
introduce
- 자바스크립트의 타입은 동적이고, 유연하다. 이 말을 바꿔말하자면, 편하지만 위험성을 내포하고 있다는 뜻이다. 조금 더 안전한 JavaScript type을 위해 공부한 내용을 정리한다.
- 본 글은 Udemy
장현석님의 클린코드 자바스크립트를 토대로 정리하고, 추가적으로 살을 붙혔습니다.
1. 타입 검사
1-1. typeof
primitive type은typeof로 검사해도 문제가 없다.- 하지만
reference type은typeof로 검사 시 문제가 생길 수 있다.
typeof '문자열'; // 'string'
typeof true; // 'boolean'
typeof undefined; // 'undefined'
typeof 123; // 'number'
typeof Symbol(); // 'symbol'
function myFunction() {}
class MyClass {}
const str = new String('문자열')
typeof myFunction // 'function'
typeof MyClass // 'function'
typeof str // 'object'
typeof null // 'object'1-2. instanceof
instanceof는 해당 인스턴스가 특정 생성자의 인스턴스인지 판별해주는 연산자이다.
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
const randomPerson = {
name: 'test',
age: 99
}
const hwimin = new Person('hwimin', 99)
hwimin instanceof Person // true
randonPerson instanceof Person // false
// instanceof를 활용한 타입 검사
const arr = []
const func = function() {}
const date = new Date()
arr instanceof Array // true
func instanceof Function // true
date instanceof Date // true
// 여기 까지는 문제가 없다. arr은 Array의 인스턴스이다.
// 하지만 아래의 코드를 보면 다시 혼란이 생길 수 있다.
arr instanceof Object // true
func instanceof Object // true
date instanceof Object // true
// Array, Function, Date도 결국은 Object의 인스턴스이기 때문에 true를 반환한다.1-3. Object.prototype.toString.call()
const arr = []
const func = function() {}
const date = new Date()
Object.prototype.toString.call(new String('')) // '[object String]'
Object.prototype.toString.call(func) // '[object Function]'
Object.prototype.toString.call(arr) // '[object Date]'
Object.prototype.toString.call(new String('')) // '[object String]'2.undefined, null
- JS의
undefined와null은 혼란을 줄 수 있는 가능성이 크다. 아래의 코드를 보자 undefined와null은 팀 차원에서 컨벤션을 이용해서 활용하는 것이 좋다.- 그렇지 않으면 많은 헷갈림을 유발시킬 수 있다.
