1. 자바의 synchronized를 이용한 동시성 제어
1) 사용방법
// StockService.java
/*
이때는 트랜잭션 어노테이션을 사용하면 안 된다.
threads can access transaction one by one, using 'synchronized'
*/
// @Transactional
public synchronized void decrease(Long id, Long quantity){
// get stock
// decrease quantity of stock
// save
Stock stock = stockRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow();
stock.decrease(quantity);
stockRepository.saveAndFlush(stock);
}2) 한계
- 자바의
synchronized는 하나의 프로세스 안에서만 보장된다. - 따라서 서버가 여러대라면? -> 여러 서버에서(thread에서) 동시에 데이터에 접근할 수 있기 때문에 동시성 이슈가 발생
2. MySQL을 이용한 동시성 제어
1) pessimistic lock
- 데이터에
exclusive lock을 걸면 현재 접근 중인 트랜잭션을 제외한 다른 트랜잭션에서는 해당 데이터에 접근할 수 없는 것을 이용 - (-)
deadlock의 위험성이 있음 - (+) 충돌이 빈번하다면 optimistic lock보다 성능이 좋을 수 있다.
- (+) lock을 통해 제어하기 때문에 데이터 정합성이 어느정도 보장된다.
// StockRepository.java
public interface StockRepository extends JpaRepository<Stock, Long> {
//Spring data jpa에서는 @Lock을 이용해 pessimistic lock을 구현
@Lock(value = LockModeType.PESSIMISTIC_WRITE)
@Query("select s from Stock s where s.id =: id")
Stock findByIdWithPessimisticLock(Long id);
}
// PessimisticLockStockService.java
@Transactional
public void decrease(Long id, Long quantity){
Stock stock = stockRepository.findByIdWithPessimisticLock(id); //apply pessimistic lock
stock.decrease(quantity);
stockRepository.saveAndFlush(stock);
}테스트 코드
@Test
public void try100RequestAtOnce() throws InterruptedException {
int threadCount = 100;
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(32);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
for(int i=0 ; i<threadCount; i++){
executorService.submit(()->{
try{
stockService.decrease(1L, 1L);
}finally {
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
latch.await();
Stock stock = stockRepository.findById(1L).orElseThrow();
assertEquals(0L, stock.getQuantity());
}성공했다.
쿼리에서 for update부분이 lock을 걸어서 데이터를 가져오는 부분이다!

2) optimistic lock
- 데이터를 업데이트할 때는 읽은 버전이 맞는지 확인하고 업데이트를 한다.
- 업데이트 하려는데 읽었을 때의 버전과 현재 버전이 다르다면 업데이트 불가. applicaiton에서 다시 읽은 뒤에 업데이트 작업을 다시 수행해야 한다.
먼저 repository단에서 @Lock 어노테이션을 이용해 optimistic lock 설정을 해준다.
// StockRepository.java
@Lock(value = LockModeType.OPTIMISTIC)
@Query("select s from Stock s where s.id = :id")
Stock findByIdWithOptimisticLock(Long id);service단에서 방금 설정한 메소드를 이용해 repository단에 접근한다.
// OptimisticLockService.java
@Transactional
public void decrease(Long id, Long quantity){
Stock stock = stockRepository.findByIdWithOptimisticLock(id);
stock.decrease(quantity);
stockRepository.saveAndFlush(stock);
}업데이트에 실패하면 다시 시도하는 로직을 구현한다.
여기선 Facade Layer가 사용되었다.
Facade Layer : 프리젠테이션 계층과 도메인 모델 계층 간의 논리적 의존성 분리
// OptimisticLockStockFacade.java
public void decrease(Long id, Long quantity) throws InterruptedException {
while(true){
try{
optimisticLockStockService.decrease(id, quantity);
break;
}catch(Exception e){
Thread.sleep(50); //If the decrease function fails, retry after 50ms.
}
}
}테스트 해보자!
@Test
public void try100RequestAtOnce() throws InterruptedException {
int threadCount = 100;
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(32);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
for(int i=0 ; i<threadCount; i++){
executorService.submit(()->{
try{
optimisticLockStockFacade.decrease(1L, 1L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
latch.await();
Stock stock = stockRepository.findById(1L).orElseThrow();
assertEquals(0L, stock.getQuantity());
}성공했다.
3) named lock
- 말그대로 named lock을 획득하면 그것이 해제될 때까지 다른 세션은 그 lock을 획득할 수 없다.
- transaction이 종료한다고 자동으로 lock도 해제되는 것이 아니다. 따라서 명령어를 이용해 직접 해제시켜줄 수도 있고 선점 시간이 끝나면 해제된다. 주의해서 사용하자!
- 주로 분산락을 구현할 때 사용
- MySQL에서는 get_lock을 이용해 lock을 걸 수 있는데, 앞선 pessimistic lock에서는 Stock에 lock을 걸었지만 named lock의 경우 별도의 공간에 lock을 건다.
- 실무에서는 커넥션풀이 부족해져 다른 서비스에도 영향을 주는 것을 방지하기 위해 데이터 소스를 분리하여 사용하는 것이 좋다. 예시에서는 분리하지 않고 사용하였다.
get_lock(str,timeout)- 문자열 str에 해당하는 lock을 획득한다.
