Swagger UI는 프론트엔드와 백엔드의 협업에 사용되는 툴입니다. Swagger UI를 사용하면, API를 시각화하는 코드가 자동으로 생성되기 때문에, 보다 간편하게 API를 테스트해 볼 수 있게 됩니다. 또한, API 명세서를 직접 작성할 필요가 없어지므로, API의 유지보수가 간단해진다는 이점도 있습니다.
Swagger UI를 적용하는 방법은 별로 어렵지 않지만, 버전 충돌이 쉽게 발생할 수 있으므로, 이 부분은 유의해주셔야 합니다. 그러면, 지금부터 Swagger UI를 적용하는 방법에 대해 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
1. Swagger UI 접속 관련 설정
실습에서 사용할 SpringBoot의 버전은 아래와 같다. (build.gradle 파일에서 자신의 SpringBoot 버전을 확인할 수 있다.)
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.1.4'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.3'
}Swagger의 버전은 3.x.x를 사용할 것이다. 3.0.0 버전부터 API Test를 위해 접속해야 하는 URL이 아래와 같이 변경되었으니, 반드시 확인하기 바란다.
- 2.x.x 버전: localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
- 3.x.x 버전: localhost:8080/swagger-ui/index.html
Spring 기반 애플리케이션에서 Swagger 문서를 생성할 때 사용하는 라이브러리에는 Springfox와 Springdoc이 있는데, 최신 개발 환경에 더 적합한 것은 Springdoc이다. 그러므로, 실습에서도 SpringBoot 3.1.4 + Springdoc Swagger 환경을 사용할 것이다. (SpringBoot의 버전이 2.x.x인 경우, 버전 충돌로 인해 Whitelabel Error가 발생할 수 있으므로, SpringBoot의 버전을 3.0.0 이상으로 변경할 것을 권장한다.)
① build.gradle 파일에 아래의 의존성을 추가한다.
- 아래의 의존성을 추가하고 application을 실행하면, localhost:8080/swagger-ui/index.html에 접속할 수 있게 된다.
implementation 'org.springdoc:springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui:2.2.0'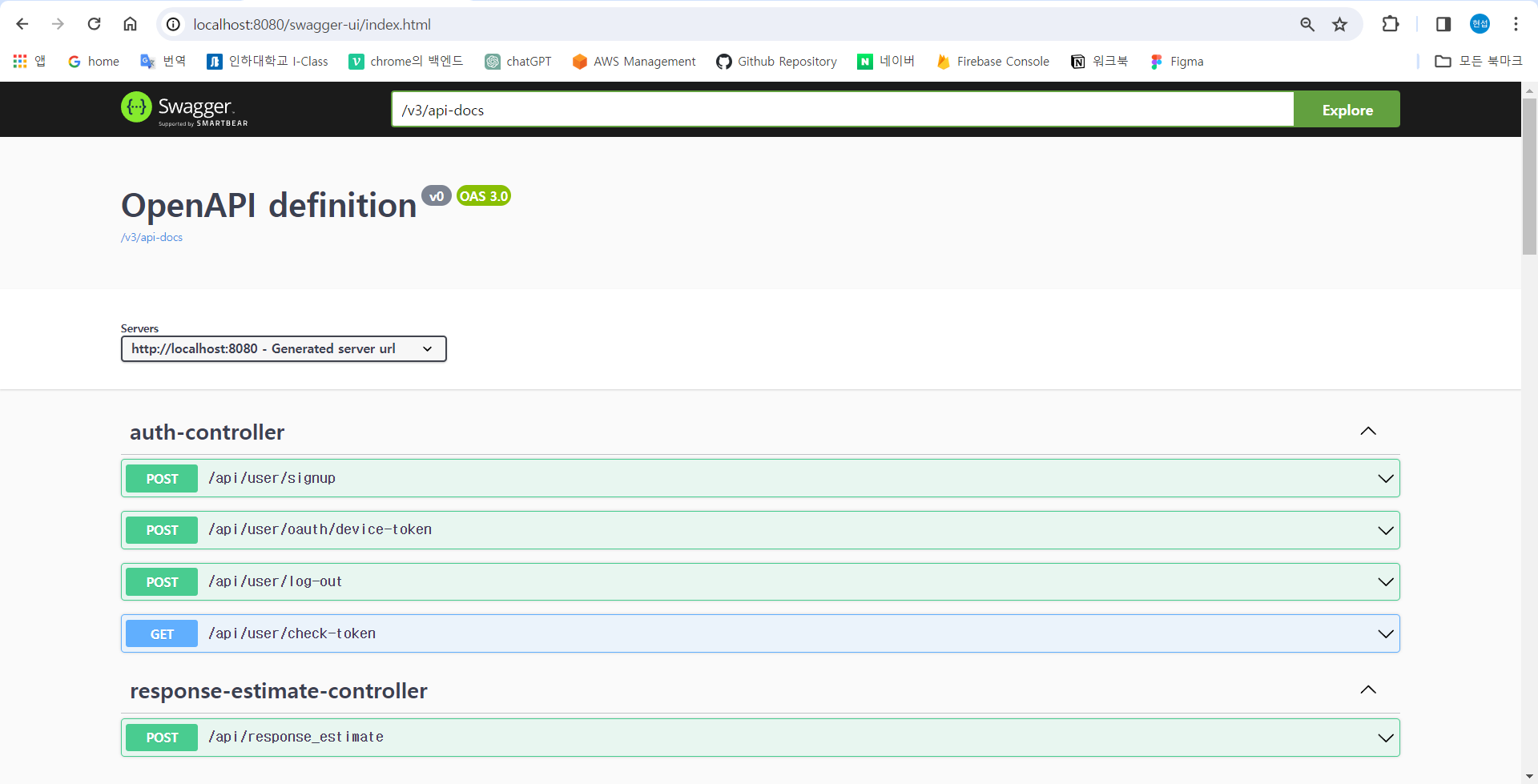
② SwaggerConfig 클래스를 생성하고, 아래의 내용을 입력한다. (JWT 사용 여부에 따라 입력해야 할 내용이 달라진다.)
