
git clone을 사용할 경우
- repository 이름을 딴 폴더가 새로 생성됨
- 원격 repository의 내용을 자동으로 가져옴
git remote을 사용할 경우
- 현재 디렉토리와 repository의 URL이 연결됨
- 내용을 가져오거나 올리려면 별도의
git pull또는git push명령어가 필요
4. git push
세 가지만 딱 기억하면 된다.
git addgit commitgit push
구체적인 내용은 다음과 같다.
# 파일 생성 혹은 옮겨오기 (예시에서는 README 파일 생성)
vi README.md # 파일 작성 후 저장
# staging area에 local 파일 전달
git add . # 현재 디렉토리의 모든 파일을 staging area로 이동시켜 커밋 준비 상태로 만듦. 혹은 git add README.md와 같이 특정 파일만을 전달할 수 있음
# (optional) 현재 상태 확인
git status # staging area와 현재 local 디렉토리 컨텐츠 상황이 다르면 알려 줌코드대로 git status를 실행하면 다음과 같이 뜬다.
On branch master
No commits yet
Changes to be committed:
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: README.mdOn branch master: 현재 작업 중인 branch가master임을 나타냄No commits yet: 아직 커밋이 없는 초기 상태임을 나타냄- `
Changes to be committed: Staging area에 올라간 파일 목록을 표시
특별한 에러가 발견되지 않는 경우로, 이 경우 바로 다음 스텝으로 가면 된다.
만약 브랜치의 이름을 바꾸고 싶다면, 다음 명령어를 사용
git branch -m branch_name다음 스텝
# .git repository에 staging area에 올린 파일 설명 전달
git commit -m "new file: README.md" # Staging area에 있는 파일 변경 사항을 기록하여 Git history에 저장
> master (root-commit) e950edf] new file: README.md
1 file changed, 7 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 README.md이제 마지막
# remote(github repository)에 커밋한 파일 최종 전달
git push origin master # 로컬 branch의 변경 사항을 원격 repository로 업로드
> Enumerating objects: 3, done.
Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done.
Delta compression using up to 112 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 431 bytes | 431.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To https://github.com/repository-name.git
* [new branch] master -> master
Branch 'master' set up to track remote branch 'master' from 'origin'.
# (optional) 현재 상태 확인
git status
> On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean더이상 커밋할 것 없이, 현재 로컬 디렉토리와 github repository가 올바르게 연동되었음을 알 수 있다.
(Optional) branch 여러 개 연동하기
규모가 큰 repository를 운영하거나 사용할 때, branch가 여러 개인 경우가 있다. 그러나 위 방식만으로는 모든 branch를 가져올 수 없다.
remote repository로부터 모든 branch들을 가져오기
git fetch --all
# 모든 branch들이 다 로딩되었는지 확인
git branch -rbranch 간 이동하기
git checkout <branch_name>여기서 <branch_name>은 이동하려는 branch 이름으로 대체해 주어야 한다!
혹은 트래킹이 되지 않은 branch로 이동해 주고 싶다면, 다음을 사용한다.
git checkout -b <branch_name> origin/<branch_name>여기서 origin/은 내 로컬(working area)을 의미한다.
References
https://medium.com/mindorks/what-is-git-commit-push-pull-log-aliases-fetch-config-clone-56bc52a3601c
