[Linux, File System] File System Structure & Analysis | VFS (Virtual File System)
File System
Programmers DevCourse Final Project
프로그래머스 데브코스 리눅스 시스템 및 커널 전문가 과정을 수강하면서 4번째 프로젝트 과제로 발표했던 내용입니다.
발표 영상 : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ebRT_yXaFhE
File System Introduction
File System
An OS component to manage storage
Layered Structure - Abstraction
- Disk (Physical): Platter, Track, Sector, Cylinder, Surface, Spindle, Head, Arm
- Disk Device Driver (Logical): Disk Blocks (4KB)
- File System: File – Stream of bytes
→ Connect File and Disk blocks - System Call: open(), read(), write(), …
Examples of Linux File System
- Ext2/3/4: block group, journaling, extent-based FS
- FAT, exFAT: FAT based FS
- F2FS: Flash friendly FS
- Btrfs: COW based FS, strong consistency
- NFS, GFS, Ceph, ..: FS for distributed systems
- XFS: Extent and journaling based FS, Parallel I/Os (scalable)
- …
File System Structure
Basic Layout
System programmer perspective: Data, Metadata
Metadata?
- Information used for managing files and file systems
- Superblock
- A record of the characteristics of a file system
- Total size, block size, location of inodes, root directory, usage, … - inode
- Represent an object such as a file, a directory, a device, …
- Stores the attributes and disk block locations - Bitmap
- Data structure to differentiate the free(0)/used(1) entry of inodes/data blocks - Others
- Group descriptor, journal, FAT, segment, …
Simple File System Example
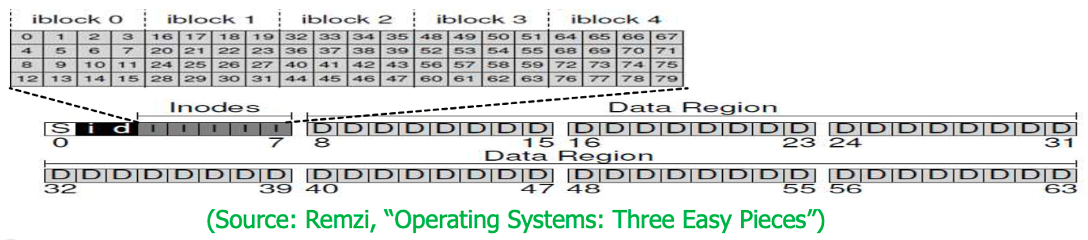
- Superblock (S) : Inode bitmap location, number of block, …
- Inode bitmap (i)
- Data bitmap (d)
- Inodes (I)
- 3 to 7, 256byte per inode