- JWT를 사용하지 않는 경우
@Configuration
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public OpenAPI openAPI() {
return new OpenAPI()
.components(new Components())
.info(apiInfo());
}
private Info apiInfo() {
return new Info()
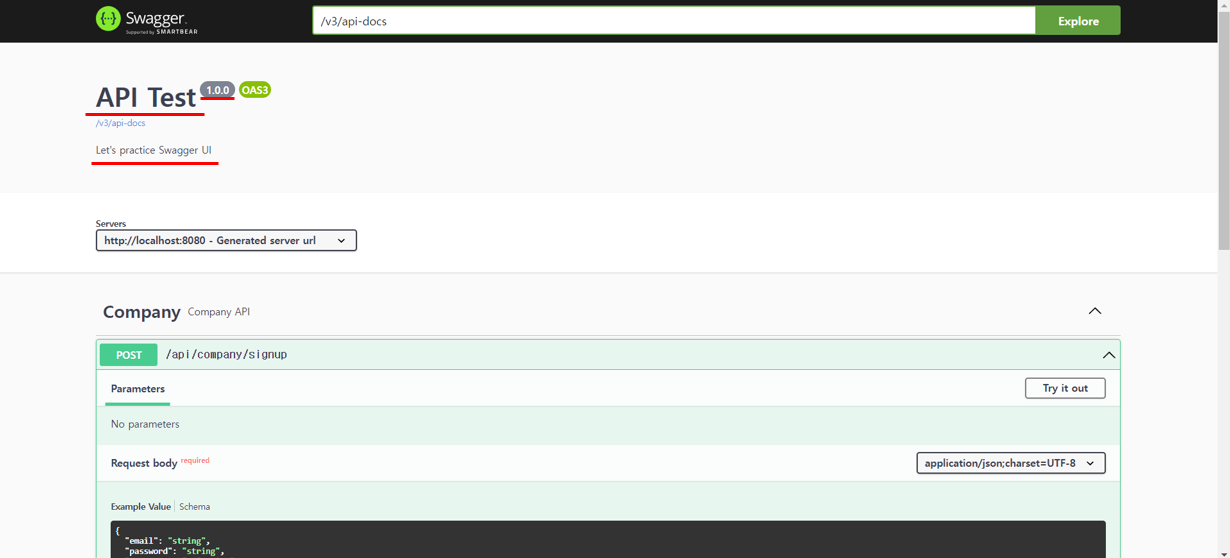
.title("API Test") // API의 제목
.description("Let's practice Swagger UI") // API에 대한 설명
.version("1.0.0"); // API의 버전
}
}- JWT를 사용하는 경우
@Configuration
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public OpenAPI openAPI() {
String jwt = "JWT";
SecurityRequirement securityRequirement = new SecurityRequirement().addList(jwt);
Components components = new Components().addSecuritySchemes(jwt, new SecurityScheme()
.name(jwt)
.type(SecurityScheme.Type.HTTP)
.scheme("bearer")
.bearerFormat("JWT")
);
return new OpenAPI()
.components(new Components())
.info(apiInfo())
.addSecurityItem(securityRequirement)
.components(components);
}
private Info apiInfo() {
return new Info()
.title("API Test") // API의 제목
.description("Let's practice Swagger UI") // API에 대한 설명
.version("1.0.0"); // API의 버전
}
}③ title, description, version은 모두 Swagger 화면 최상단에 위치한다.
④ application.yml 파일에서 추가적인 설정을 진행할 수도 있다.
- 아래의 내용은 필수적인 것은 아니다.
springdoc:
swagger-ui:
path: /api-test # swagger-ui 접근 경로에 대한 별칭, 해당 주소로 접속해도 http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui/index.html로 리다이렉션 됨.
groups-order: DESC # path, query, body, response 순으로 출력
tags-sorter: alpha # 태그를 알파벳 순으로 정렬
operations-sorter: method # delete - get - patch - post - put 순으로 정렬, alpha를 사용하면 알파벳 순으로 정렬 가능
paths-to-match:
- /api/** # swagger-ui에 표시할 api의 엔드포인트 패턴2. API 설정 관련 어노테이션
① @Tag 어노테이션을 사용하여 API를 그룹화할 태그명을 지정할 수 있다.
- 태그명을 지정하지 않으면, Controller의 이름을 Kebab Case(ex: AuthController → auth-controller)로 변환하여 API를 그룹화한다.
- 여기서는 API의 도메인을 태그명으로 사용하여 그룹화하였다.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/response_estimate")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Tag(name = "Response Estimate", description = "Response Estimate API")
public class ResponseEstimateController {
...
// 이와 같은 방식으로 모든 Controller에 @Tag를 적용한다.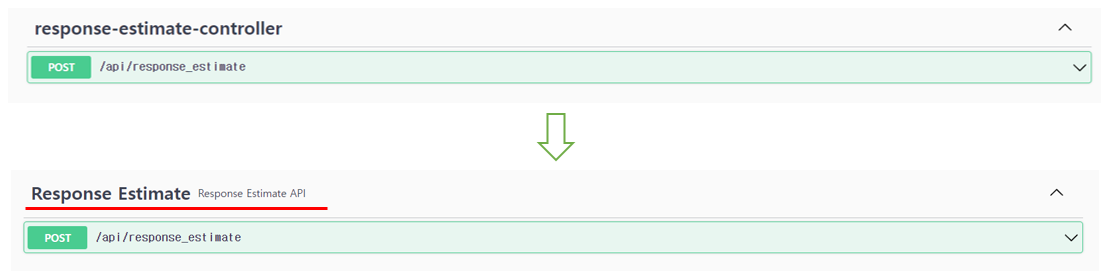
② @Operation 어노테이션을 사용하여, 각 API에 대한 설명을 추가할 수 있다.
@PostMapping("/signup")
@Operation(summary = "업체 회원가입", description = "업체 측에서 회원가입 할 때 사용하는 API")
public BaseResponse<CompanySignupRes> signUp(@RequestBody CompanySignupReq request) {
try {
return new BaseResponse<>(companyService.signup(request));
} catch (BaseException exception) {
return new BaseResponse<>(exception.getStatus());
}
}
...
