오늘 할일
1. Leetcode
2. 서버 커리잡기
오늘 한일
1. LeetCode
- Reorder Routes to Make All Paths Lead to the City Zero 는 시험 끝나고 좀 논 뒤에야 다시 돌아왔는데, 미루고 미루던 접근을 해보았다. 도시의 연결을 set형태로 큰 그룹들로 엮은 뒤에, 그 그룹들 안에서 DFS를 수행하여 계산한다. 초기 코드는 다음과 같다.
class Solution {
public int minReorder(int n, int[][] connections) {//n은 노드의 개수, connections는 a->b방향관계
//모든 노드는 수도까지 접근 가능하다. 트리구조
//connections는 정렬불가능하다. 노드가 순차적으로 배치되어 있다는 가정이 없기 때문이다.
//각각의 연결 queue를 만든다음 루트에 도달하는 순간, 그 방향을 기반으로 change 횟수를 센다.
List<List<Integer>> queues=new ArrayList<>();
for(int[] conn : connections){//모든 연결관계를 순회하면서 구조 재정립
int start=conn[0], end=conn[1];
boolean is_exist=false;
for(int i=0; i<queues.size(); i++){//모든 큐를 둘러보면서
List<Integer> iter=queues.get(i);
if (iter.contains(start) || iter.contains(end)){//기존에 있는 값이라면
iter.add(start);//둘을 방향 관계를 유지하며 2쌍 씩 추가한다.
iter.add(end);
is_exist=true;
break;//존재하는 그룹을 찾았다면 escape
}
}
if(!is_exist){//존재하는 그룹이 없다면 새로 만들어서 추가한다.
List<Integer> new_list=new ArrayList<>();
new_list.add(start);
new_list.add(end);
queues.add(new_list);
}
}
//모든 연결관계 재정립이 끝났다면, 모든 노드는 수도에 접근 가능하기에 0을 무조건 가지고 있다.
//각각의 원소에 대하여 방향성을 검토한다.
int result=0;
for(List<Integer> queue : queues){
//0의 인덱스를 저장한다. 초기세팅
Queue<Integer> indexes=new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=0; i<queue.size(); i++)
if(queue.get(i)==0)
indexes.add(i);
//0부터 시작해서 DFS진행
while(!indexes.isEmpty()){
int index=indexes.remove();
if(index%2==0) {//짝수라면 시작지점
result++;
indexes.add(index+1);
} else{//홀수라면 도착지점