- return 1이면 lock 획득 성공
- return 0이면 timeout 동안 lock 획득 실패
- return null이면 에러 발생
release_lock(str)- 문자열 str에 해당하는 lock 해제
- return 1이면 lock 해제
- return 0이면 해제할 lock 없음
코드로 구현해보자.
// LockRepository.java
public interface LockRepository extends JpaRepository<Stock, Long> {
@Query(value = "select get_lock(:key, 3000)", nativeQuery = true)
void getLock(String key);
@Query(value = "select release_lock(:key)", nativeQuery = true)
void releaseLock(String key);
}// StockService.java
@Service
public class StockService {
private StockRepository stockRepository;
public StockService(StockRepository stockRepository) {
this.stockRepository = stockRepository;
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public synchronized void decrease(Long id, Long quantity){ // threads can access transaction one by one, using 'synchronized'
// get stock
// decrease quantity of stock
// save
Stock stock = stockRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow();
stock.decrease(quantity);
stockRepository.saveAndFlush(stock);
}
}// NamedLockStockFacade.java
@Component
public class NamedLockStockFacade {
private final LockRepository lockRepository;
private final StockService stockService;
public NamedLockStockFacade(LockRepository lockRepository, StockService stockService) {
this.lockRepository = lockRepository;
this.stockService = stockService;
}
public void decrease(Long id, Long quantity){
try{
lockRepository.getLock(id.toString());
stockService.decrease(id,quantity);
}finally {
lockRepository.releaseLock(id.toString());
}
}
}
테스트 해 보자!
예시에서는 같은 데이터 소스를 사용하기 때문에 커넥션풀을 늘려줌.
spring:
datasource:
hikari:
maximum-pool-size: 40테스트 코드
// NamedLockStockFacadeTest.java
@SpringBootTest
class NamedLockStockFacadeTest {
@Autowired
private NamedLockStockFacade namedLockStockFacade;
@Autowired
private StockRepository stockRepository;
@BeforeEach
public void before(){
// 초기세팅
Stock stock = new Stock(1L, 100L);
stockRepository.saveAndFlush(stock);
}
@AfterEach
public void after(){
stockRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
public void try100RequestAtOnce() throws InterruptedException {
int threadCount = 100;
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(32);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
for(int i=0 ; i<threadCount; i++){
executorService.submit(()->{
try{
namedLockStockFacade.decrease(1L, 1L);
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
latch.await();
Stock stock = stockRepository.findById(1L).orElseThrow();
assertEquals(0L, stock.getQuantity());
}
}성공했다.
3. Redis를 이용한 동시성 제어
1) Lettuce
-
setnx(set if not exists) 명령어를 이용하여 분산락 구현- key, value를 set할 때 해당 key값이 이미 존재하지 않을 때만 set
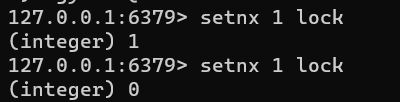
- key, value를 set할 때 해당 key값이 이미 존재하지 않을 때만 set
-
spin lock 방식 -> 개발자가 직접 retry 로직을 작성해줘야
-
spin lock : lock을 획득하려는 쓰레드가 획득할 수 있는지 반복적으로 확인하면서 lock 획득 시도
-
(+) 구현이 간단하다.
-
(-) spin lock 방식이 redis에 부하를 줄 수 있기 때문에
thread.sleep()을 이용해 lock 획득 재시도 간에 텀을 줘야 한다.
2) Redisson
- pub-sub 기반으로 lock 구현을 가능케 함
- lock을 점유중인 쓰레드가 lock을 해제할 때 채널을 통해 lock을 획득하려고 대기중인 쓰레드에게 알려주면 대기중이던 쓰레드가 lock 획득을 시도한다.
- 별도의 retry 로직을 작성하지 않아도 됨.
- 계속 lock 획득을 시도하는 lettuce와는 달리 메시지를 통해 lock이 해제되었다는 것을 알게되면 lock 획득을 시도하기 때문에 redis의 부하를 줄여준다.
// RedissonLockStockFacade.java
public void decrease(Long key, Long quantity){
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock((key.toString()));
try{
boolean available = lock.tryLock(5, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // Try lock for 5 sec. If they succeed, unlock in 1 sec.
if(!available){
System.out.println("lock 획득 실패");
}
stockService.decrease(key, quantity);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}테스트
// RedissonLockStockFacadeTest.java
@Test
public void try100RequestAtOnce() throws InterruptedException {
int threadCount = 100;
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(32);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
for(int i=0 ; i<threadCount; i++){
executorService.submit(()->{
try{
redissonLockStockFacade.decrease(1L, 1L);
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
latch.await();
Stock stock = stockRepository.findById(1L).orElseThrow();
assertEquals(0L, stock.getQuantity());
}성공했다.
인프런의 [재고시스템으로 알아보는 동시성이슈 해결방법] 강의를 듣고 배운 내용을 정리하게 위해 작성하였습니다.