// 이와 같은 방식으로 모든 API에 @Operation을 적용한다.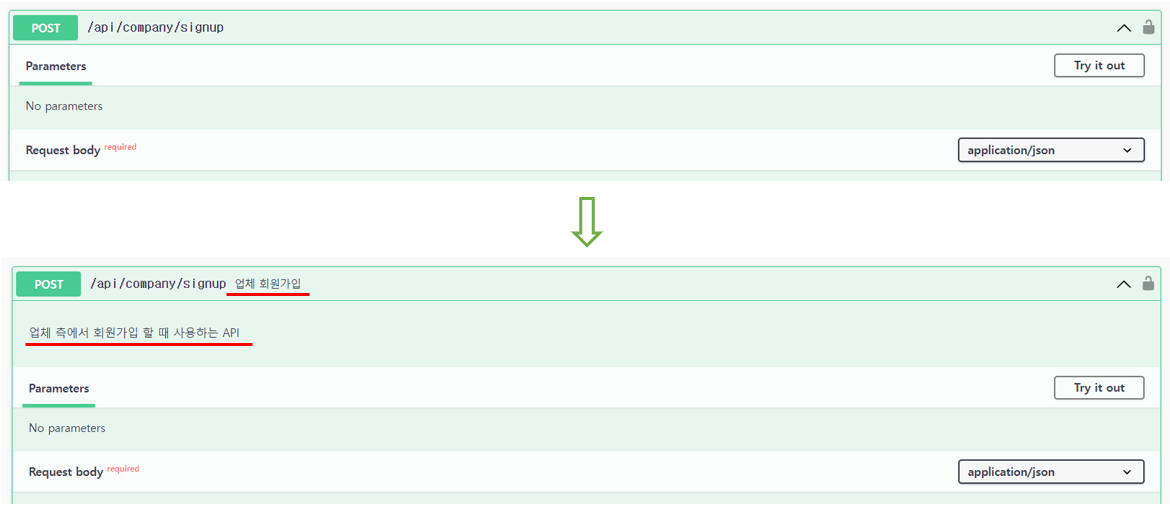
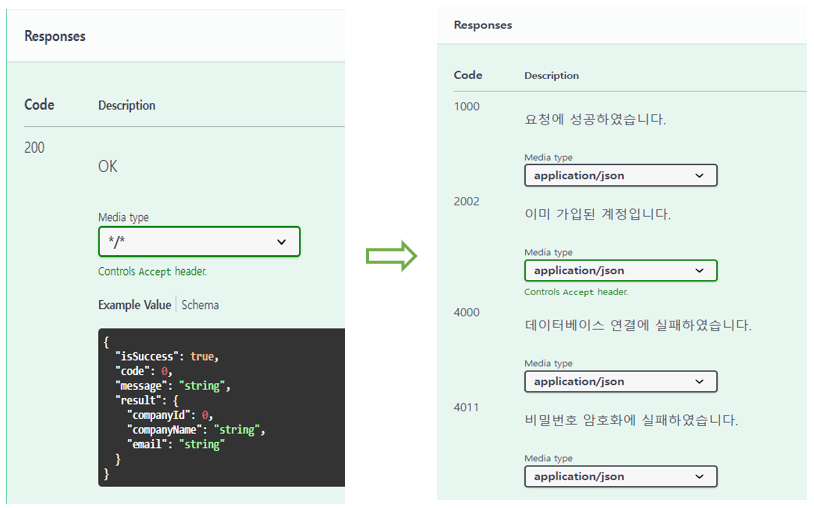
③ @ApiResponses 어노테이션을 사용하여, 응답 코드에 대한 정보를 나타낼 수도 있다.
- 서버에서 사용하는 응답 code와 message 값을 보여줄 수 있다.
- 커스텀 응답 코드를 사용하는 경우라면, 필수적으로 사용해주는 게 좋다.
@PostMapping("/signup")
@Operation(summary = "업체 회원가입", description = "업체 측에서 회원가입 할 때 사용하는 API")
@ApiResponses(value = {
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "1000", description = "요청에 성공하였습니다.", content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json")),
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "2002", description = "이미 가입된 계정입니다.", content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json")),
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "4000", description = "데이터베이스 연결에 실패하였습니다.", content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json")),
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "4011", description = "비밀번호 암호화에 실패하였습니다.", content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json"))
})
public BaseResponse<CompanySignupRes> signUp(@RequestBody CompanySignupReq request) {
...
- 성공 코드만 나타내고 싶다면, @ApiResponse 어노테이션만 사용하면 된다.
@PostMapping("/signup")
@Operation(summary = "업체 회원가입", description = "업체 측에서 회원가입 할 때 사용하는 API")
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "1000", description = "요청에 성공하였습니다.", content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json"))
public BaseResponse<CompanySignupRes> signUp(@RequestBody CompanySignupReq request) {
...
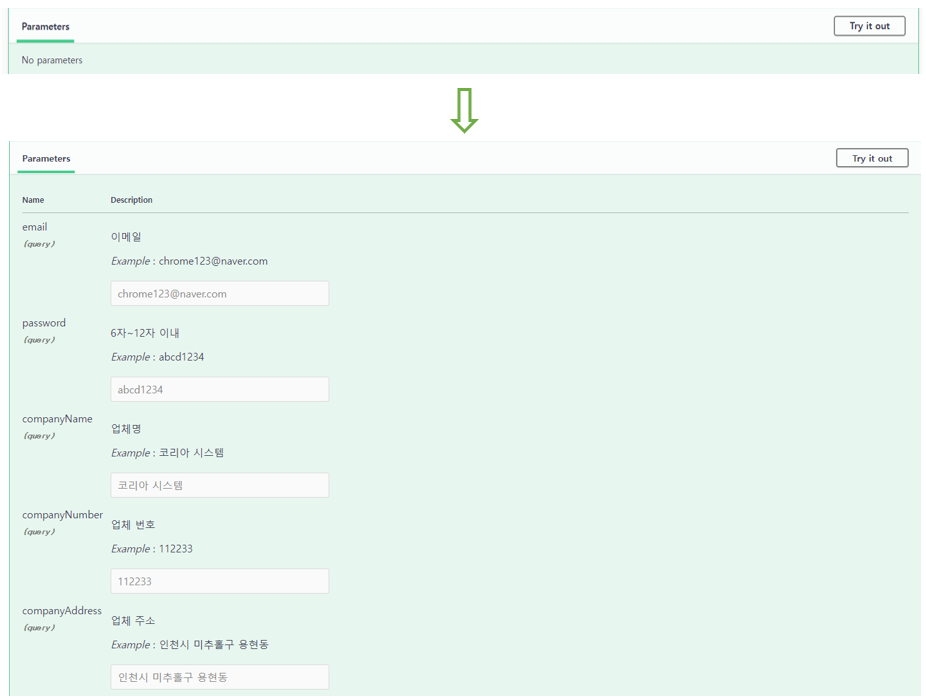
④ @Parameters 어노테이션을 사용하여, 파라미터에 대한 정보를 나타낼 수 있다.