indexes.add(index-1);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}그런데, 생각해보니 위에 이중 리스트처럼 만들지 않고 바로 하나의 list로 int[][] connections를 변환한 다음 int result=0부터의 코드를 수행해도 될 것 같아 코드 형태를 변경하고, 디버깅 한 후 실행해보았다.
class Solution {
public int minReorder(int n, int[][] connections) {//n은 노드의 개수, connections는 a->b방향관계
//connections를 List형태로 순서를 유지하며 저장한다.
List<Integer> queue=new ArrayList<>();//연결관계 저장소
for(int[] conn : connections){//모든 연결관계를 순회하면서 구조 재정립
queue.add(conn[0]);
queue.add(conn[1]);
}
//DFS를 위해 도시(0)이 위치하는 인덱스 정보를 큐에 넣어 준비를 한다.(초기값 세팅)
int result=0;
Queue<Integer> indexes=new LinkedList<>();//접근할 인덱스의 목록
for(int i=0; i<queue.size(); i++)
if(queue.get(i)==0)
indexes.add(i);
//0부터 시작해서 DFS진행
while(!indexes.isEmpty()){
int index=indexes.remove();
if(index%2==0) {//짝수라면 시작지점
result++;
int target_index=index+1;
int target_val=queue.get(target_index);
queue.set(target_index, -1);//현재 index와 같이 처리한 쌍의 데이터 무시를 위함
for(int i=0; i<queue.size(); i++){
if(queue.get(i)==target_val){
indexes.add(i);
}
}
} else{//홀수라면 도착지점
int target_index=index-1;
int target_val=queue.get(target_index);
queue.set(target_index, -1);//현재 index와 같이 처리한 쌍의 데이터 무시를 위함
for(int i=0; i<queue.size(); i++){
if(queue.get(i)==target_val){
indexes.add(i);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
} 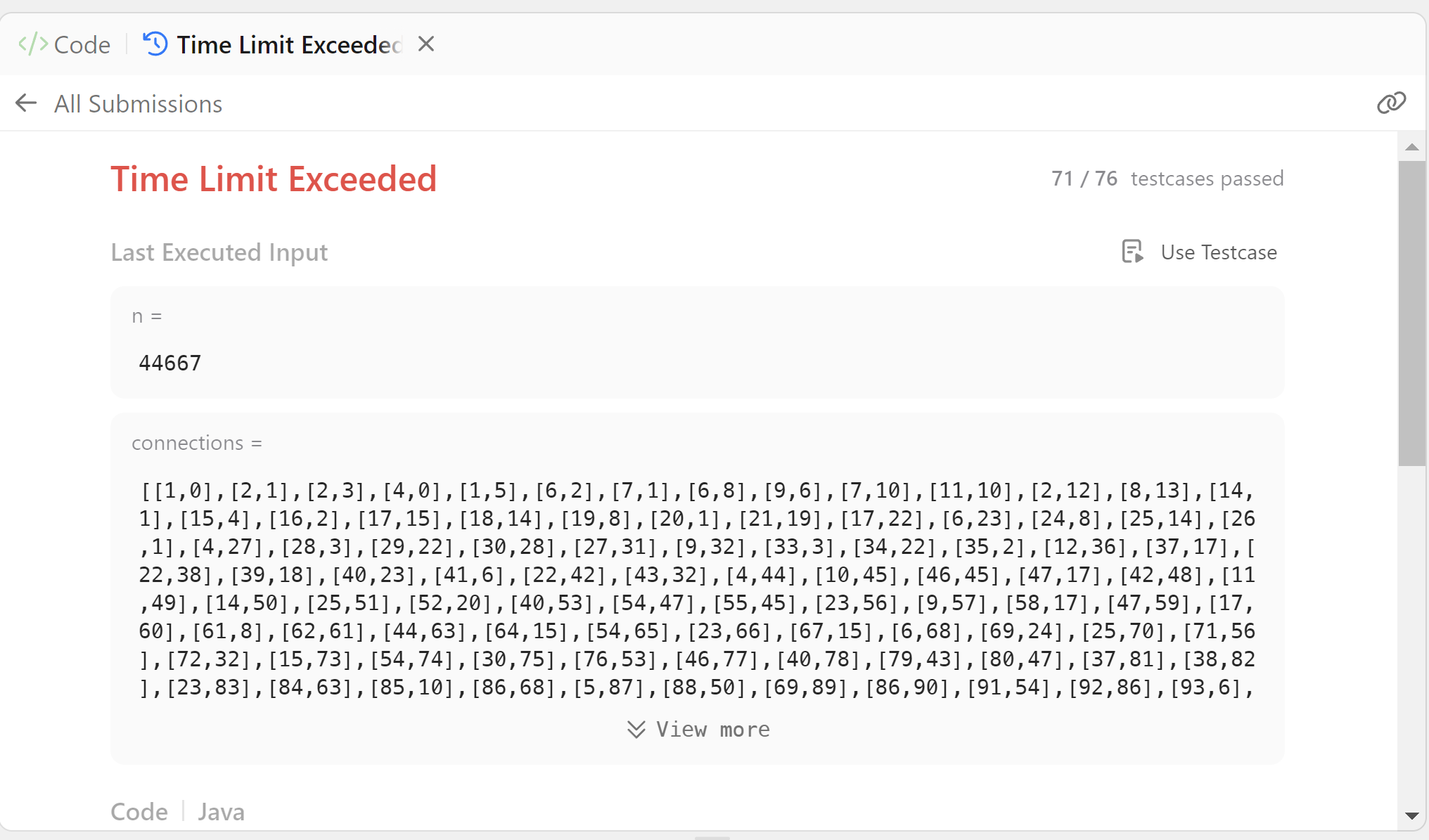
이전에 시도했던 무작정 배열[][]형태와 같은 테스트 케이스에서 막혔다. 상당한 진전이 있다고 보는게, 최종적으로 돌파한 테스트 케이스는 같지만 현재의 방법이 이전의 방법들과 비교하여 빠른 방법이기 때문이다. 최적화를 추가적으로 진행해보자.
