Dining-Philosophers Problem(철학자들의 저녁식사 문제)
동시성 제어문제들 중 1
철학자들이 생각하고 먹고 생각하고 먹고하는데 다섯개의 젓가락을 공유한다.
배가고파지면 두개의 젓가락으 사용한다.
배가고파서 두개를 동시에 쓸려고하면 어떻게 될까
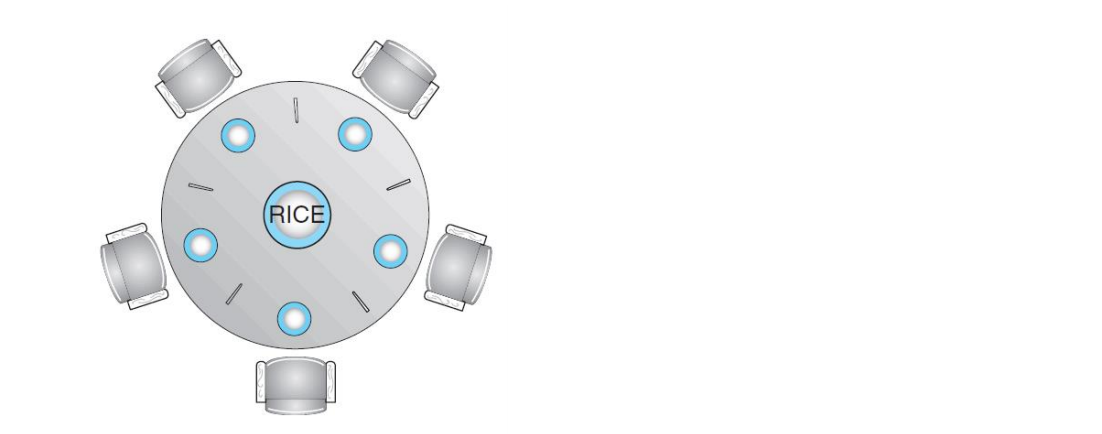
양쪽 두명이 가운데 젓가락을 공유한다. -> 두명이 같이잡으려고하면 critical scetion -> 상호배제 시켜주면 됨
여러개의 리소스, 여러 프로세스들 -> deadlock, starvation 발생
식사하는 철학자들 해결안 방법 : 세마포어(Semaphore)
세마포어 해결안은 각각의 젓가락이 세마포어를 설정
한 철학자는 wait() 연산을 수행함으로써 대기하다가 젓가락을 얻는다.
젓가락을 얻은 철학자가 밥을 다 먹은 후에 signal() 연산을 호출함으로써 젓가락을 놓는다.
각 젓가락에다가 semaphore을 걸어준다.
철학자가 젓가락을 요구할때, wait을 시켜준다.
젓가락을 놓을 때 signal 오퍼레이션
semaphore chopstick[5]
while(true){
wait(chopstick[i];
wait(chopstick[(i+1) % 5]);
// 왼쪽 젓가락 i, 오른쪽 젓가락 i+1
/* eat for a while */
signal(chopstick[i]);
signal(chopstick[(i+1) % 5]);
// 젓가락 놓기
/* think for awhile */
}-> 상호배제 o , deadlock free x , starvation free x
데드락 발생 :
5명의 철학자가 동시에 배가고프고, 각 한명이 젓가락을 한개씩 잡고있다 -> 그럼 안내려놓음 -> 아무도 집을 수없어서
1.철학자를 4명으로 제한한다. 한자리를 비워두면 그 양쪽은 항상먹을 수있다.
모든 철학자들이 젓가락을 왼쪽을 집었더라도 하나의 젓가락은 남기 때문에 반드시 1명의 철학자는 밥을 먹고 젓가락을 내려놓을 수 있다.
2.양쪽 젓가락이 놓여있을때만 젓가락을 집자
3.홀수 철학자들은 왼쪽을 집고 오른쪽을 집자, 짝수번호는 오른쪽을 먼저 집고 왼쪽을 집자, 동시에 잡히는경우는 critical section으로해준다. 그면 둘중하나는 반드시 잡음
=> starvation 까지는 해결하지 못함
Monitor Solution:
철학자들은 왼쪽 젓가락, 오른쪽 젓가락 두개다 이용가능할때만 젓가락을 집는다.