@PostMapping("/signup")
@Operation(summary = "업체 회원가입", description = "업체 측에서 회원가입 할 때 사용하는 API")
@ApiResponses(value = {
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "1000", description = "요청에 성공하였습니다.", content = @Content(mediaType = "appl
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "2002", description = "이미 가입된 계정입니다.", content = @Content(mediaType = "app
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "4000", description = "데이터베이스 연결에 실패하였습니다.", content = @Content(mediaType
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "4011", description = "비밀번호 암호화에 실패하였습니다.", content = @Content(mediaType =
})
@Parameters({
@Parameter(name = "email", description = "이메일", example = "chrome123@naver.com"),
@Parameter(name = "password", description = "6자~12자 이내", example = "abcd1234"),
@Parameter(name = "companyName", description = "업체명", example = "코리아 시스템"),
@Parameter(name = "companyNumber", description = "업체 번호", example = "112233"),
@Parameter(name = "companyAddress", description = "업체 주소", example = "인천시 미추홀구 용현동")
})
public BaseResponse<CompanySignupRes> signUp(@RequestBody CompanySignupReq request) {
try {
return new BaseResponse<>(companyService.signup(request));
} catch (BaseException exception) {
return new BaseResponse<>(exception.getStatus());
}
}
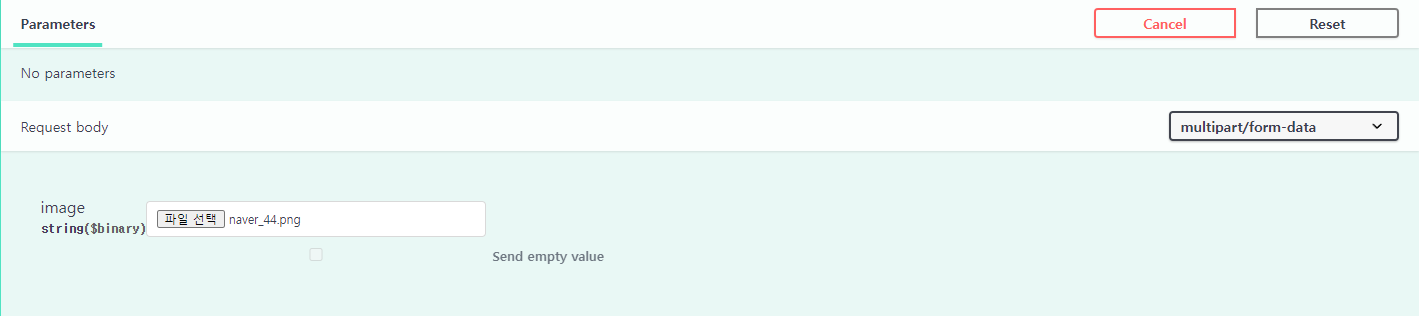
⑤ 이미지(MultiPart File)를 입력 데이터로 받아야 할 경우, @PostMapping(또는 @PatchMapping) 어노테이션 안에 consumes, produces 속성을 추가해주어야 한다.
- value 속성은 api의 엔드포인트일 뿐이므로 무시하자.
@PatchMapping(value = "/image", consumes = MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
...
3. Swagger UI를 활용한 API Test
Swagger UI의 사용 방법은 Postman에서 API를 Test 할 때와 거의 비슷하거나 더 쉽다. 직접 실습하면서 사용법을 익혀보기로 하자.
1) 회원가입 API 테스트
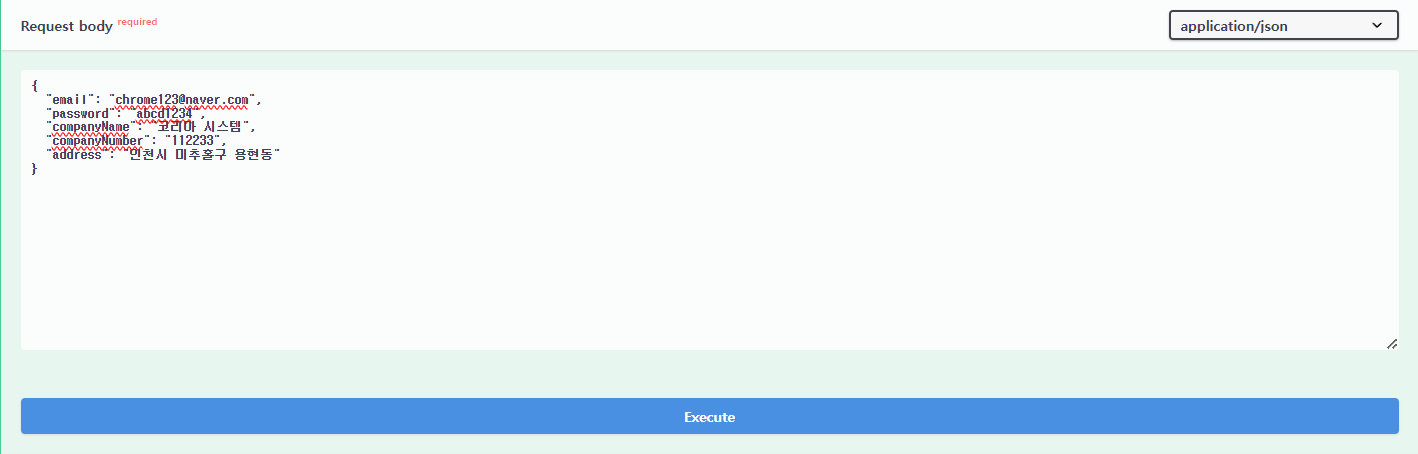
① 업체 회원가입 API를 클릭한 후, Try it out 버튼을 클릭한다.