!null; // true
!!null; // false
Boolean(null); // false
null === false; // false
!null === true; // true
// null은 수학 연산에서 0으로 취급된다.
null + 123; // 123
// undefined는 선언했지만 값은 정의되지 않고 할당 X
let varb;
typeof varb; // 'undefined';
undefined + 10; // NaN
!undefined; // true
undefined == null; // true
undefined === null; // false
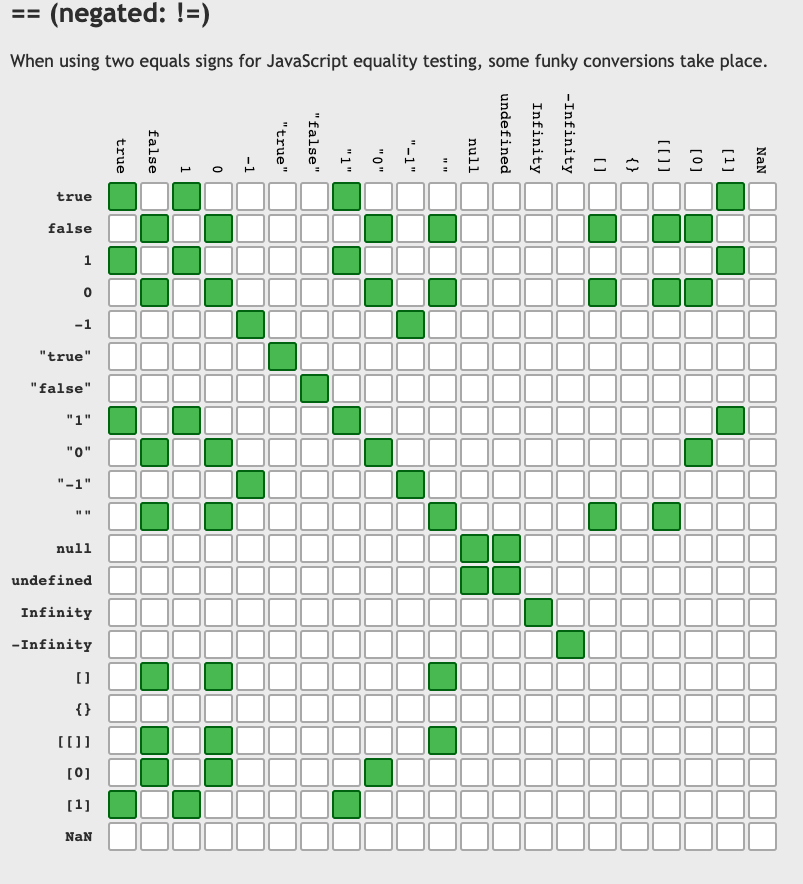
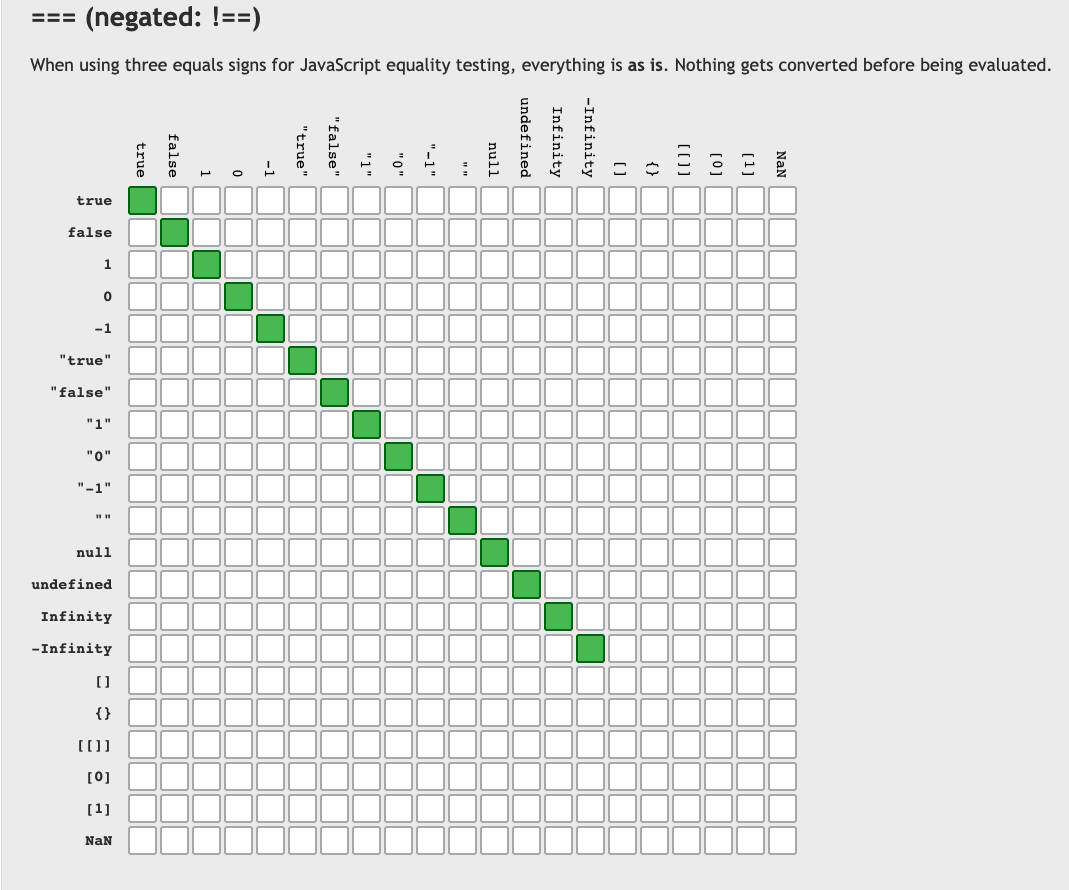
!undefined === !null; // true3. equality(==)을 줄이고 strict equality(===)을 사용하자.
- 비교하려는 값의 자료형이 다르면 자바스크립트는 이 값들을 숫자형으로 바꾼다.
==을 사용시 형변환(type casting)이 일어난다.
'1' == 1; // true, 문자열 '01'이 숫자 1로 변환된 후 비교가 진행된다.
1 == true; // true, 불린형 true가 숫자 1로 변환된 후 비교가 진행된다.
0 == false // true, 불린형 false가 숫자 0으로 변환된 후 비교가 진행된다.
let a = 0;
Boolean(a) // false
let b = "0";
Boolean(b) // true
a == b // true : ?? b 변수에 담긴 "0"가 숫자로 변환된 후 비교하기 때문에 true를 반환한다.
이러한 위험성과 모호성을 피하기 위해
==보다는===를 사용하자.
3-1. == 사용 case
3-2. === 사용 case
4. 형변환 주의하기
- 자바스크립트에서는 동적으로 타입이 정해지기 때문에 형변화에도 주의를 기울여야 한다.
- 크게
명시적 변환과암묵적 변환이 있는데,암묵적 변환이 일어나는 부분도 명시적으로 코드를 작성하여, 코드를 보는 사람으로 하여금 혼란을 일으키지 않도록하자.
// 암묵적 변환
100 + 'str'; // '100str'
!!'str'; // true
!!''; // false
// 명시적 변환
// parseInt() 사용 시 대부분 10진수를 기대한다. 하지만 두 번째 인수를 생략한다면 무조건 10진수를 반환하지는 않는다.
// 그러므로 두 번째 인수를 넣어주자.
parseInt('9.999', 10); // 9
String(100 + 'str'); // '100str'
Boolean('str'); // true
Boolean(''); // false
Number('11'); // 115. isNaN vs Number.isNaN
isNaN()은 인수의 값이 NaN이라면 true를 반환한다.- 하지만 NaN이 아니라도 true를 반환하는 경우가 많다. 그러므로 엄격한 검사를 위해
Number.isNaN()을 사용하자.
isNaN(); // 인수의 값이 NaN이라면 true를 반환한다.
isNaN('a'); // true
Number.isNaN(123 + '문자'); // false
isNaN(123 + '문자') // true
console.log(123 + '문자'); // '123문자' : 엄밀히 말하면 문자열이지 NaN은 아니다.
console.log(undefined + 11); // NaN
Number.isNaN(undefined + 11); // true