- 16 inodes per disk block (disk block: 2^12, inode: 2^8)
- Total 16 × 5 = 80 inodes - Data region (D) : User data
- 8 to 63 (56 blocks)
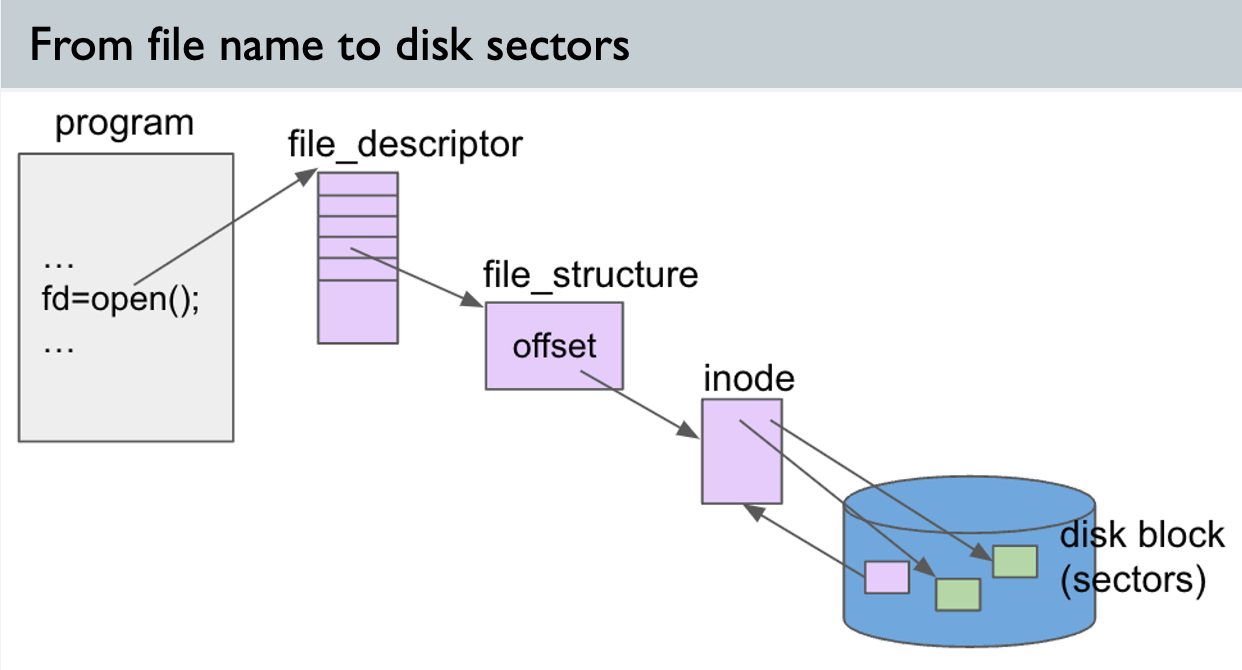
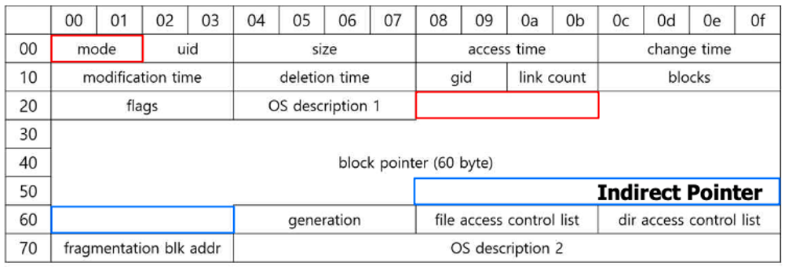
inode
- File metadata
- Components
- File information : mode, uid, size, time, link count, blocks, ..- Access: stat()
- Disk block location (inode = index node)
- Direct block pointers(12 or 15)
- Single/Double/Triple Indirect block pointers(1/1/1)
- Direct block pointer → Points disk block directly
- Indirect block pointer → Points Index block(pointer for Disk block
Example) Root directory → hello.c (7KB)
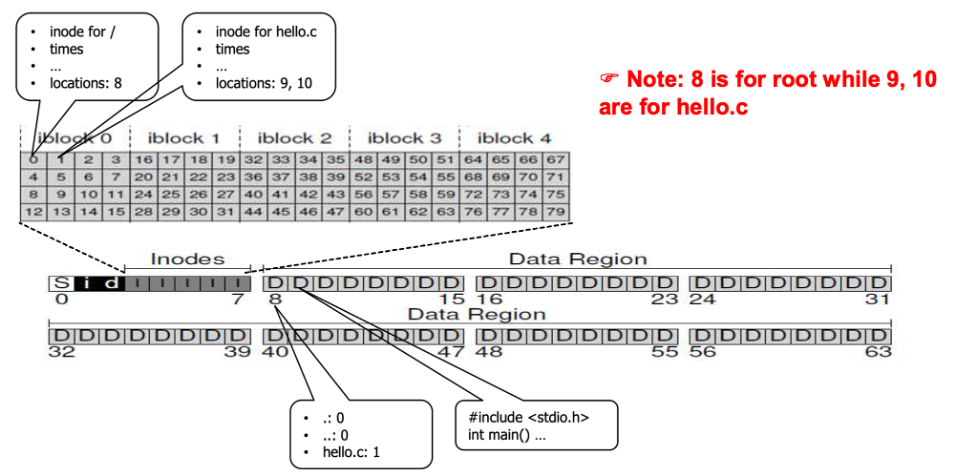
-
/(root) → inode 0, disk block 8
- Directory entry: <file name, i_number> -
hello.c→ inode 1, disk block 9, 10
File System Analysis