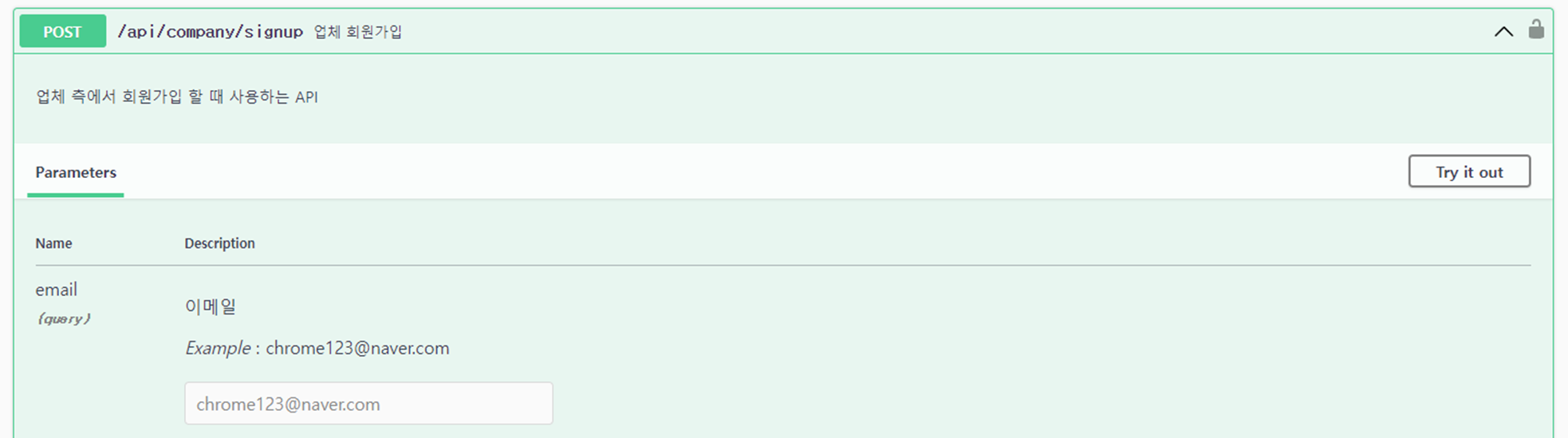
② Request body 부분에 Json 데이터를 입력하고, Execute 버튼을 클릭한다.
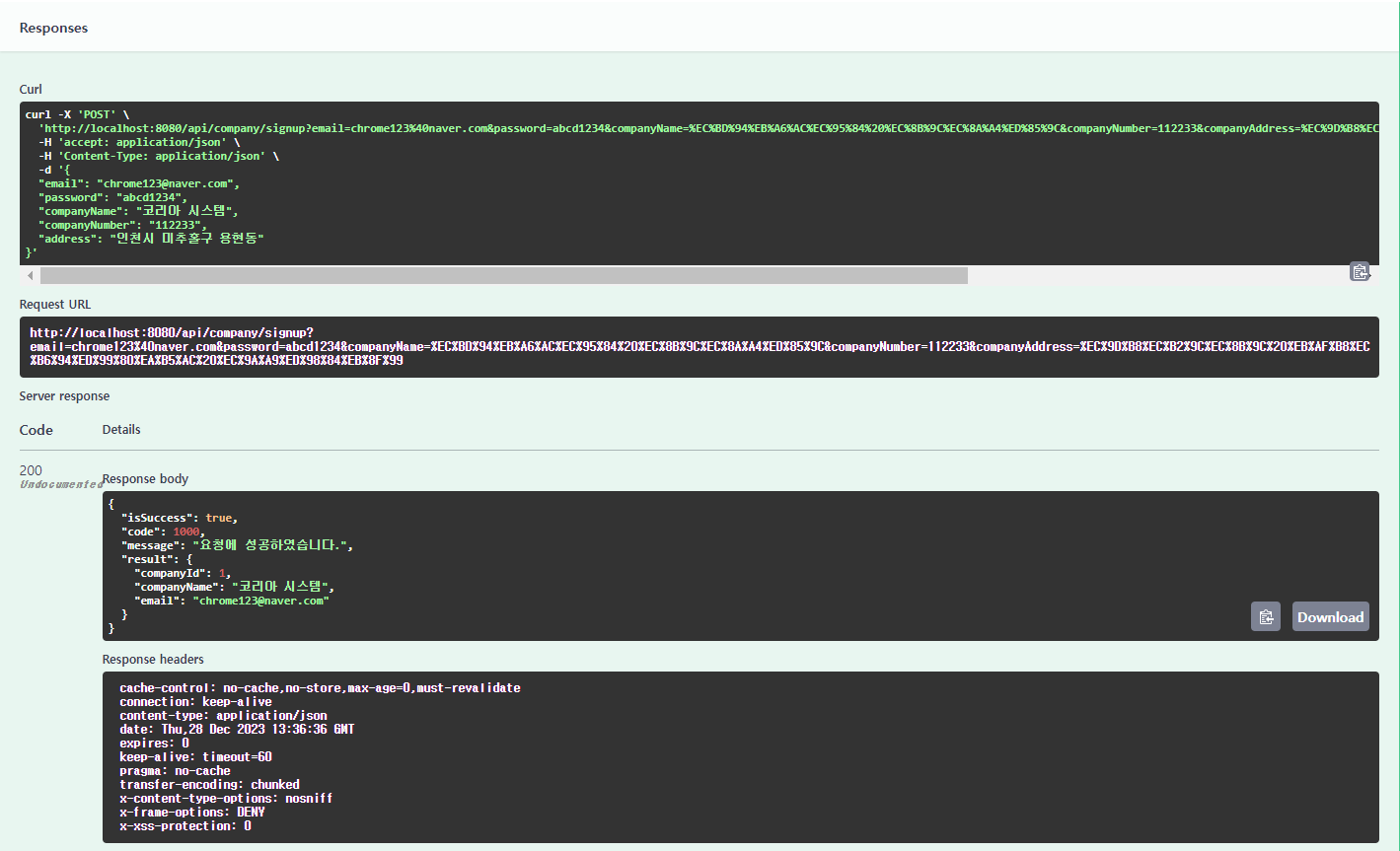
③ Curl을 통해 전송되는 데이터를 확인할 수 있으며, 아래의 Server response에서 응답 데이터를 확인할 수 있다.
- -X: HTTP 요청 메서드를 지정한다. 여기서는 POST로 지정하고 있다.
- -H: 요청 헤더에 포함할 내용을 지정한다.
