연결 리스트
각 노드가 값(Value)과 포인터(Next)를 가지고 한 줄로 연결되어 있는 Data 저장 구조, 모든 노드가 연결되어 있는 구조로 포인터가 다른 노드를 가리키고 있다.
종류: 단일 연결 리스트, 이중 연결 리스트
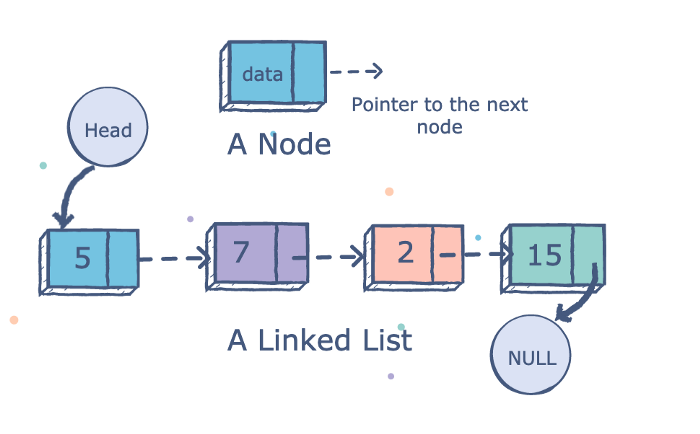
Source: https://www.educative.io License: Creative Commons -Attribution -ShareAlike 4.0 (CC-BY-SA 4.0)
예시 :
head: Node { value: 4, next: Node { value: 5, next: [Node] } },
tail: Node { value: 7, next: null },JavaScript 구현
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this._size = 0;
}
addToTail(value) {
let node = new Node(value);
this._size++;
if (!this.head) {//=> 노드가 없다면 해더가 곧 테일.
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {//=> 노드가 있다면 맨뒤에 노드를 추가하고 테일에 노드를 추가한다.
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
}
}
remove(value) {
if (this.head.value === value) {
this.head = this.head.next;
//=>맨앞 해더가 삭제할 대상이라면 그냥 당기면 됨
} else {
let cur = this.head;
let nextNode = cur.next;
//=> 각부분을 변수의 저장
while (nextNode) {//=> 첫번째 노드가 삭제할대상이 아니니 두번째부터 찾기 시작함.
if (nextNode.value === value) {
break;//=> 만약에 삭제할 대상이 맞다면 if문을 깨버린다.
} else {//=> 아니라면 노드를 한 단계씩 당긴다.
cur = nextNode;
nextNode = nextNode.next;
}
}
cur.next = nextNode.next; //=> if문의 꺠진다면 그노드(nextNode)를 지워버리고 다시 연결한다.
this._size--;
}
}
getNodeAt(index) {
let curNode = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this._size; i++) {
if (i === index) {
return curNode;
}
curNode = curNode.next;//=> 이 부분이 있어야 for문이 돈다.
}
}
contains(value) {
//=> 노드 삭제 부분과 비슷하다
if (this.head.value === value) {
return true;
} else {
let cur = this.head;
let nextNode = cur.next;
while (nextNode) {
if (nextNode.value === value) {
return true;
} else {
cur = nextNode;
nextNode = nextNode.next;
}
}
return false;
}
}
indexOf(value) {
//=> getNodeAt와 비슷함.
let curNode = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this._size; i++) {
if (curNode.value === value) {
return i;
}
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return -1;
}
size() {
return this._size;
}
}