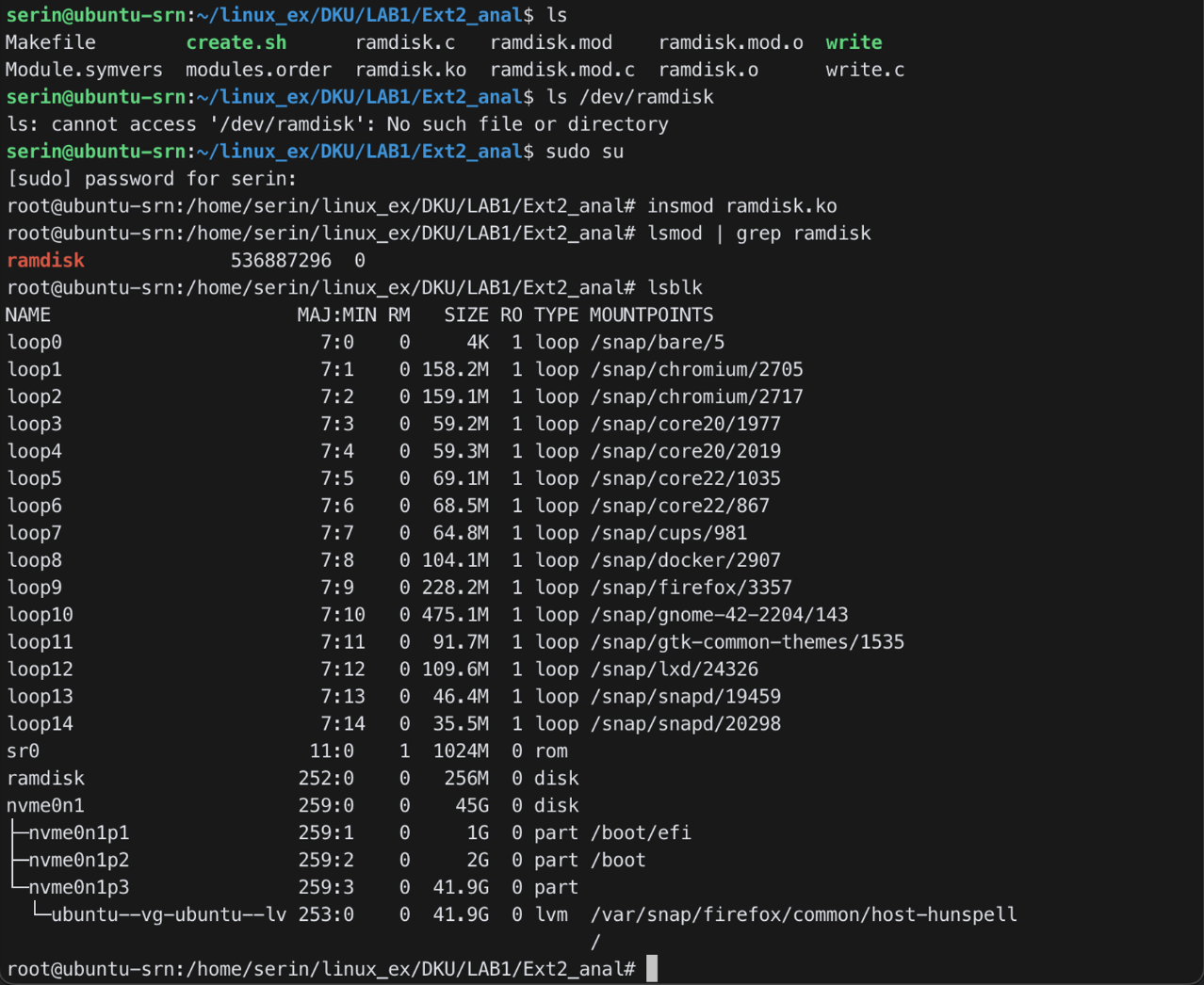
- Install ramdisk
insmod ramdisk.ko
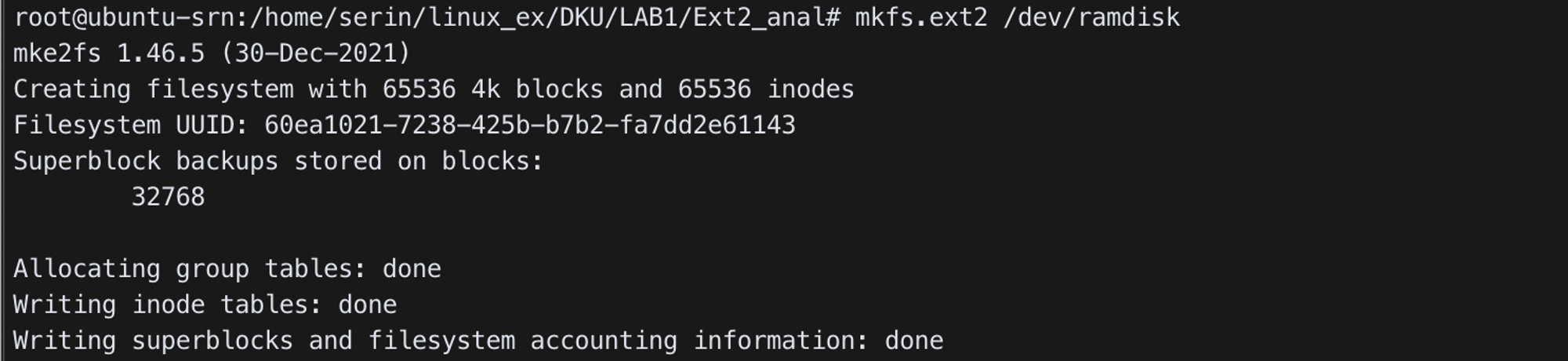
- Make ext2 file system on ramdisk
mkfs.ext2 /dev/ramdisk
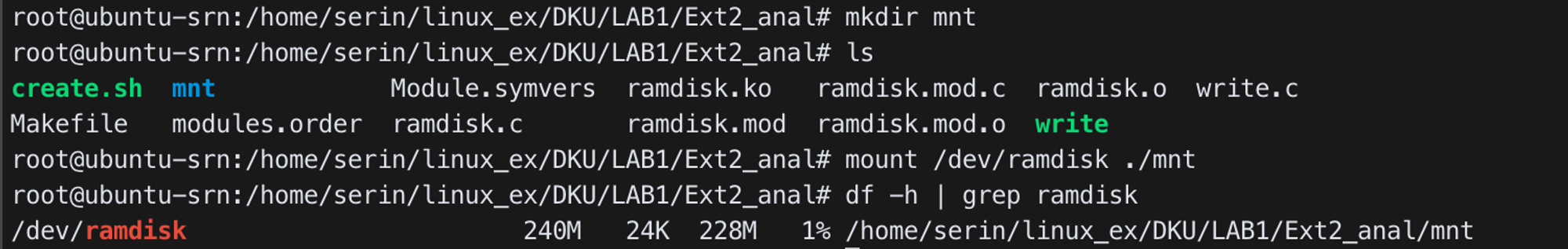
- Mount ext2 file system
mkdir mnt
mount /dev/ramdisk ./mnt
- Create file, directory
/a/a1(10KB),/a/a2(70KB),/b/b1(10KB),/c/c1(70KB)
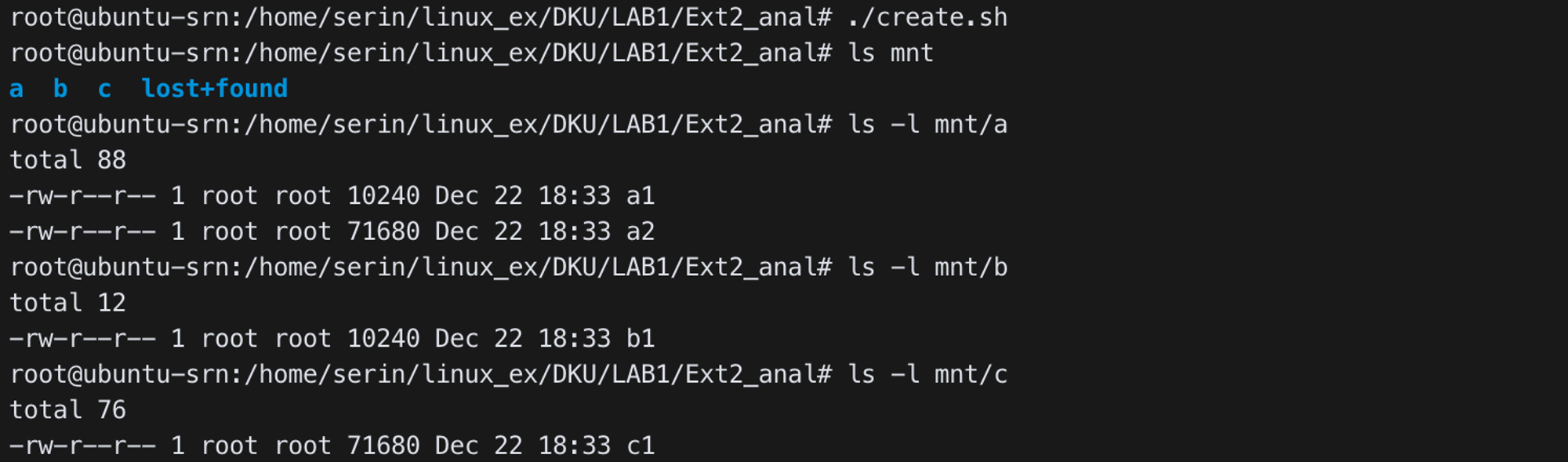
- Examine ramdisk using
xxdxxd→ Display a (binary) file in a hex format
--s [+/-] <offset>→ start at bytes offset
--l <len>→ Stop after writing
-g <bytes>→ Groupsize, separate the output of every bytesxxd -g 4 -l 0x100 -s 0x400 /dev/ramdisk→ Display from 0x400 to 0x500 with 4bytes groupsize
Boot block & Superblock
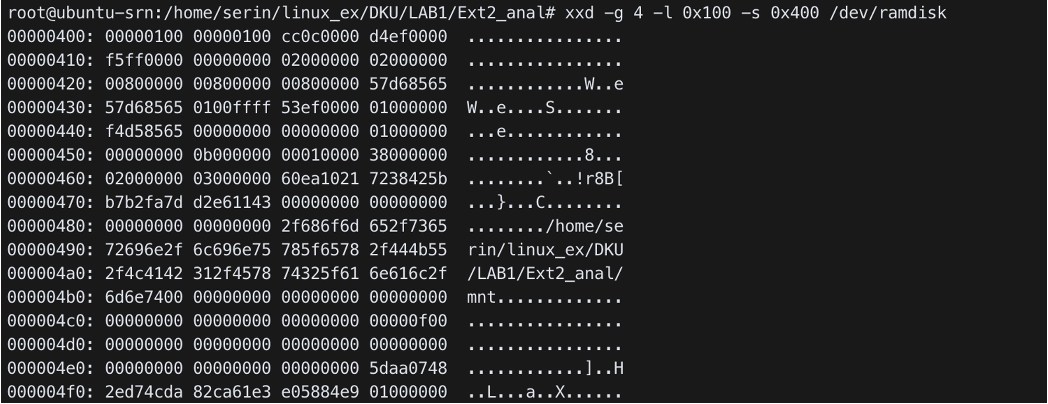
- Boot block : Data related to booting, 2 sectors (0~0x400)
- Superblock : Starts at 0x400, Group descriptor: Starts at