- -d: POST 메서드에서 사용할 데이터를 지정한다.
※ Curl
Curl(Client for URLs)은 URL로 데이터를 전송하는 방식으로, 서버에 데이터를 보내거나 서버로부터 데이터를 받기 위해 사용된다. 다양한 프로토콜과 주요 OS에서 사용 가능하다는 점에서 널리 이용되고 있으며, HTTP/HTTPS 프로토콜 기반의 REST API 테스트에 주로 사용된다.
Curl 명령을 사용하면, 커맨드라인에서 간단하게 HTTP 요청을 생성/전송/출력할 수 있게 된다. 또한, 옵션과 함께 사용하여 요청 헤더, 요청 메서드, 요청 바디 등을 지정하는 것도 가능하다.
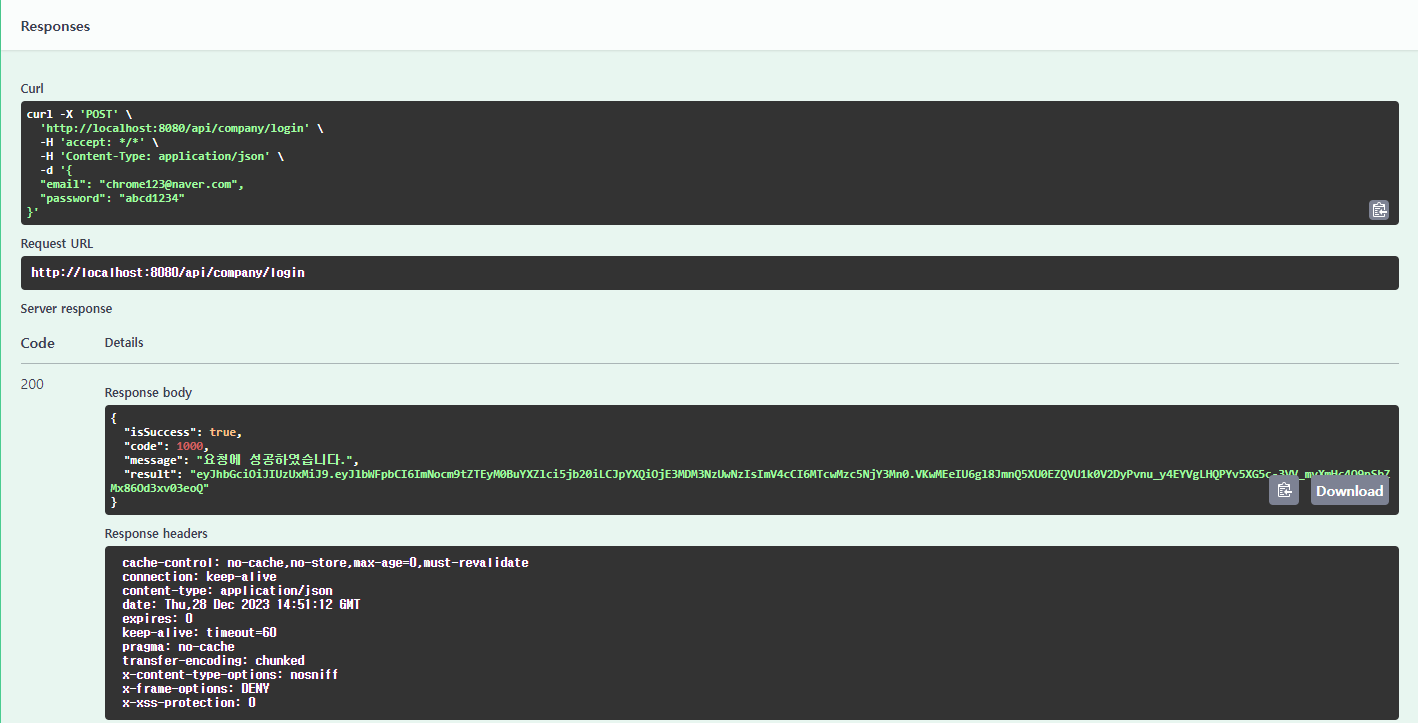
2) JWT를 사용하는 API 테스트
① 먼저 로그인 API를 호출하여 Access Token을 발급 받는다.
- 발급 받은 Access Token을 복사한다.
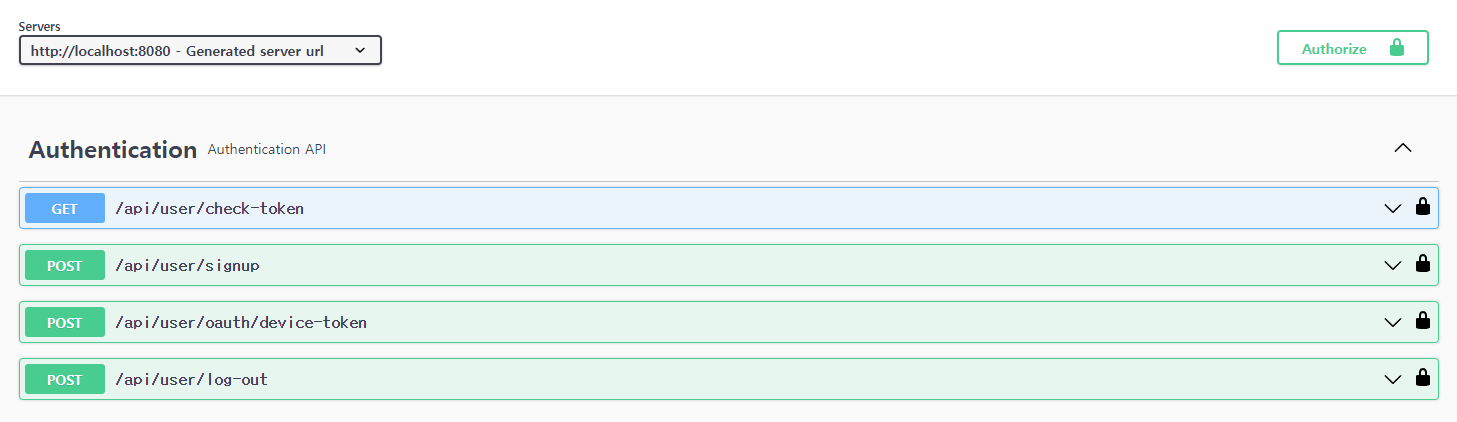
② SwaggerConfig 클래스에 JWT 관련 설정을 추가했다면, 아래와 같이 우상단에 Authorize 버튼이 생성되어 있을 것이다. 이 버튼을 클릭하자.