양쪽 젓가락 available 할때만 젓가락 집을 수 있도록 하자
3개의 상태로 나누자.
thinking -> hungry -> eating
젓가락을 잡으면 eating으로 넘어감, 못잡으면 wait, notify(signal)
철학자는 자기 상태를 hungry -> eating 상태로 바꿀수 있다. 양쪽 철학자가 eating 하고 있지 않을때 그때만 먹도록 하자
=> 모니터로 구현
condition variable을 선언해줘야한다.
조건변수는 철학자가 배가 고프고 철학자가 원하는 젓가락을 얻지 못할때 철학자 스스로 대기한다.
자기가 hungry 할때 delay(wait()) 시킨다. 밥을먹고나면 signal 한다.
젓가락의 배포(distribution)를 담당하고있는 diningPhilosopher monitor 선언하고 모니터로 구현하자
pickup(), putdown() 젓가락집기 젓가락내려놓기 오퍼레이션을 제어한다.
=> mutual exclusion, deadlock 은 해결 starvation은 x

enum : 생각중, hungry, eating , 5개
condition variable : 자기 상태 나타냄
void pickup : hungry 할당, test(양쪽이 avilable 한가?) if( waiting이 아니면) wait 한다.
void putdown : thinking 할당, 왼쪽, 오른쪽 test
void test: 왼쪽 오른쪽이 not eating이고 hungry 면 내가 eating 하겠다. self[i]에 나 밥먹고있다고 signal 보냄
initialization_code : 철학자들 나 thinking 상태이다.
상호배제(Mutual Exclusion)과 교착상태(DeadLock) 해결은 보장하지만 기아(Starvation) 발생은 여전히 가능성이 있다.
한 철학자가 배가 고파 젓가락을 집고자 해도 다른 철학자가 계속 빠르게 선점하여 젓가락을 집는다면 철학자는 굶어 죽을 수 있다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define true 1
#define NUM_PHILS 5 //5 명
enum {THINKING, HUNGRY, EATING} state[NUM_PHILS];
//state 배열에 둠
pthread_mutex_t mutex_lock; // 락 선언
pthread_cond_t cond_vars[NUM_PHILS]; // 컨디션 valuable 선언
// condition valuale에 접근하는거는 항상 sinchronized 된다.
int main() {
int i;
pthread_t tid;
init(); // 초기화
for (i = 0; i < NUM_PHILS; i++)
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, philosopher, (void *)&i);
// 철학자 5개 pthread 생성 , id 0,1,2,3,4
for (i = 0; i < NUM_PHILS; i++)
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
// join 하고 기다림
return 0;
}
void init() { // 초기화
int i;
for (i = 0; i < NUM_PHILS; i++) {
state[i] = THINKING; // state i 다 thinking
pthread_cond_init(&cond_vars[i], NULL);
// condition valuable 다 초기화
}
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_lock, NULL);
// mutex lock 초기화
srand(time(0)); // 랜덤함수 초기화
}
int leftOf(int i) {
return (i + NUM_PHILS - 1) % NUM_PHILS;
// 왼쪽
}
int rightOf(int i) {
return (i + 1) % NUM_PHILS;
// 오른쪽
}
void *philosopher(void *param) {
int id = *((int *)param); //철학자 id
while (true) { // 무한루프
think(id); // 생각
pickup(id); // 집기
eat(id); // 밥먹기
putdown(id); // 내려놓기
}
}
void think(int id) {
printf("%d: Now, I'm thiking...\n", id);
usleep((1 + rand() % 50) * 10000);
// 0.1 ~ 0.5 초 랜던값으로 생각
}
void eat(int id) {
printf("%d: Now, I'm eating...\n", id);
usleep((1 + rand() % 50) * 10000);
// // 0.1 ~ 0.5 초 랜던값으로 먹기
}
void test(int i) {
// If I'm hungry and my neighbors are not eating,
// then let me eat.