0x1000(4KB)
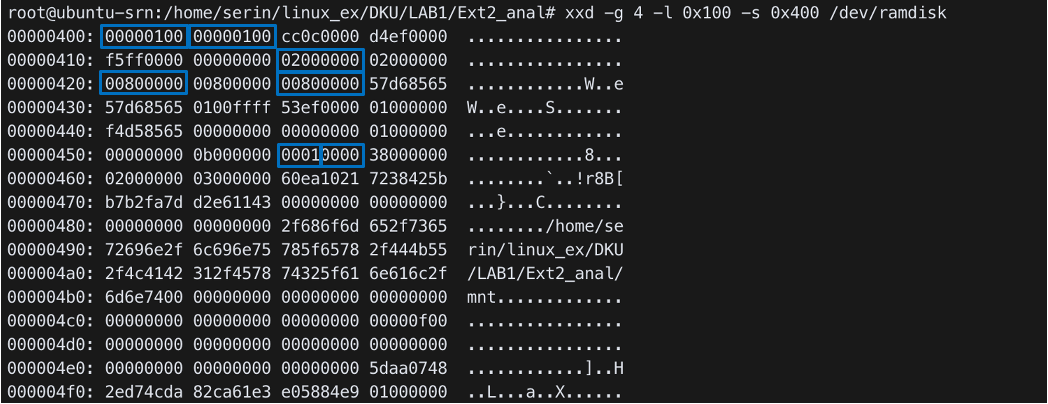
-xxd -g 4 -l 0x200 -s 0x400 /dev/ramdisk- Display a (binary) file in a hex format
- Starting from 0x400, display 0x200 bytes with 4bytes groupsize
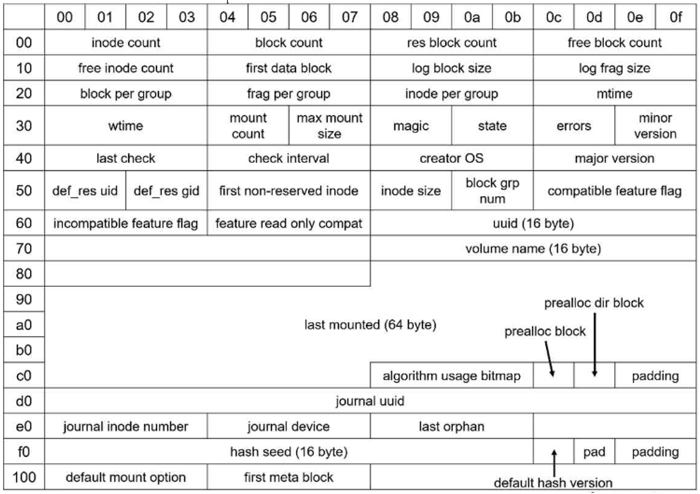
ext2_super_block source: https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.30/source/fs/ext2/ext2.h#L414
 |  |
|---|
(Big Endian / Little Endian 확인 후 Kernel 자료구조 참고하여 해석)
- inode count:
0x10000 - block count:
0x10000 - log block size:
0x2 - blocks per group:
0x8000 - inodes per group:
0x8000 - block group number:
0x0 - inode size:
0x100
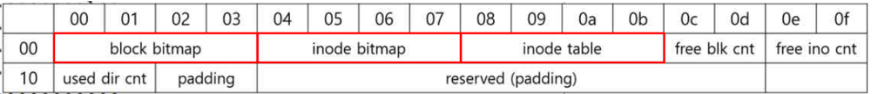
Group descriptor
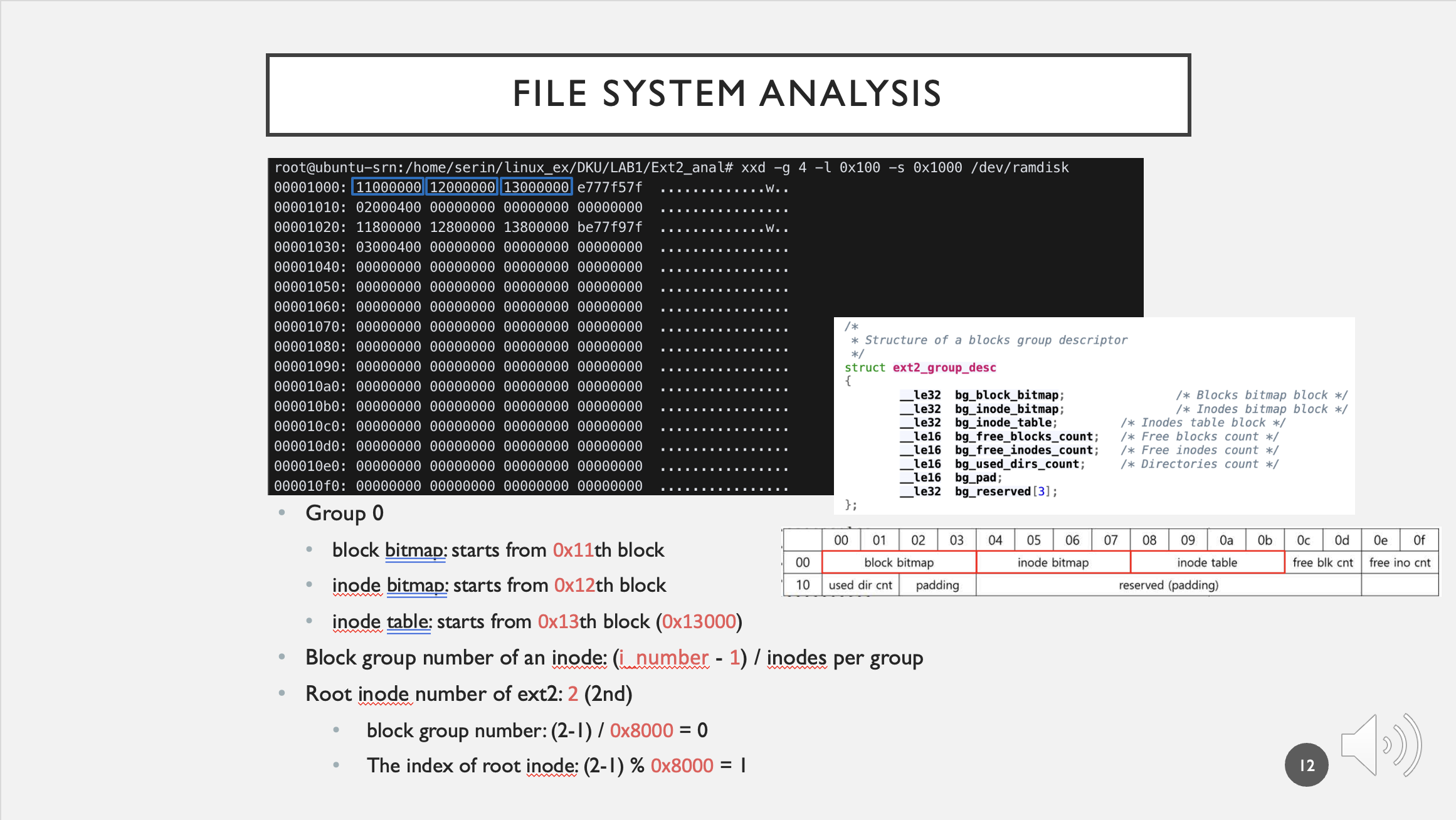
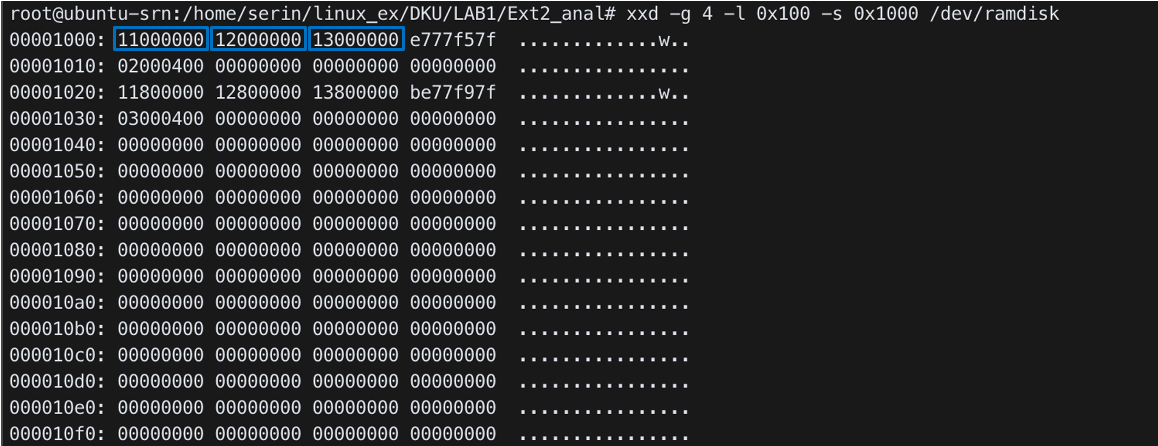
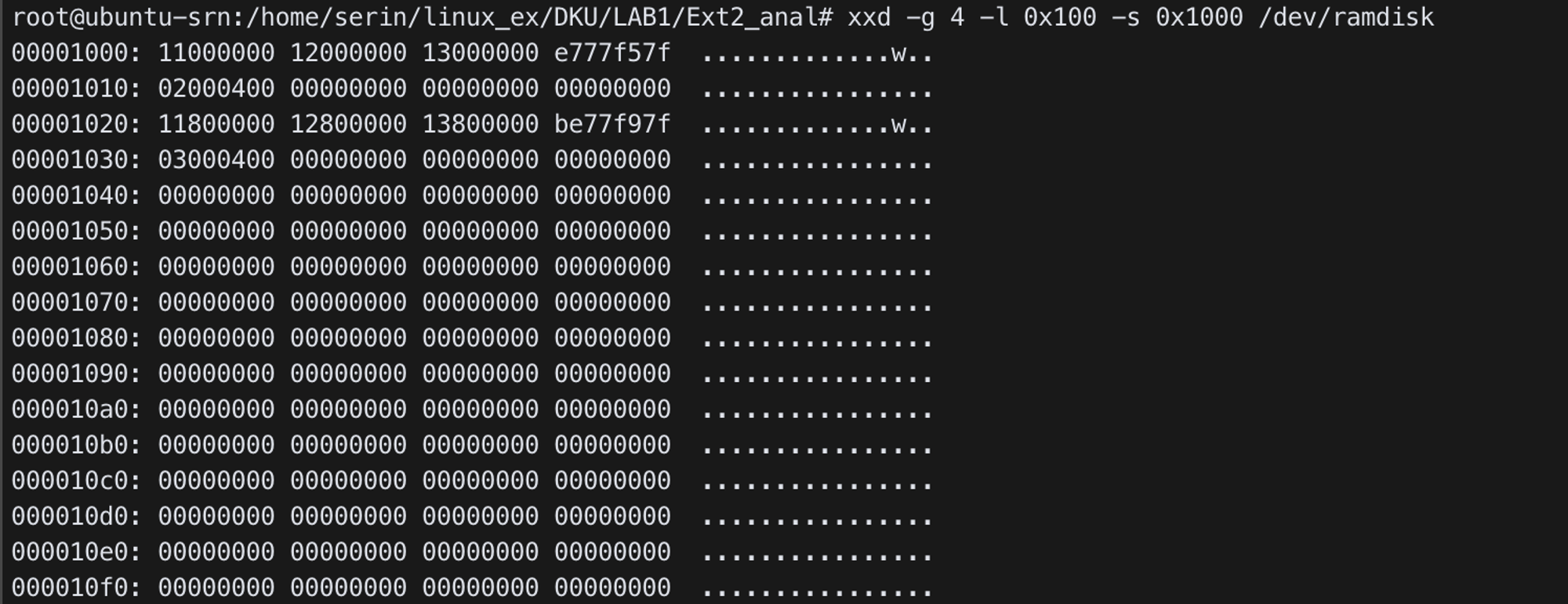
xxd -g 4 -l 0x100 -s 0x1000 /dev/ramdisk