③ 복사한 Access Token을 붙여넣고, Authorize 버튼을 클릭한다.
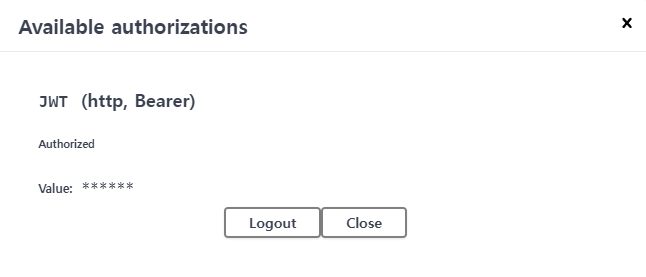
④ Authorize 버튼과 API 우측의 좌물쇠가 잠긴 것을 확인할 수 있는데, 이는 로그인 되었음을 의미한다.
⑤ 이제부터 호출하는 모든 API의 Authorization 헤더에 'Bearer Access_Token'이 포함된다.
- JWT가 필요하지 않은 API에도 Access Token이 포함된다.
- Bearer는 자동으로 포함되므로, 반드시 Access Token만 붙여넣는다.
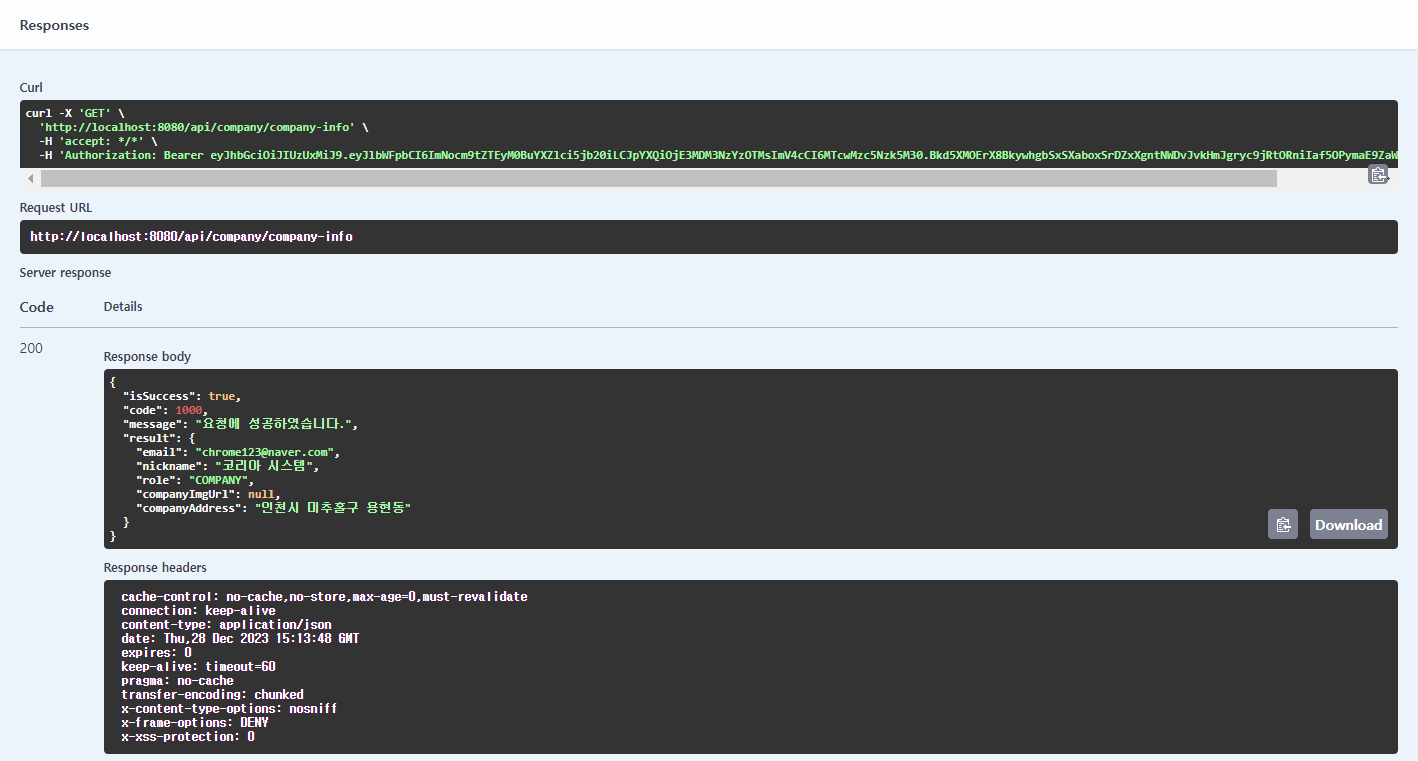
⑥ JWT를 통해 업체를 식별하여, 해당 업체의 정보를 반환하는 API를 호출해보자.
- Curl 명령의 -H 옵션을 통해 Authorization 헤더가 잘 포함되었음을 확인할 수 있다.
3) 이미지를 입력으로 받는 API 테스트
① 이제 업체의 프로필 이미지를 설정하는 API를 호출해보자.