if (state[i] == HUNGRY &&
state[leftOf(i)] != EATING && state[rightOf(i)] != EATING)
// 배고프고, 왼쪽 오른쪽 eating 아닐때
{
state[i] = EATING;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond_vars[i]); // 내가먹을때까지 기다려주세요
}
}
void pickup(int i) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_lock);
// mutex lock 획득
--- critical section
state[i] = HUNGRY; // hungry 선언
test(i); // 왼쪾오른쪽 비었는지확인
while (state[i] != EATING) {
// 왼쪽오른쪽 안비어있으면 기다림
pthread_cond_wait(&cond_vars[i], &mutex_lock);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_lock);
//mutex lock 해제
}
void putdown(int i) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_lock);
state[i] = THINKING; // thinking
test(leftOf(i));
test(rightOf(i));
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_lock);
}=> deadlock 문제 해결
java 예시
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
enum State {
THINKING, HUNGRY, EATING
}
public class DiningPhilosophers {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int numOfPhils = 5;
Philosopher[] philosophers = new Philosopher[numOfPhils];
DiningPhilosopherMonitor monitor = new DiningPhilosopherMonitor(numOfPhils);
for (int i = 0; i < philosophers.length; i++)
new Thread(new Philosopher(i, monitor)).start();
}
}
class Philosopher implements Runnable {
private int id;
private DiningPhilosopherMonitor monitor;
public Philosopher(int id, DiningPhilosopherMonitor monitor) {
this.id = id;
this.monitor = monitor;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
think();
monitor.pickup(id);
eat();
monitor.putdown(id);
}
}
private void think() {
try {
System.out.println(id + ": Now I'm thinking.");
Thread.sleep((long)(Math.random()*500));
} catch (InterruptedException e) { }
}
private void eat() {
try {
System.out.println(id + ": Now I'm eating.");
Thread.sleep((long)(Math.random()*50));
} catch (InterruptedException e) { }
}
}
class DiningPhilosopherMonitor {
private int numOfPhils;
private State[] state;
private Condition[] self;
private Lock lock;
public DiningPhilosopherMonitor(int num) {
numOfPhils = num;
state = new State[num];
self = new Condition[num];
lock = new ReentrantLock();
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
state[i] = State.THINKING;
self[i] = lock.newCondition();
}
}
//……
}
private int leftOf(int i) {
return (i + numOfPhils - 1) % numOfPhils;
}
private int rightOf(int i) {
return (i + 1) % numOfPhils;
}
private void test(int i) {
if (state[i] == State.HUNGRY &&
state[leftOf(i)] != State.EATING &&
state[rightOf(i)] != State.EATING)
{
state[i] = State.EATING;
self[i].signal();
}
}
public void pickup(int id) {
lock.lock();
try {
state[id] = State.HUNGRY;
test(id);
if (state[id] != State.EATING)
self[id].await();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void putdown(int id) {
lock.lock();
try {
state[id] = State.THINKING;
test(leftOf(id)); // left neighbor
test(rightOf(id)); // right neighbor
}
finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
Thread-Safe Concurrent Applications
쓰레드-안전(Thread-Safe) 동시성 애플리케이션
concurrent 어플리케이션은 멀티코어 시스템에서 뮤텍스 락, 세마포어, 모니터와 같은 기술을 사용하여 좋은 성능을 발휘한다. mutex locks, semaphores, monitor 써도 race conditions와 liveness hazards(deadlock) 자주발생한다.
대안:
thread-safe concurrent하게 돌려도 문제가 발생안하니까 스레드 구현 함수에써도 됨
1.transactional memory:
트랜잭션: atomic operation, 원자적인 실행단위,( 계좌 입금 출금 )
메모리 영역 자체를 트랜잭션 자체로 만들자는 의미
2.OpenMP: 공유 메모리 환경에서 프로그램을 병렬화
OpenMP 표준은 컴파일러 지시자의 집합을 정의하고 지시자는 컴파일러에게 코드의 블럭을 어떻게 처리할 지 알려준다.
코드의 특정 영역을 임계 구역으로 선언하여 해당 구역을 임계 영역으로 만들어 준다.
#pragma omp parallel 해주면 pararel하다, critical 하면 critical section이다.
3.Functional Programming Language :
함수형 프로그래밍 언어를 사용하여 명령형 프로그래밍 언어에서 발생하는 동기화 문제를 원천적으로 막는다.
수형 프로그래밍 언어는 스칼라, 하스켈 등
함수형 프로그래밍 언어를 쓰면 이런문제가 발생안한다.
명령어 프로그래밍언어 x