ext2_group_desc source: https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.15.30/source/fs/ext2/ext2.h#L201
 |  |
|---|
- Group 0
- block bitmap: starts from
0x11th block - Inode bitmap: starts from
0x12th block - Inode table: starts from
0x13th block (0x13000)
- block bitmap: starts from
- Block group number of an inode: (
i_number-1) / inodes per group- (inode는 1,2,3,… 으로 시작하는데 실제 index는 0부터라서 1을 빼준다)
- Root inode number of ext2:
2(2nd)- block group number: (2-1) /
0x8000= 0 - The index of root inode: (2-1) %
0x8000= 1
- block group number: (2-1) /
inode table
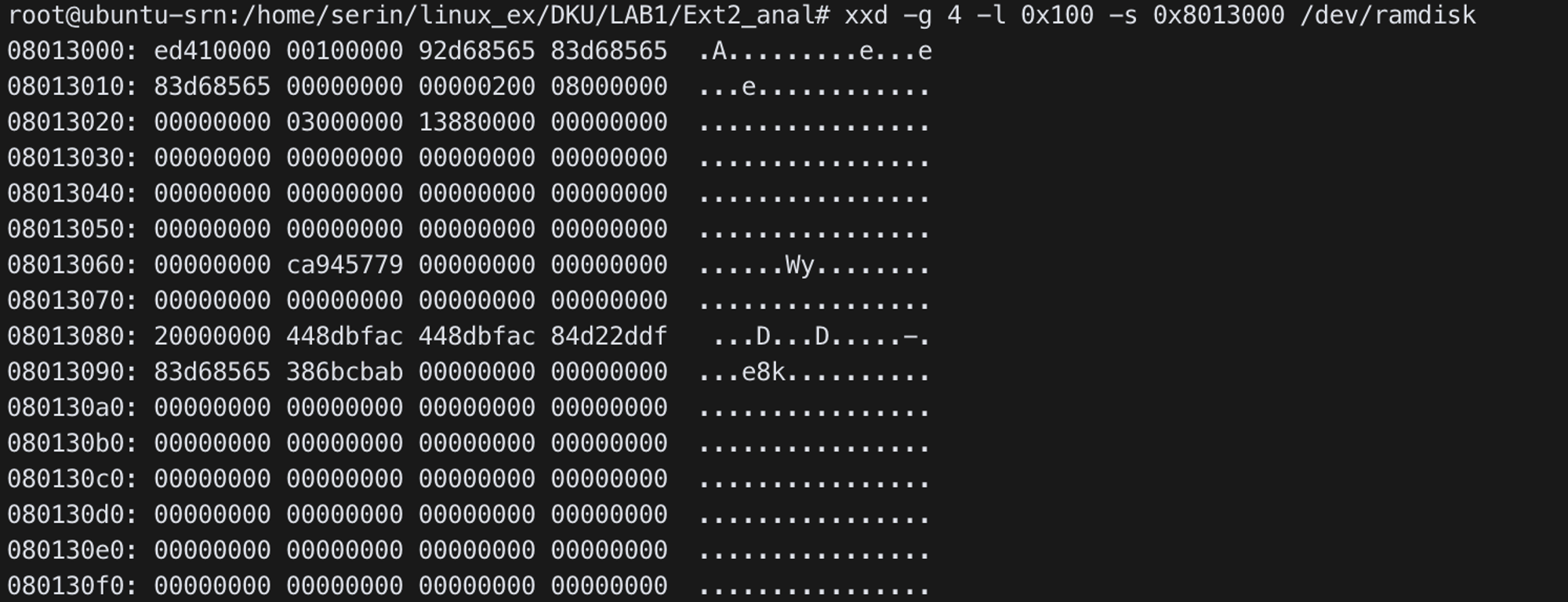
xxd -g 4 -l 0x200 -s 0x13000 /dev/ramdisk
(block size는 4KB(0x100)이므로 000을 추가)
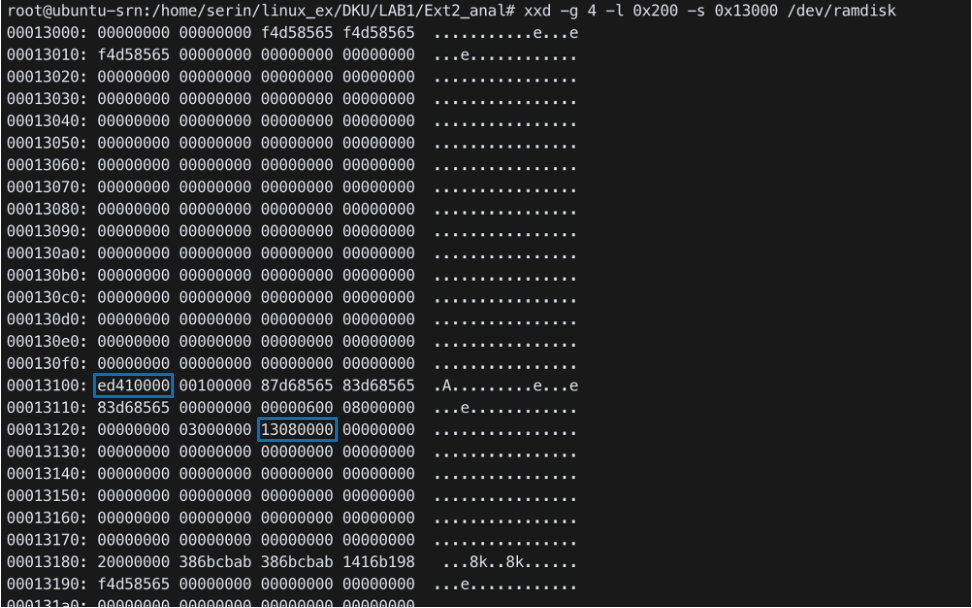
- Mode:
0x41ed
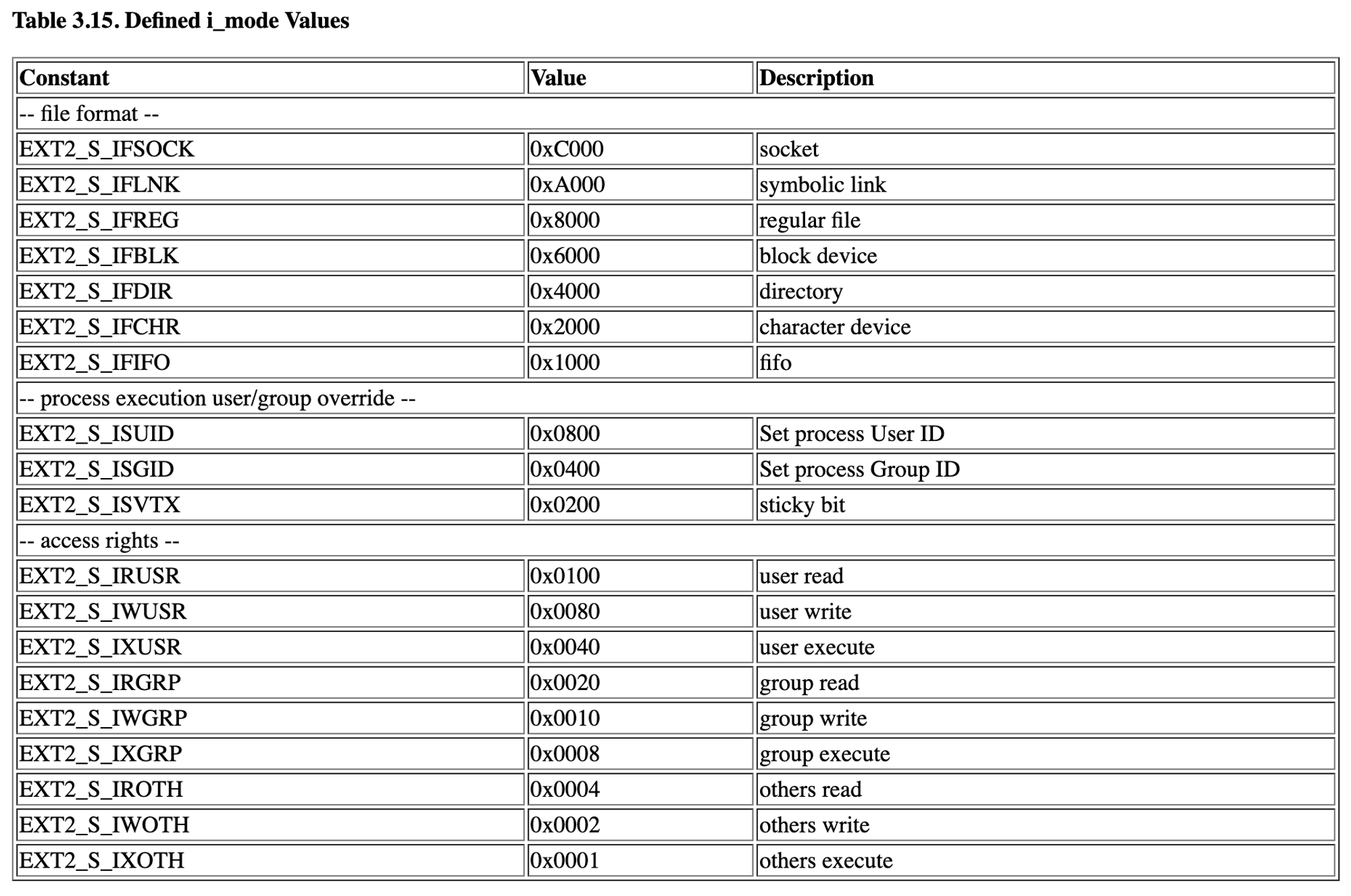
- Dir +
rwxr-xr-x(0x1ed)
- Dir +