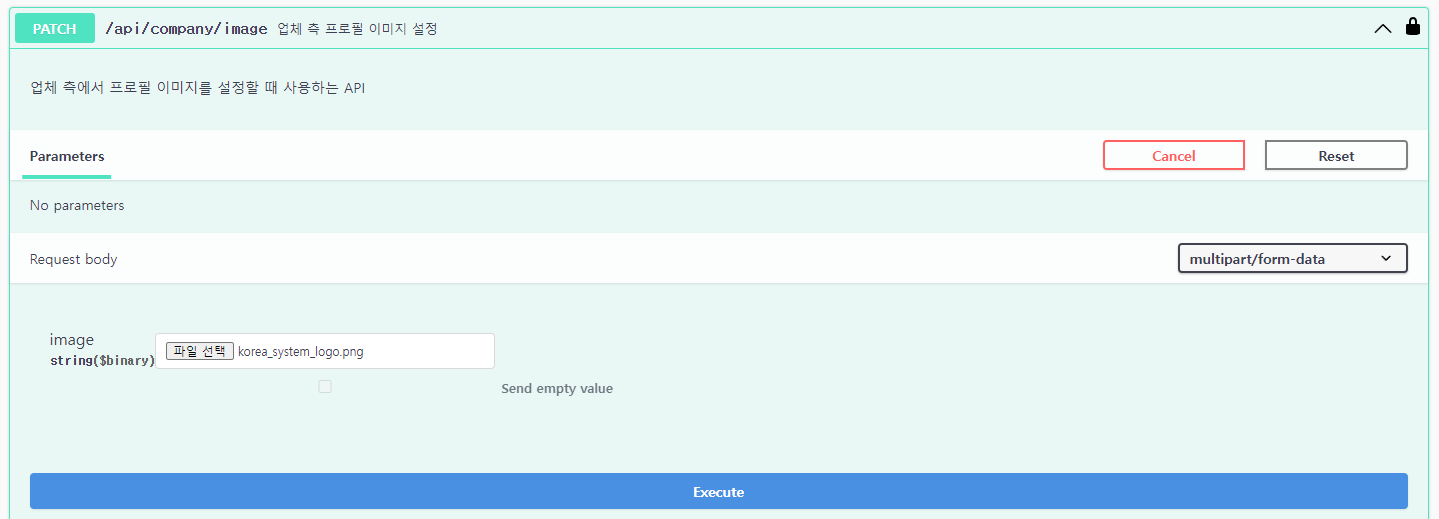
② 코리아 시스템 업체의 로고 이미지를 선택한 후 Execute 버튼을 클릭한다.
③ 업체 프로필 이미지가 정상적으로 설정되었음을 확인할 수 있다.
- Curl 명령의 -F 옵션을 통해 MultiPart File을 포함시킬 수 있음을 알 수 있다.
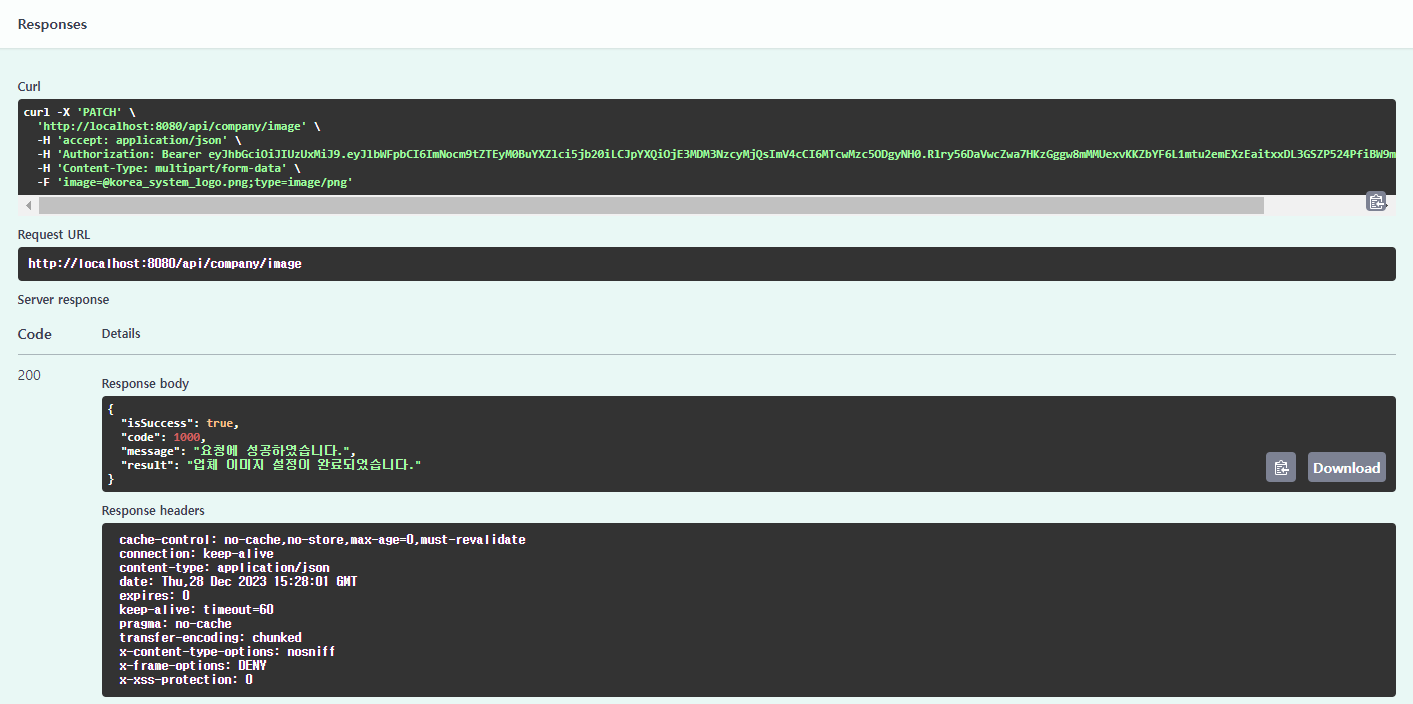
④ API 테스트의 결과는 모두 데이터베이스에 반영된다.
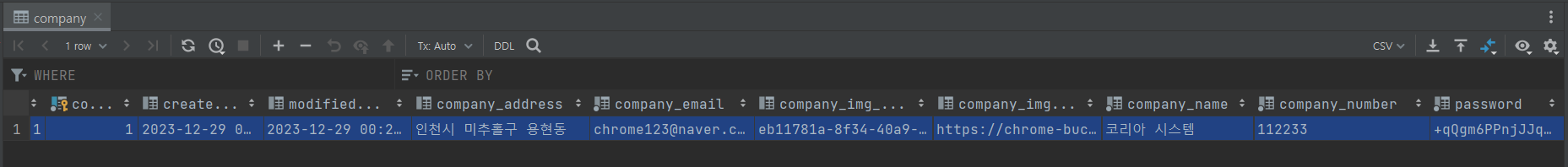
⑤ 데이터베이스의 저장된 이미지 URL에 접속하여, 코리아 시스템 업체의 로고 이미지를 확인할 수 있다.


What are the rates for Escorts in Delhi ? Looking to plan something special.