(24.12.12)
-
문제 이해: spells[i]는 스펠의 힘, potions[j]는 포션의 힘을 의미한다. 이때 success정수는 스펠과 포션 힘의 곱의 최솟값을 의미한다. 이때 구해야하는 정수값은, spells값을 차례로 potions에 곱한 배열에서 success 이상의 값이 몇개인지를 나타내는 것이다. 예시를 통해 이해하면 쉽다.

-
문제 접근 1: 순차적으로 접근하면 될 듯 하다. spells 길이만큼의 result integer array를 만들고, 곱한 값들이 몇개 초과하는지를 계산하여 array에 담으면 된다.
class Solution {
public int[] successfulPairs(int[] spells, int[] potions, long success) {
int[] result=new int[spells.length];
for(int i=0; i<spells.length; i++){
long score=0;
for(int j=0; j<potions.length; j++){
score=spells[i]*potions[j];
if(score>=success){
result[i]++;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
- 문제 접근 2: 문제에 주어진 Hint에서 score값이 아닌 success/spell[i]꼴로 potions의 limit을 이용하라는 것을 참고하여 코드를 작성하였다.
class Solution {
public int[] successfulPairs(int[] spells, int[] potions, long success) {
int[] result=new int[spells.length];
for(int i=0; i<spells.length; i++){
double limit=success*1.0/spells[i];
for(int j=0; j<potions.length; j++){
if(potions[j]>=limit){
result[i]++;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
- 최적화 1: TLE 해결을 위해 반복문 루프마다 실행되는 success*1.0부분을 double형의 success변수를 생성하여 수정하였다.
class Solution {
public int[] successfulPairs(int[] spells, int[] potions, long success) {
int[] result=new int[spells.length];
double success_d=success*1.0;
for(int i=0; i<spells.length; i++){
double limit=success_d/spells[i];
for(int j=0; j<potions.length; j++){
if(potions[j]>=limit){
result[i]++;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}하지만 여전히 TLE가 발생하였다.
- 최적화 2: potions를 정렬해보자.
class Solution {
public int[] successfulPairs(int[] spells, int[] potions, long success) {
int[] result=new int[spells.length];
double success_d=success*1.0;
Arrays.sort(potions);
for(int i=0; i<spells.length; i++){
double limit=success_d/spells[i];
for(int j=0; j<potions.length; j++){
if(potions[j]>=limit){
result[i]+=potions.length-j;
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
다음 케이스에서 TLE가 발생하였다.
- 최적화 3: 이진탐색을 사용해보자.
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] successfulPairs(int[] spells, int[] potions, long success) {
int[] result=new int[spells.length];
double success_d=success*1.0;
Arrays.sort(potions);
for(int i=0; i<spells.length; i++){
int limit= (int) Math.ceil(success_d/spells[i]);
int start=0, end=potions.length, mid=(start+end)/2;
while(start<=end){
if(potions[mid]==limit){
result[i]+=spells.length-mid;
break;
} else if(potions[mid]>limit){
end=mid-1;
} else{
start=mid+1;
}
mid=(start+end)/2;
}
}
return result;
}
}문제는 pottions[mid]==limit이 아닐 수도 있다는 점에서 case1에서 실패하였다. limit은 limit일 뿐 완전히 같은 값이 존재하지 않을 수있기에 그 경계를 정확히 찾아내는 것이 중요하다. 하지만 아직 이진탐색이 익숙치 않아서인지.. 정확한 값을 찾아내는 이진탐색을 응용해서 경계값을 찾아내는 이진탐색이 바로 생각나지 않는다.
- 최적화 4: GPT를 이용하였다.
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] successfulPairs(int[] spells, int[] potions, long success) {
int[] result = new int[spells.length];
Arrays.sort(potions);
for (int i = 0; i < spells.length; i++) {
long limit = (long) Math.ceil((double) success / spells[i]);
int start = 0, end = potions.length;//end로 length값 그대로 사용하고 while 조건을 start<end로 <를 사용함.
// 이진 탐색으로 lower bound를 찾음
while (start < end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (potions[mid] >= limit) {//같은 경우도 고려하여 end를 mid값으로 조정한다.
end = mid; // 조건을 만족하면 왼쪽 영역 탐색
} else {
start = mid + 1; // 조건을 만족하지 않으면 오른쪽 영역 탐색
}
}
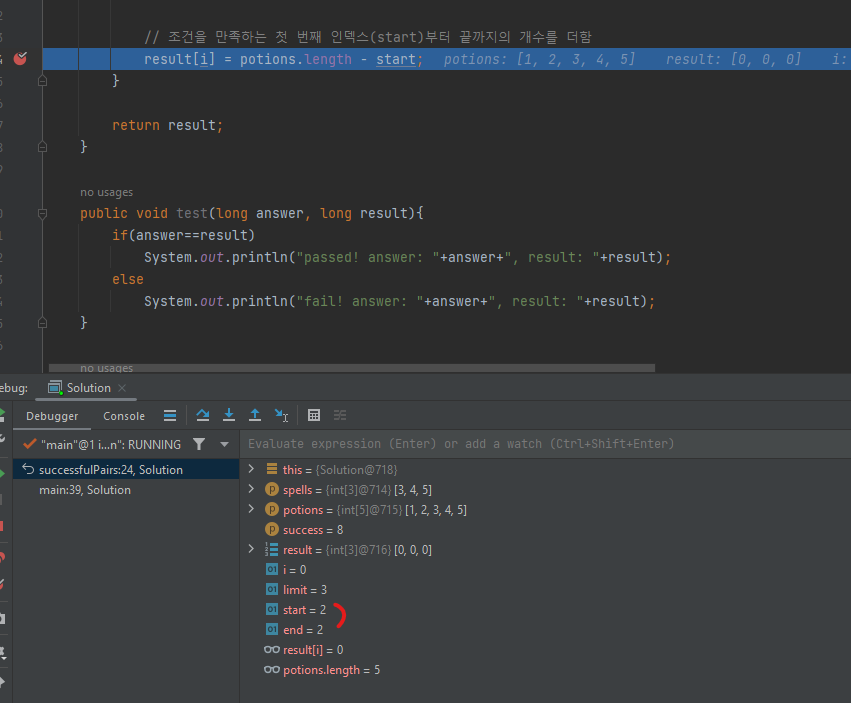
// 조건을 만족하는 첫 번째 인덱스(start)부터 끝까지의 개수를 더함
result[i] = potions.length - start;//while start<end로 했기에 깨질 때 에는 start와 end값이 같아진다.
}
return result;
}
}
내 이진 탐색 코드와 다른 점은 end를 potions.length로 두고 while문의 조건을 start<=end가 아닌 start<end로 두었다는 것이다. 이를 이용하여 start와 end가 같아지는 지점, 즉 완전히 같지는 않더라도 start와 end가 맞물리는 지점을 정확히 얻어낼 수 있었다. 그렇기에 if(potions[mid]==limit)코드도 존재하지 않는다.