- Root inode index: 1
- inode size:
0x100 - Root inode begins at
0x13100 - 1st block:
0x813000
Directory (data block)
xxd -g 4 -l 0x100 -s 0x813000 /dev/ramdisk
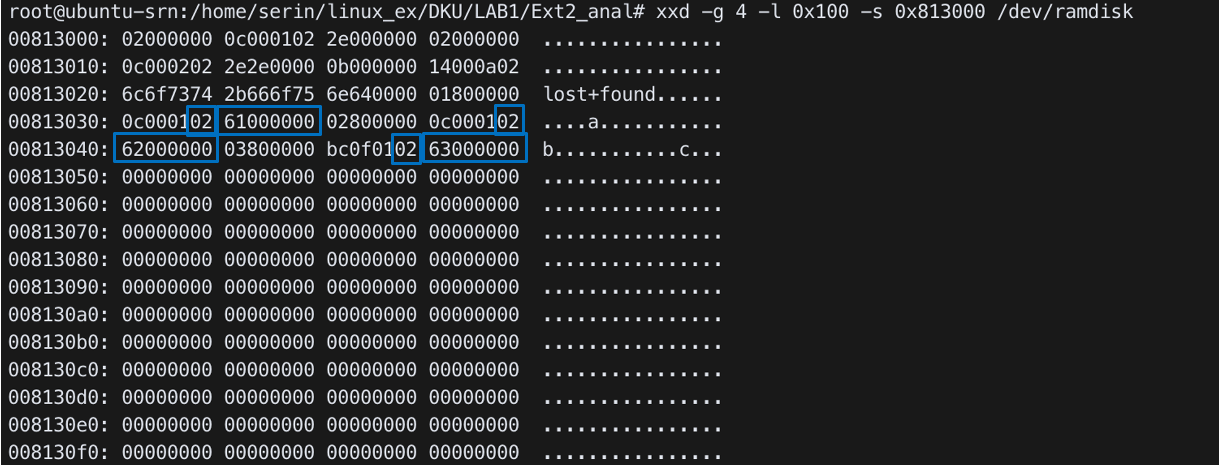
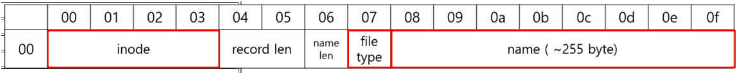
- Name
0x61: a,0x62: b,0x63: c (ascii code)
adirectory inode number:0x8001- File type
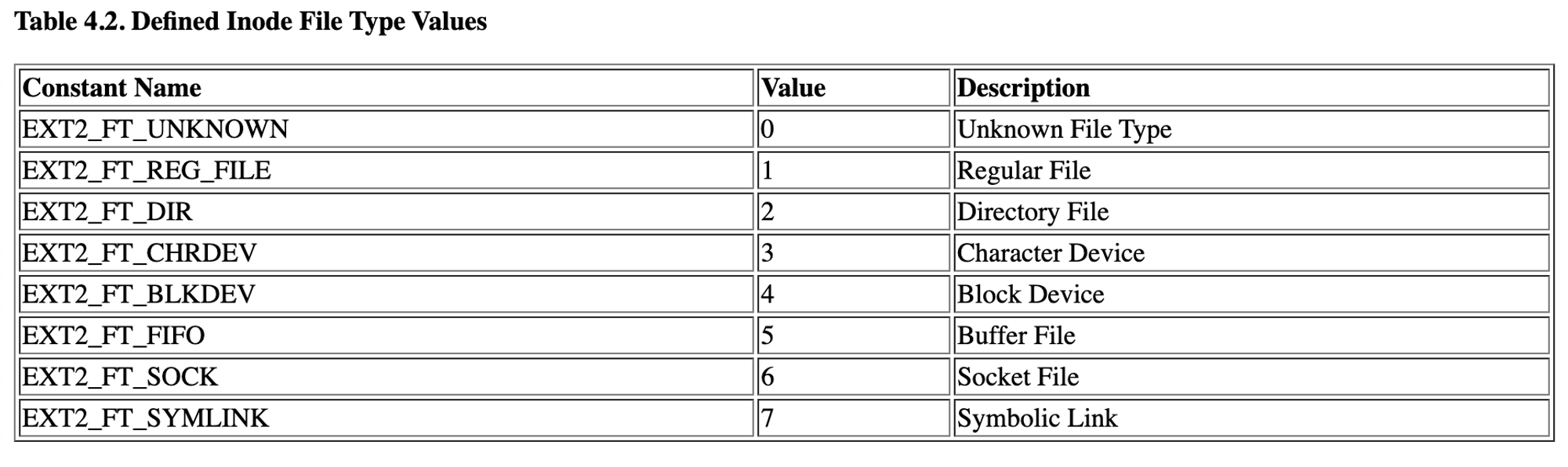
0x02= directory0x01= file
- block group number: (
0x8001-1) /0x8000= 1 - inode table index: (
0x8001-1) %0x8000= 0
+ Group1 inode table: 0x8013
- Group descriptor table that we checked before
0x13800000→ Big endian,0x8013
Virtual File System (VFS)
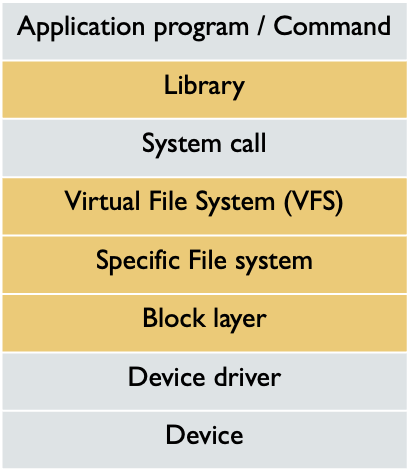
Layered Sturcture Revisit
- File system layer → Many file systems
-ext2_read(),ext4_read()→ Different interfaces… - System call layer → Just one
read()exists → How?
Layered Stucture for Various File Systems
Why VFS?
1. Virtualization Viewpoint
- Map (override) FS specific interfaces to generic interfaces
- Ex: User just callsopen()→ VFS redirects toext4_open(),f2fs_open(),nfs_open() - Make use of various operations in VFS
2. Data Structure Viewpoint
struct file
- Manage an opened file (user perspective): open flags, current position
-file_operations: open, read, write, lseek, ioctl, …struct inode
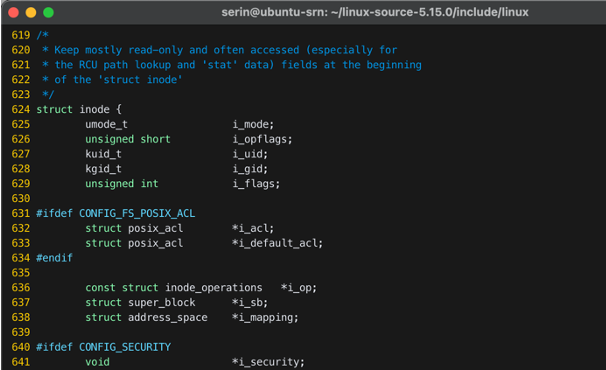
- Manage a file (fs perspective): mode, inode number, …
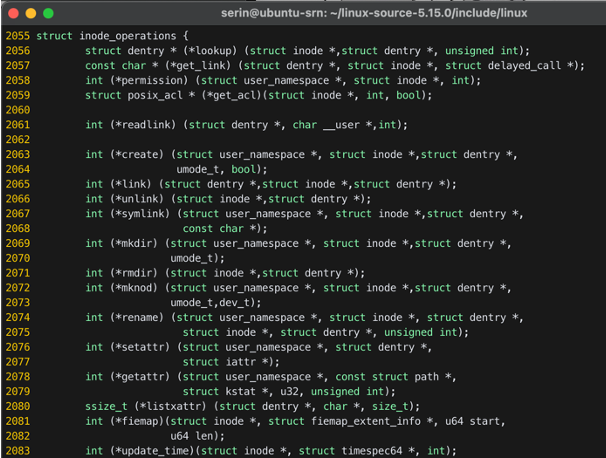
-inode_operations: create, link, unlink, mkdir, lookup, …struct address_space
- Manage page cache: map a file to address space for I/Os
-address_space_operations: readpage, writepage, set_page_dirty, …struct dentry
- Manage the relation between a file name and its inode
-dentry_operations: d_hash, d_compare (for lookup), d_revalidate, …struct super_block
- Manage a file system: file_system_type, inode table, bitmap, …
-super_operations: alloc_inode, write_inode, statfs, sync_fs, …
3. Source Code Viewpoint
linux-source-5.15.0/include/linux/fs.h
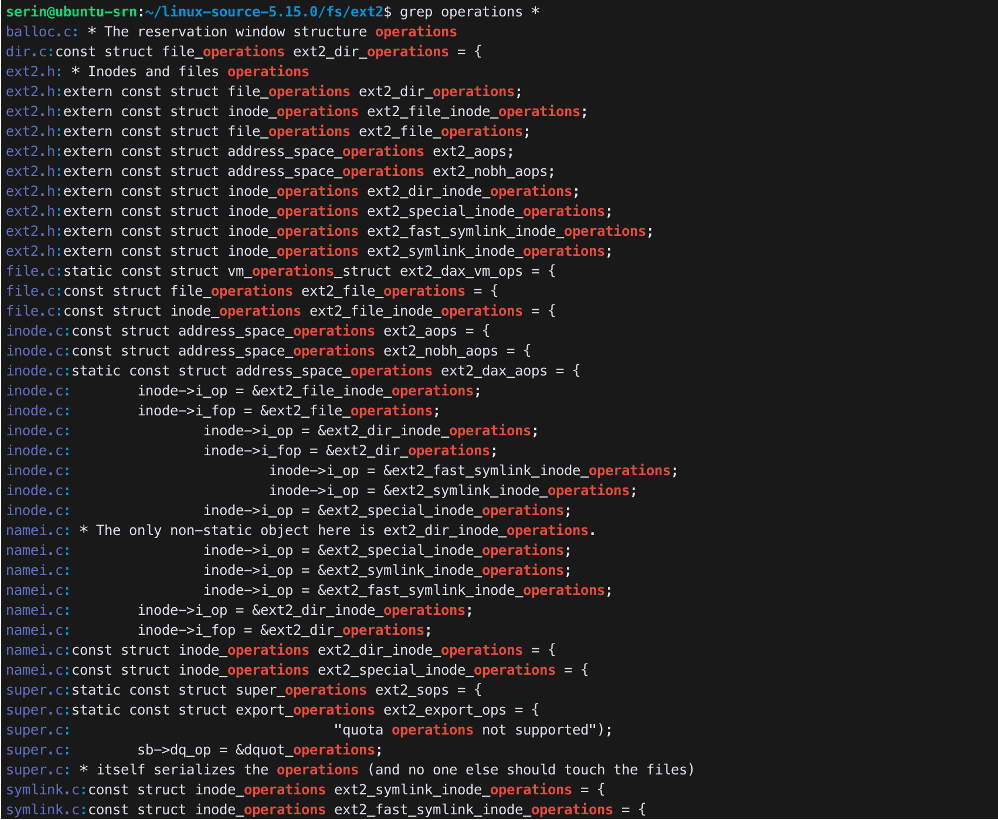
struct file→file_operationsstruct inode→inode_operationsstruct address_space→addr_space_operationsstruct dentry→_dentry_operationsstruct super_block→super_operations
Operations are implemented as function pointers
 |  |
|---|
Operations are frequently used in ext2